
Key Insights
- OpenGov is officially released. OpenGov, Polkadot’s new decentralized governance model, introduces parallel voting, community-centered governance bodies, and more flexible delegation mechanisms, making the decision-making process more efficient and transparent.
- XCM V3 is officially released. The new iteration of this message format introduces advanced programming capabilities, bridging capabilities with external networks, cross-chain locking, improved fee payment mechanisms, and support for NFTs.
- The US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has not classified Polkadot’s native token DOT as a security. Following this statement, the Web3 Foundation stated that the nature of DOT has changed and, after three years of dialogue with the SEC, DOT is no longer considered a security.
- Acala and Moonbeam have re-leased their parallel chain slots, and the initial leases for the first batch of parallel chains will expire in October. With new projects seeking to join and existing projects seeking to renew lease agreements, competition for parallel chain slots will become more intense.
Preliminary Understanding of Polkadot
Polkadot is a nominated proof-of-stake (NPoS) blockchain network designed to support various interconnected, application-specific Layer 1 chains, referred to as parallel chains. Each built-in chain in Polkadot uses the Substrate blockchain development framework developed by Blockingrity Technologies, which allows developers to choose specific components that best suit their specific application chain. Polkadot refers to the entire ecosystem composed of all parallel chains that connect to the “relay chain.” The relay chain does not support application functionality but instead carries all validators and is responsible for the security, governance, and connection of parallel chains.
Polkadot website: https://polkadot.network/
Official Twitter: https://twitter.com/Polkadot
- Messari: Ethereum Q2 2023 Analysis Report, Market Share Reaches 18%, Outperforming Bitcoin for Two Consecutive Quarters
- A glimpse of the new narrative of old blue-chip DeFi: application chains, RWA, LSD, stablecoins.
- Is NFT the same as a wallet? Objective analysis of the pros and cons of ERC-6551.
Discord community: https://dot.li/discord
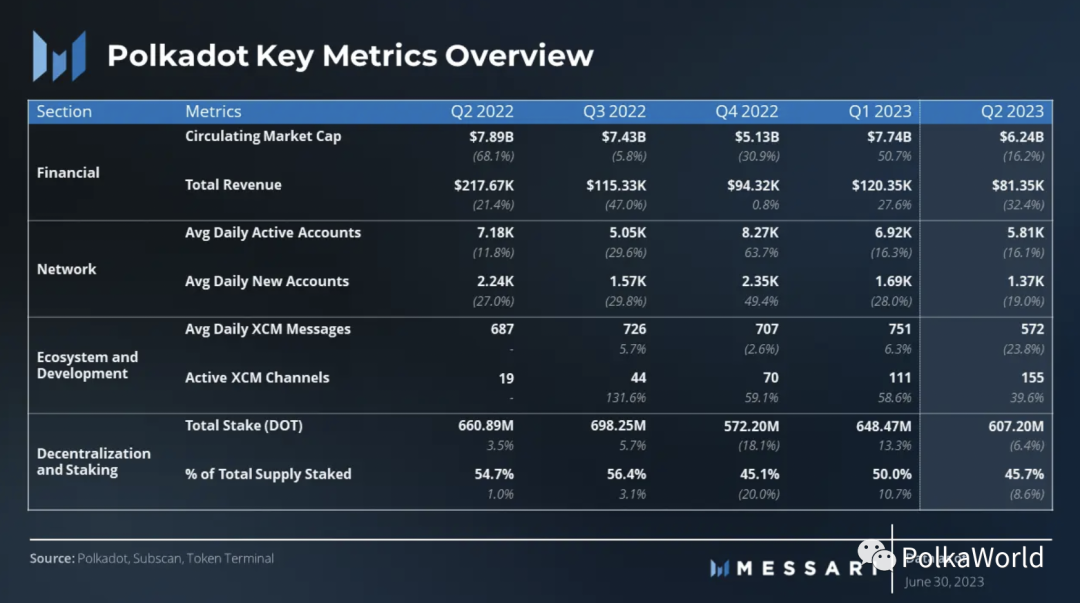
Key Metrics
Introduction
In the second quarter, the crypto industry witnessed significant developments and events, with the largest undoubtedly being the US Securities and Exchange Commission’s (SEC) lawsuit against Binance and Coinbase. These lawsuits accused certain underlying layer tokens of being securities; however, it is worth noting that Polkadot’s native token DOT was noticeably absent from the SEC’s list. Later, Web3 Foundation issued a statement stating that after extensive discussions with the SEC, DOT had undergone a transformation and is no longer considered a security.
Throughout the second quarter, Polkadot has been focused on developing and expanding its network, demonstrating consistency in key network infrastructure such as staking, treasury usage, and parachain activity. Notable milestones achieved during this time include the launch of OpenGov, which introduced an advanced governance model, and the introduction of XCM V3 on Polkadot’s mainnet. XCM V3 has shown an increase in use cases for XCM and is expected to see further growth in the future. In addition, parachains continue to renew slot leases, resulting in a surge in locked DOT.
