Until today, blockchain technology can still be considered a new technology. Although the basic concepts related to blockchain (cryptography, decentralization, peer-to-peer networks and transactions) have been studied for decades, it wasn’t until the birth of Bitcoin in 2008 that people believed these concepts could indeed be combined to create usable products. Especially with Ethereum, it didn’t appear in people’s field of vision in an open and usable form until 2015. Although the expected development timeline and specific details have changed, Ethereum still insists on advancing according to plan, constantly upgrading its protocol to ensure usability, security, functionality, and decentralization.
This year, Ethereum will undergo two important upgrades according to plan, the Shanghai upgrade that was completed on April 12th, and the Cancun upgrade expected to take place in the fourth quarter. According to the official Ethereum documentation, since the release of the white paper in 2013, 24 milestone events have occurred, most of which are hard forks, with 12 relatively important upgrades. This article will review and sort out the important hard forks and upgrades in Ethereum’s history, as well as introduce the changes that the Cancun upgrade may bring.
Frontier Upgrade – July 30, 2015

July 30, 2015, the date on which the Ethereum genesis block was generated and the date on which the first phase of Ethereum began. The launch of Frontier marked the official launch of the Ethereum blockchain network. This phase mainly targets blockchain developers, with node participants participating in the form of mining. This phase already supports uploading smart contracts.
- BITKRAFT Ventures: How can blockchain games acquire users?
- Deep dive into a16z’s active address comments: user and usage growth stagnate, short-term not optimistic
- Interpreting the LSTFi project’s unshETH
The Frontier protocol includes the following key features:
Block reward: When miners successfully mine a block on the Ethereum blockchain, they receive a reward in ETH. In the Frontier phase, the block reward for miners is 5 ETH per block.
Gas: In the early days after Frontier was released, the gas limit for each block was hard-coded to 5000 gas. This basically means that there won’t be any big moves on the network. This leaves a buffer period for miners to start working on Ethereum and early users to install clients. A few days later, the gas limit was automatically lifted and the network could begin processing transactions and smart contracts as planned.
Canary Contract: This contract is used to inform users which chain has been or is susceptible to attack. The Canary contract is assigned a value of 0 or 1. If the contract is assigned a value of 1, the client can recognize that this is a faulty chain and avoid this invalid chain when mining. Essentially, the Canary contract’s functionalities allow the Ethereum core development team to pause the network’s operation when problems arise on the network. In the early stages of Ethereum, the Canary contract was an extremely centralized yet indispensable protection mechanism.
Usability: All developer operations are executed through the command line as there is no graphical user interface. The entire network is available, but the user interface is very rough, and only those familiar with Ethereum and experienced in operating it are capable of using it.
In the cutting-edge version, the Gas limit for each block was hardcoded to 5000Gas, which was then removed in the Frontier thawing upgrade two months later. The Gas default price was set to 50gwei, and the difficulty bomb was introduced in this upgrade. The purpose of introducing the difficulty bomb was to provide the network with a mechanism for migrating from PoW to PoS. When the computing power is too high to allow miners to mine any blocks, it will be the best time for the network to transition to PoS. It can be said that there was already a plan to transition to PoS in the initial stage of Ethereum.
From this point on, Ethereum officially entered the quasi-available PoW mining era, with the Ethereum price at $1.24 each.
Homestead Upgrade – March 14, 2016

Homestead Upgrade is the second major version released by Ethereum, which is Ethereum’s first hard fork and the start date of the second phase of the roadmap. The most important feature in this version is that smart contracts have been optimized and a new code has been introduced for the Solidity smart contract language. In addition, the desktop wallet Mist was released in this version, allowing users to hold/trade ETH and write/deploy smart contracts. Later, the Mist project announced its termination in early 2019.
The Homestead upgrade is one of the earliest Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs) to be implemented, and it includes three EIPs, namely 2, 7, and 8: EIP-2: Increases the cost of creating smart contracts through transaction from 21000 Gas to 53000 Gas. Previously, the cost of creating contracts through contracts (recommended method) was higher than that of creating contracts through transactions. With the increase in gas costs for creating contracts through transactions, EIP 2 encourages users to revert to creating contracts through contracts.
EIP-7: Added a new DELEGATECALL function for code reuse. This opcode is similar to CALLCODE, but it sends the sender and value from the parent scope to the child scope, meaning that the created call has the same sender and value as the original call.
EIP-8: A forward-looking network upgrade proposal that improves the devp2p network protocol for forward compatibility. This improvement ensures that all client software on the Ethereum network can adapt to future network protocol upgrades.