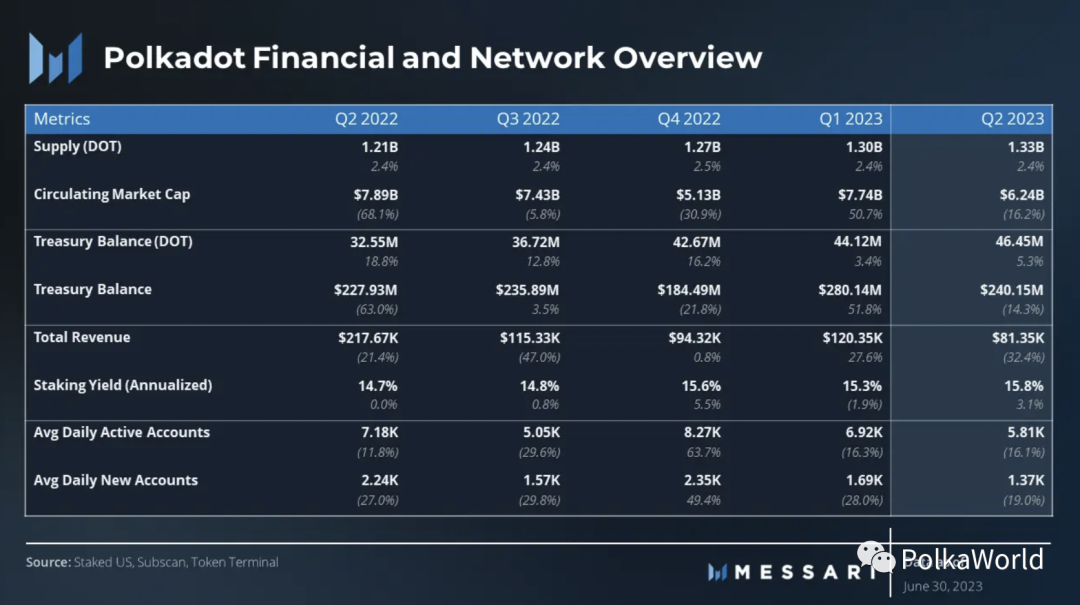
Financial and Network Overview
Note: The financial and network overview pertains only to the Polkadot relay chain and, unless specified otherwise, does not apply to parachains.
Market Cap and Revenue
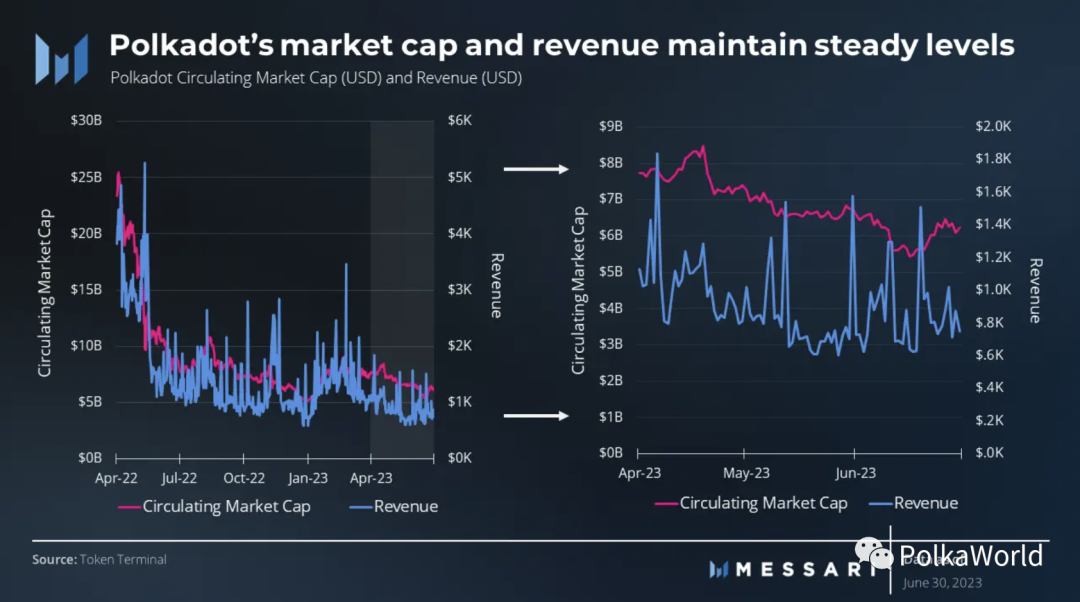
Polkadot’s market cap decreased by 16% on a quarterly basis, falling from $7.47 billion to $6.24 billion. In comparison, the overall crypto market cap increased by 2% on a quarterly basis, with BTC up 7% and ETH up 6%. The growth in BTC, ETH, and the overall crypto market is primarily driven by the emergence of spot BTC ETF applications.
As of the end of the quarter, Polkadot ranked as the 12th largest crypto project by market cap globally and the fourth-largest layer-1 protocol after Ethereum, Cardano, and Solana.