At this time, the Ethereum price was $12.5 per unit.
DAO Fork – July 20, 2016
In addition to planned Ethereum upgrades and hard forks, there was an unplanned forking event that should be remembered. In 2016, The DAO, a decentralized autonomous organization project, raised $150 million through the issuance of tokens. In June, The DAO’s contract was exploited by hackers, and millions of dollars worth of ETH was stolen by unknown hackers. Most participants in the Ethereum community decided to implement a hard fork to recover the stolen ETH from wallets and fix the vulnerability. However, the hard fork did not receive unanimous support from all participants in the community, and some continued to mine and trade on the original chain. The original chain, where stolen ETH was not recovered, became known as Ethereum Classic (ETC). Since then, Ethereum has split into two networks, ETH and ETC.
At this time, the Ethereum price was $12.54 per unit.
Metropolis: Byzantium Upgrade – October 16, 2017
By this time, Ethereum had undergone two major milestone upgrades, Homestead and Frontier, and the next step according to the plan was the Metropolis upgrade. However, since the Metropolis upgrade had more content, the plan was divided into two phases at the time: Byzantium and Constantinople.
This hard fork included 9 improvement proposals (EIP 100, 658, 649, 140, 196, 197, 198, 211, 214). In addition to updates related to low-level operations, smart contracts, and other underlying features, the “difficulty bomb” was delayed by a year and a half, and the block reward was reduced from 5 ETH to 3 ETH. Before the difficulty bomb was dismantled, the block generation time was close to 30 seconds. The ability to make non-state-changing calls to other contracts was added; some cryptographic methods were added to allow for Ethereum’s Layer2 scalability.
At this time, the Ethereum price is $334.32 each.
Metropolis: Constantinople Upgrade – February 28, 2019
The second stage of the Metropolis upgrade, Constantinople, was originally scheduled to go live on January 15, 2019, at block height 7,080,000. However, on January 15, ChainSecurity, an independent security audit firm, published a report indicating that one of the five major system upgrades would give attackers the opportunity to steal funds. In response to the report, Ethereum core developers and other members of the community voted to postpone the upgrade until the security issue was resolved.
Eventually, the Ethereum Foundation decided to carry out the final step of the “Metropolis” on February 28, 2019, which is the hard fork called “Constantinople”, consisting of 6 improvements: ensuring that the blockchain will not be frozen before implementing the PoS working mechanism; optimizing the gas cost issue in the Ethereum virtual machine; adding interactive capabilities for address creation. Interestingly, there is also a hard fork called “St. Petersburg” that will take place at the same time as the Constantinople upgrade, removing an improvement proposal (EIP-1283) previously included in Constantinople. Among the five major updates, in addition to technical adjustments, the difficulty bomb was postponed for another 12 months and the block reward was reduced from 3 ETH to 2 ETH.
At the same time, a new instruction called CREATE2 was introduced in EIP1014, which can pre-calculate the contract address before the contract is formally deployed, thus introducing the concept of state channels similar to the Bitcoin Lightning Network into Ethereum and allowing corresponding contracts to be deployed off-chain and settled on-chain.
At this time, the Ethereum price is $136.29 each.
Istanbul Upgrade – December 8, 2019
Ethereum 2.0 plans to launch phase 0 in 2020. Before 2.0 is fully online, most users and developers will likely use Ethereum 1.X primarily, so subsequent updates to 1.X are also very important. The Istanbul hard fork was activated on December 8, 2019, and includes six improvements: continuing to optimize the gas cost issue in the Ethereum virtual machine; improving the recovery capability against distributed denial of service attacks; improving the performance of Layer2 extension solutions developed based on SNARKs and STARKs verification mechanisms; implementing interoperability between Ethereum and Zcash; and allowing Ethereum smart contracts to introduce more creative features.
Vitalik Buterin stated that after this upgrade, the ordinary transactions per second (TPS) will increase by about 5% to 10%, and for Layer 2 technology Rollup, it can increase by about 4 times. At this time, the Ethereum price was $151.06 each.
Muir Glacier Upgrade – January 2, 2020
Less than a month after completing the Istanbul Upgrade, Ethereum urgently conducted another upgrade. Consecutive hard forks within a month are very rare, but users and developers have discovered a slight increase in Ethereum’s block generation interval, which will cause the TPS of the Ethereum network to decrease. Ethereum developers discussed and proposed to perform a hard fork named “Muir Glacier” at block height 9,200,000 to remove the difficulty bomb, which is expected to occur around December 31, 2019. According to the data provided by developers in the discussion group, Ethereum’s block generation time will continue to increase before the difficulty bomb is removed, and it may reach 25 to 30 seconds around January 6.
At this time, the Ethereum price was $127.18 each.
Berlin Upgrade – April 15, 2021

Starting from this version, the upgrade code name will follow the order of the Ethereum developer conference Devcon, and the first Devcon 0 was held in Berlin. Ethereum has planned many improvements for the Istanbul Upgrade, but due to various reasons, the improvement proposals that were not included in Istanbul will be moved to Berlin. This optimization solves the gas cost problem in the Ethereum virtual machine and adds support for multiple transaction types.
At this time, the Ethereum price was $2,454 each.
London Upgrade – August 5, 2021

This upgrade involves five proposals: EIP-1559, EIP-3198, EIP-3529, EIP-3541, and EIP-3554. One of the proposals that has the greatest impact on Ethereum is EIP1559, which aims to change the existing Ethereum fee structure by splitting the fee into a base fee and miner fee, and reducing the circulation of ETH by destroying part of the base fee.
It directly changed Ethereum’s economic model. Previously, block packaging was an auction mechanism and the miner received all the gas fees. EIP1559 splits the gas fee into two parts, one part is given to the miner and the other part is burned, bringing Ethereum into the era of deflation.
At this time, the price of Ethereum is $2,621 per ether.
The Merge (Paris Upgrade) – September 15, 2022
This upgrade (merge) directly modifies the execution layer and consensus layer of Ethereum and is an important upgrade that transforms the Ethereum mainnet from a PoW consensus mechanism to a PoS consensus mechanism. This upgrade has brought some rule changes to the Ethereum network, as follows:
Changes to verification nodes: The original miner nodes will be replaced by verification nodes. Verification nodes need to have 32 ETH as a deposit and run corresponding software to participate in network verification and block packaging.
Changes to block rewards: The original block rewards will be cancelled and replaced by revenue obtained through transaction fees.
Changes to transaction fee mechanism: In the new version, transaction fees will be paid directly to verification nodes instead of the Ethereum Foundation.
Improvement of dynamic transaction fee mechanism: A new feature called “EIP-1559” has been added in the new version, which can dynamically adjust the transaction fee price, allowing users to complete transactions faster and reducing high transaction fees.
Optimization of state storage method: The new version uses a technology called “Rollups” to store a large amount of data on the side chain and aggregate it to the main chain, thereby reducing the burden on the main chain and improving the efficiency and scalability of the entire system.
Improvement of contract execution method: A new virtual machine called “EVM 384” has been added to the new version, which can improve the efficiency and security of contract execution.
Overall, the Ethereum Paris upgrade significantly improves the scalability and efficiency of the Ethereum network by improving the consensus mechanism, optimizing the transaction fee mechanism, improving the state storage method, and improving the efficiency of contract execution.
At this time, the price of Ethereum is $1,472 per ether.
Shanghai Upgrade – April 12, 2023

The Shanghai upgrade will be the first major upgrade of the Ethereum network after the merge, and it is also an important milestone on the Ethereum roadmap. The main changes it brings are as follows:
-
Shanghai upgrade unlocked the staking withdrawal function for Ethereum. This is not only beneficial for maintaining the vitality of the Ethereum network, but also for the sustainable development of Ethereum in the future, continuing to attract more validators into the Ethereum network.
-
Reduce the Gas cost of Layer-2 solutions running on the Ethereum blockchain, which to some extent makes Ethereum faster and cheaper. The Shanghai upgrade will further optimize the Gas cost of transactions on Ethereum.
-
As the largest blockchain network that supports smart contracts, the Shanghai upgrade will maintain Ethereum’s leading position in this field by introducing EOF (EVM Object Format).
At this time, the price of Ethereum is $1917 each.
Cancun Upgrade – Q4 2023 (estimated)
The Cancun upgrade is an additional upgrade to the ETH blockchain after the Shanghai upgrade, with EIP-4844 and possible EIP-6969 mainly to achieve the goal of reducing costs and increasing speed for Ethereum L2: By then, it will increase the speed of Ethereum Layer2 10 times, and even have the opportunity to increase 100 times at lower cost.