Polkadot’s financial structure is based on a weight fee model, where transaction fees are determined and collected before execution, distinguishing it from the gas billing model. Fee calculation consists of three components: weight fee reflecting computational resources, length fee based on transaction size, and optional tips to incentivize block validators. These fees come from various activities such as token transfers, staking, validator elections, governance voting, and parachain slot auctions. It should be noted that transaction fees do not apply to parachain transactions, meaning that when transacting between parachains, no transaction fees similar to those for transfers or smart contract executions are required.
In the second quarter, Polkadot’s revenue reached $81,000, a 32% decrease on a quarterly basis. It is worth noting that due to the network’s structural design, Polkadot’s revenue is typically lower relative to its competitors. Therefore, when evaluating the protocol, alternative evaluation models such as the security needs model (https://messari.io/report/layer-1-value-thesis-the-expected-demand-for-security-model?referrer=author:kunal-goel) and Multicoin Capital’s partial-sum framework (https://messari.io/report/solana-deep-dive-reframing-the-narrative), in addition to traditional revenue metrics, should be considered.
DOT Token
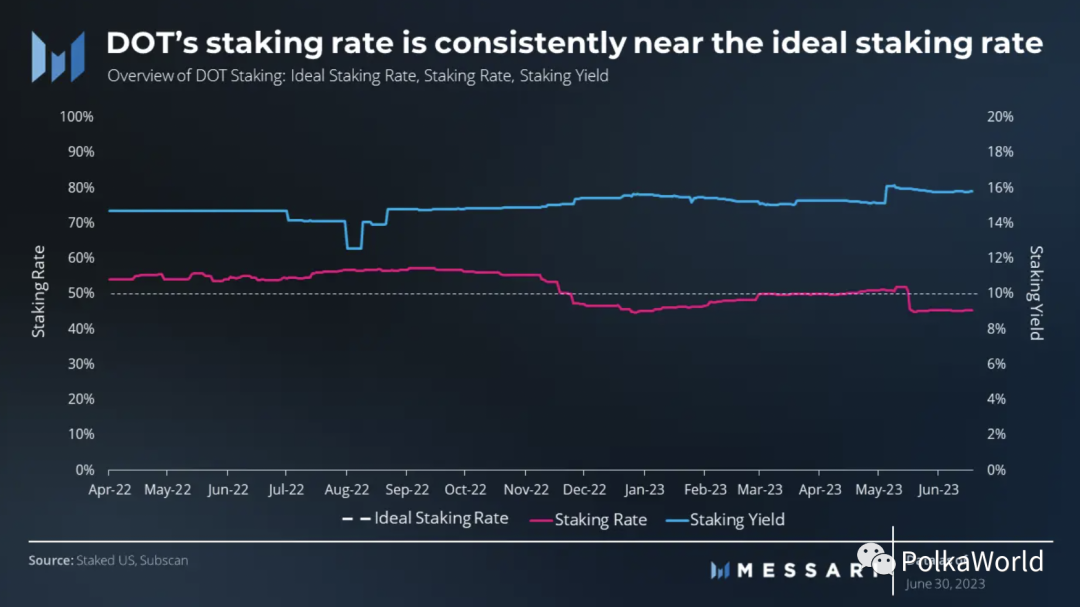
The native token of Polkadot, DOT, has three main uses: governance, staking, and binding to parachains. DOT adopts an inflationary monetary policy and has no maximum supply. Its monetary policy is determined by its adherence to the ideal staking rate, taking into account the sufficient liquidity support of the native token while preventing potential security compromises. If the amount staked is lower than the ideal rate, the staker’s rewards will increase, which encourages more stakers. Conversely, if the rate exceeds the ideal, the staking reward will decrease.
As of the end of the second quarter, Polkadot’s staking rate was 46%. This indicates that the amount of DOT staked is lower than the ideal staking rate, triggering an increase in staking rewards. At the current staking rate, DOT stakers can earn 16% annual staking returns, providing 9% actual return.
Treasury
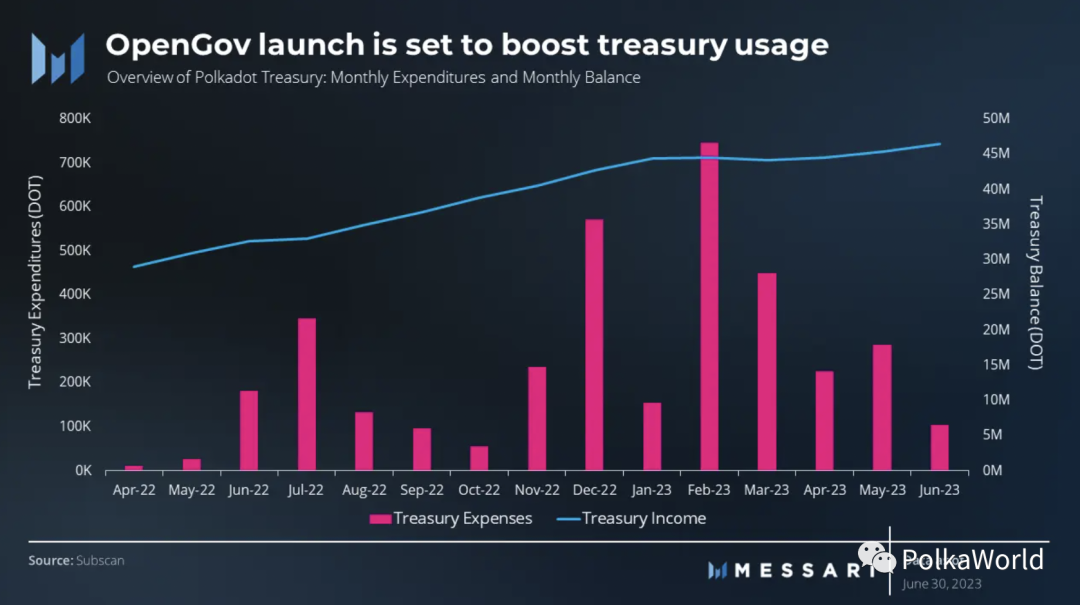
The Polkadot treasury’s funds come from block rewards, validator slashes, transaction fees, and staking inefficiencies. The treasury’s funds are kept in a system account and allocated within a 24-day spending period, with any unused funds burned at a 1% rate. It is worth noting that all treasury expenditures are executed automatically on-chain, ensuring transparency and accountability.