The cost of Ethereum Layer1 has always been high and urgently needs necessary improvements to reduce overall operating costs. Currently, the main expansion solution on Ethereum is Layer2 Rollups. Rollups do help users save a lot of Gas Fee, such as the representative project Optimism, the regular expense of Gas Fee is only 0.001 gwei, far lower than the regular expense of Ethereum Layer 1 mainnet; ZK Rollups solution has better data compression performance and does not need to include signature data, the cost is lower, and can even be reduced to one percent of the Ethereum Layer 1 mainnet. However, for more extensive users, even with Rollups solutions, Gas Fee is still a relatively expensive burden. In addition, Ethereum’s efficiency in processing parallel transactions is still low, and it can only process two-digit transaction volumes per second at most, which requires new improvement plans to help improve scalability.
Sharding is a powerful improvement method to solve the above problems, but Ethereum cannot implement it now, and the timely proposal of improvement plan EIP-4844 is a compromise for solving the above requirements and implementing the shard upgrade, laying the technical foundation for the overall data sharding of Ethereum in the future. Therefore, EIP-4844 is also called “Proto-danksharding”.
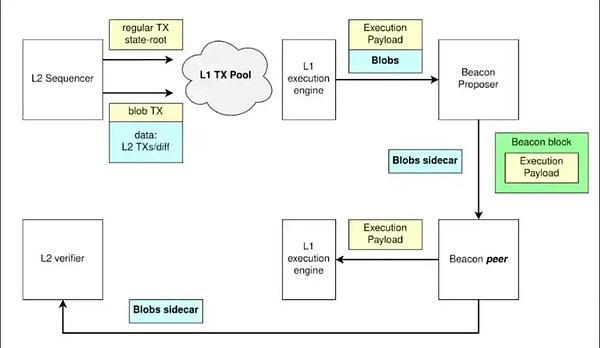
EIP-4844 introduces a new transaction type to Ethereum that can store data in a space called Blob at a lower cost, allowing data previously stored in Layer1 before Layer2 to exist in Blob, greatly reducing the cost of Layer2.
In addition to the much-discussed EIP-4844, the improvement proposals that have been confirmed for the Cancun upgrade include:
EIP-1153: Adding Transient Storage Opcodes. Transient storage is a solution specifically designed to solve internal block communication.
EIP-6780: Modify the functionality of the SELFDESTRUCT opcode to prepare for the future Ethereum application Verkle Tree architecture.
In addition to ETH itself, there are some projects worth laying out under the Cancun upgrade:
Layer2
The biggest beneficiary of the Cancun upgrade is undoubtedly Layer2, with enough first-mover advantage, and leading L2s Arbitrum and Optimism are worth watching; while leading applications in the Arbitrum ecosystem such as GMX, RDNT, and Magic will also rise with the explosion of L2. In addition, projects based on OptimisticRollup, such as Metis, which are built and improved, and Boba Network, which mimics Optimism, are also expected to benefit from the Cancun upgrade.
ZK-Rollups
As a more advanced solution recognized by the industry, zkRollup also has the potential to shine with the Cancun upgrade. zkSync, StarkNet, and Scroll are the three most well-known projects in this field; these three projects have not yet issued coins, but their potential cannot be underestimated.
zkSync is an extended solution based on the ZK-Rollup architecture developed by Matter Labs. It mainly targets the 1.0 mainnet for payment purposes and the general 2.0 testnet fully compatible with EVM. Recently, zkSync has also upgraded its 2.0 entrance, supporting the use of any token to pay network fees, greatly improving user flexibility.
Starknet is a decentralized Validity-Rollup, which runs on Ethereum as L2, allowing any application to scale massively without affecting Ethereum’s composability and security.
Scroll is a zkRollup based on zkEVM on Ethereum, which solves Ethereum’s congestion problem as an L2 solution.
Others
In addition to the above two categories, the Cancun upgrade will also benefit other centralized projects. Including cross-chain protocols with L2 functions; due to the short storage time of Blob data, it will benefit data availability layer projects. Representatives include: Layerzero is currently the most popular cross-chain protocol. It is a cross-chain communication protocol that can pass “information” on one chain to another chain, and realizes decentralized information cross-chain services by deploying a series of smart contracts (Endpoints) on the chain.
Celestia is a data availability layer project. Based on the Cosmos architecture, it provides a data layer and consensus layer for other L1 and L2 chains, building modular blockchains. The principle is similar to Ethereum’s sharding scheme, which can reduce the “data storage cost” bottleneck of current Rollup to a certain extent.
With the implementation of EIP-4844, L2 will be more competitive than other L1s, and the future development prospects are also relatively promising. In addition to greatly reducing the transaction costs of L2, EIP-4844 also provides a good soil for the future application of Danksharding, making it easy to achieve data sharding in the future. Lower transaction costs, better transaction experience, and even more application scenarios may emerge. The Cancun upgrade will become a turning point for Ethereum L2.
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!