In the second quarter, the Polkadot treasury supported various initiatives, including wallet upgrades and integrations, client upgrades, and community events such as meetups and hackathons. The introduction of OpenGov on June 15 represented a significant milestone, as it completely changed the way the treasury is governed, enabling proposals with different requirements to run in parallel. The implementation of OpenGov is expected to drive an increase in treasury utilization, bringing substantial benefits to the Polkadot community. By the end of the quarter, the Polkadot treasury held approximately 46.5 million DOT (worth $240 million).
Accounts
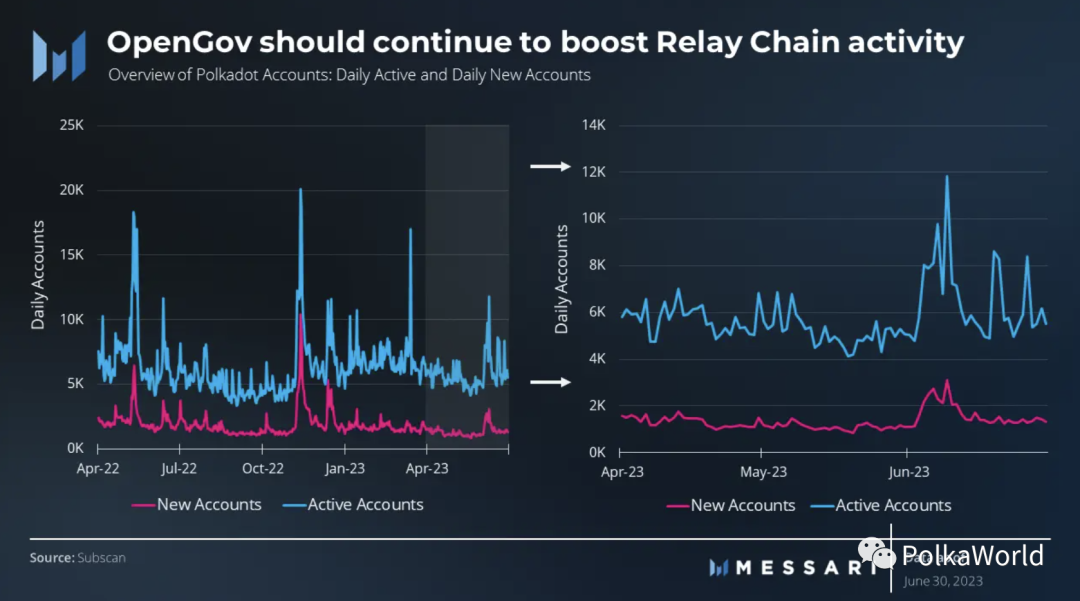
Polkadot Relay Chain has several main functions, including providing security, governance, and connecting parachains. Therefore, its end-users typically conduct transactions and use the network through parachains. However, the Relay Chain does support some end-user functionalities, including token transfers, staking, validator elections, governance voting, and participation in parachain slot auctions.
With the launch of OpenGov in June, there has been an increase in account activity on the Polkadot Relay Chain. This surge can be attributed to an increase in governance activities, as the Relay Chain plays a crucial role in facilitating the governance process. In Q2, the average daily active accounts on the Relay Chain were 5,800, a 16% decrease from the previous quarter. By the end of June, there were 3.9 million unique accounts (public key addresses) in the Polkadot ecosystem, an increase of 200,000 compared to the previous month, and a total of 600,000 added so far this year.
It must be emphasized that the activity on the Relay Chain does not necessarily represent the activity of the entire network. To gain a comprehensive understanding of network activity, activity on parachains and XCM activity must be considered.
Developer Activity
Polkadot has one of the largest developer bases in the cryptocurrency industry, as highlighted by the Electric Capital Developer Report, with over 750 full-time developers and a total of 2,000 developers. The platform provides comprehensive support to developers through its open-source technology stack, covering various categories such as user interfaces, tools, APIs and languages, smart contracts, chains and modules, network maintenance tools, consensus, and networking.
To further develop its developer community, Polkadot has made significant investments in initiatives such as the Polkadot Blockchain Academy, which is planning its third cohort of students at the University of California, Berkeley. The academy aims to provide engineers with Web3 technology skills. In addition, the Polkadot Developer Heroes program has been launched to promote collaboration and recognize outstanding developers. The specific launch date for the Polkadot Developer Heroes program has not yet been announced.
Ecosystem Overview
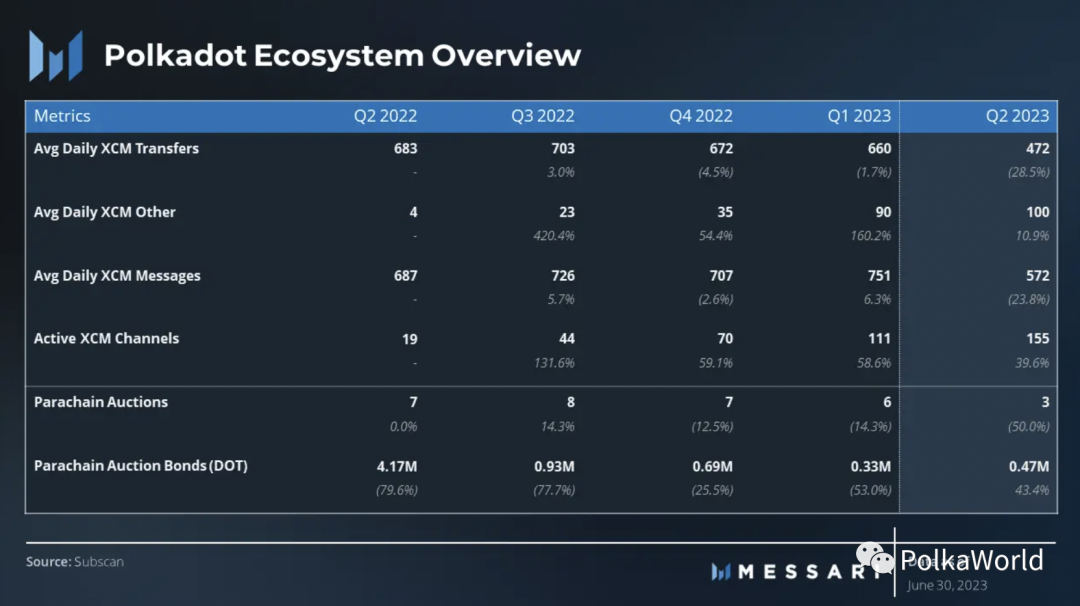
Cross-Consensus Message Format XCM
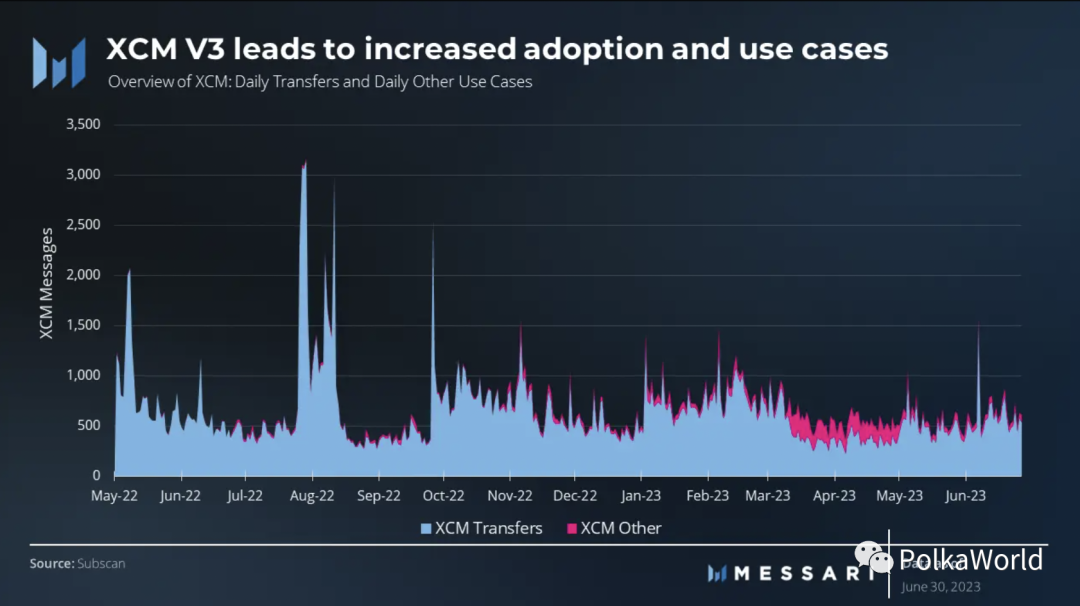
The Cross-Consensus Message Format XCM is a standardized message format and language that enables seamless communication between parachains and other consensus-based systems. XCM plays a critical role in facilitating interoperability and complex cross-consensus interactions. It allows blockchains to exchange messages, perform operations, transfer assets, and more.
XCM V3, which was released on June 15th, has generated a lot of attention. This new message format introduces advanced programming capabilities, bridging capabilities with external networks, cross-chain locking, an improved fee payment mechanism, and support for non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
Prior to its release, XCM had already begun to attract attention due to its potential for multiple use cases, a trend that is expected to further accelerate. Notably, non-asset transfer use cases accounted for 18% of the total XCM messages. While the overall message count has decreased, the number of active XCM channels has increased from 111 to 155. Major XCM channels include Moonbeam <> Acala, Acala <> Moonbeam, Acala <> Blockingrallel, Interlay <> Moonbeam, and Blockingrallel <> Acala, based on total transfer volume.
Parallel Chain Accounts
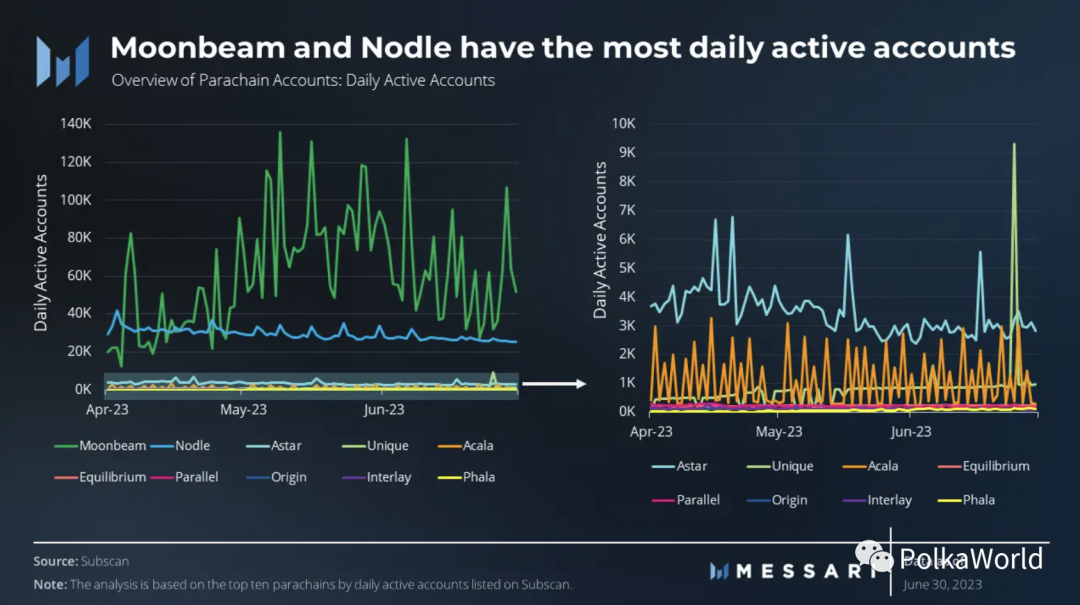
When examining daily active users on parallel chains, Moonbeam and Nodle are clearly in the lead. Moonbeam saw an increase in activity after the release of Uniswap V3 in June, indicating continued attention on the network. Nodle comes in second, as a decentralized wireless network operator aimed at IoT devices.
Astar ranks third in parallel chains, followed closely by Acala and Unique Network. Astar recently publicly disclosed details about Astar 2.0, an upcoming upgrade aimed at improving various aspects of the network, and the core development team announced a $3.5 million investment from Sony. Similarly, Acala launched the Acala Exodus plan, with a focus on improving token economics, staking mechanisms, and introducing new infrastructure and features. Unique Network, the last of the top five, operates as a parallel chain optimized for NFTs with 777 daily active users.
In Q2, the average monthly active users across the entire Polkadot ecosystem was 295,000, including external signers and token receivers.
Parallel Chain TVL
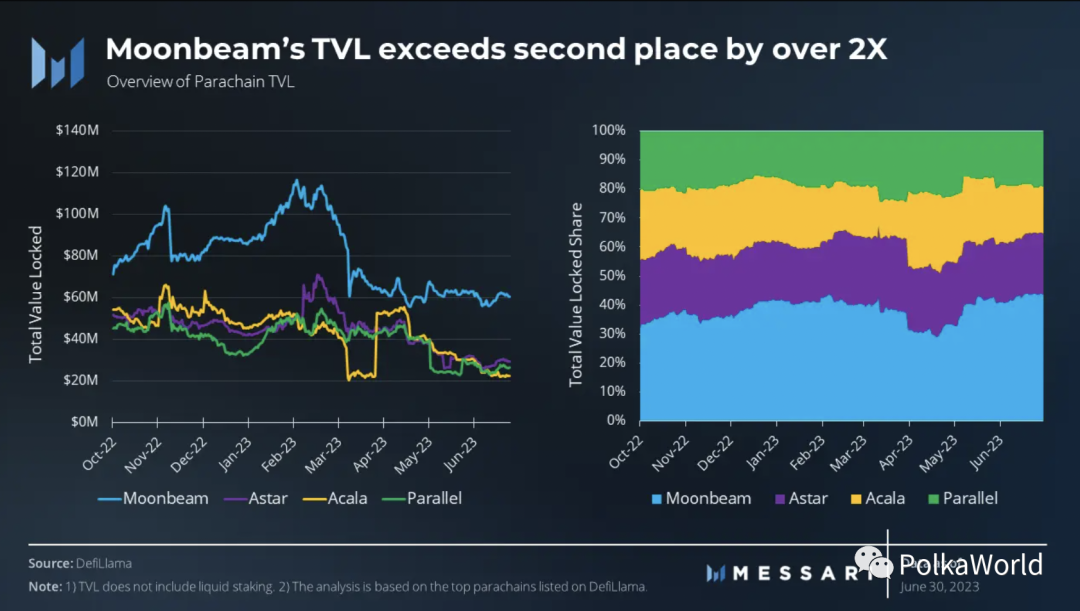
In terms of active accounts, Moonbeam is the leader in total value locked (TVL). Moonbeam has a TVL of $60 million at the end of this quarter, which is more than double the value of the second place. The next three parallel chains, Acala, Astar, and Blockingrallel, all maintain a TVL of $20 million. These top four parallel chains together contribute to a total TVL of $140 million. However, it is important to note that the total TVL of all parallel chains is higher, but accurately determining this value remains challenging.
When considering liquidity collateral, the TVL landscape has changed significantly. Blockingrallel became the highest TVL protocol, reaching $190 million, driven mainly by its liquidity crowd-lending platform. Acala is the second largest protocol, with a TVL of $170 million, also supported by its liquidity crowd-lending platform.
Parallel Chain Auction
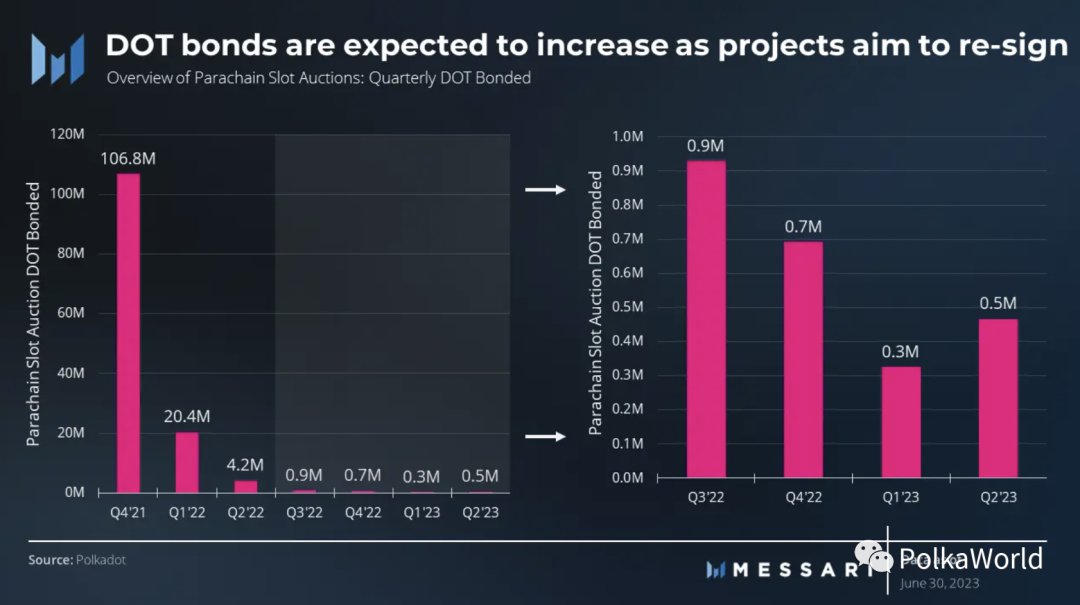
The initial slot auction plan conducted 41 auctions from November 2021 to March 2023, with a new slot auction held every two weeks. However, in the second quarter of 2023, after completing the first 41 auctions, the slot auctions were changed to once a month, and the number of winners in that quarter’s slot auctions reached three. Six slot auctions are planned for the third quarter.
In the second quarter, two of the three winners were re-signed: Acala and Moonbeam. The initial leases for Acala and Moonbeam are expected to expire on October 24th. Therefore, it is reasonable to expect that more protocols from the first batch of teams, including Astar, Blockingrallel, and Clover, will try to win slots to extend their leases. This combination of existing projects seeking re-signing and new projects hoping to join the network will intensify competition and should lead to an increase in the amount of DOT collateralized.
The only new parallel chain this quarter is Moonsama. Moonsama is the first NFT marketplace on the Moonriver network designed for generative NFTs. The platform helps exchange digital assets between on-chain and off-chain applications and is designed to integrate with various metaverses. Moonsama’s main features include an automatic chess-style battle engine and Moonsama Multiverse Chat.
Finally, in the second quarter of 2023, 467,000 DOTs ($2.4 million) were collateralized, reflecting a quarter-on-quarter increase of 43%.
Other highlights in the ecosystem
- Mythical Games announced plans to migrate its Mythical Chain from Ethereum to Polkadot to launch its new Mythos ecosystem.
- Kilt announced a partnership with Deloitte and Polimec to issue reusable KYC credentials.
- Frequency and social media app MeWe announced a partnership to bring MeWe’s 20 million users onto the blockchain.
- Composable Finance shared the launch of the Centauri IBC Bridge, allowing bridging between Polkadot and Kusama as well as Cosmos.
- Aventus Network and Beatport announced a partnership and plan to launch a music NFT marketplace.
- Energy Web announced plans to pivot to Polkadot and launch a parallel chain.
- Binance launched support for USDT deposits and withdrawals on Polkadot.
Roadmap
Since the September update, Polkadot’s roadmap has made significant progress. Key projects that have been successfully implemented include the launch of Collectives’ parachain, nomination pools, staking dashboard, OpenGov, and XCM V3. Looking ahead, the following roadmap projects are still to be implemented:
- System parachains – These parachains benefit the entire Polkadot ecosystem and obtain access to the relay chain through on-chain governance rather than the traditional parachain slot auction process. Some system chains are already live, including Asset Hub, Encointer, Collectives, and Bridge Hubs.
- Asynchronous support – This major optimization for parachain consensus aims to reduce the block time of parachains to 6 seconds, increase block space by 10x, and allow for the reuse of parachain blocks that did not enter the relay chain. Blockingrity expects that asynchronous support will significantly increase the network’s transactions per second, potentially reaching between 100,000 and 1,000,000.
- Blockingrathreads – Blockingrathreads are on-demand parachains that can be launched and run without participating in the parachain slot auction. Blockingrathreads provide the same level of security as parachain blocks and offer another entry point for developer teams seeking rapid iteration within the Polkadot ecosystem.
Decentralization and Staking Overview

Polkadot uses a unique consensus mechanism called Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS). Validators receive a payout every 24 hours based on the provable actions they have completed, also known as “era points.” Every four hours, a subset of validators is randomly selected to validate all parachains and a multiplier is applied to their era points. The combination of era points and random parachain validation provides probability guarantees for validators to receive almost equal rewards. Since validators receive nearly equal rewards and distribute those rewards proportionally to their nominators, nominators have an incentive to collaborate with validators who have lower stakes to earn higher rewards. The design of the validator-nominator reward model aims to decentralize Polkadot’s validator set.
Validators
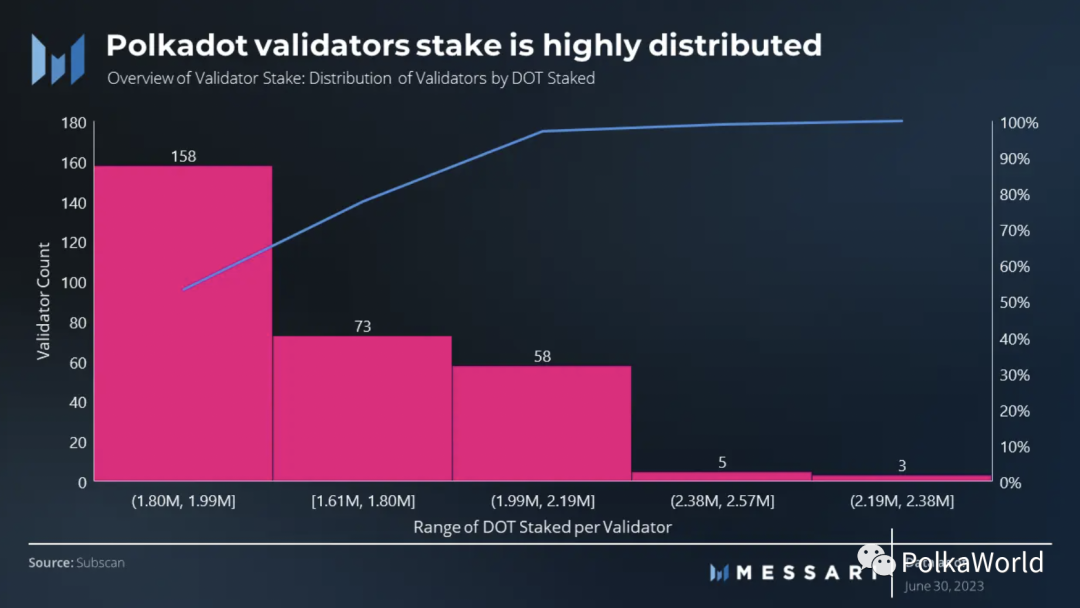
Throughout the second quarter, the number of active validators on Polkadot remained steady at 297, with no immediate plans for a change. The validator rewards model continues to prove its effectiveness in promoting decentralization of validator staking. Of the 297 validators, 97% (289 validators) have staked amounts between 1.6 million and 2.2 million DOT.
The validator model’s equal reward distribution encourages node operators to operate multiple validators. This strategy has been adopted by entities such as Coinbase Cloud (with 12 validators), P2P.org (with 18 validators), Zug Capital (with 14 validators), and Jaco (with 9 validators).
Staking
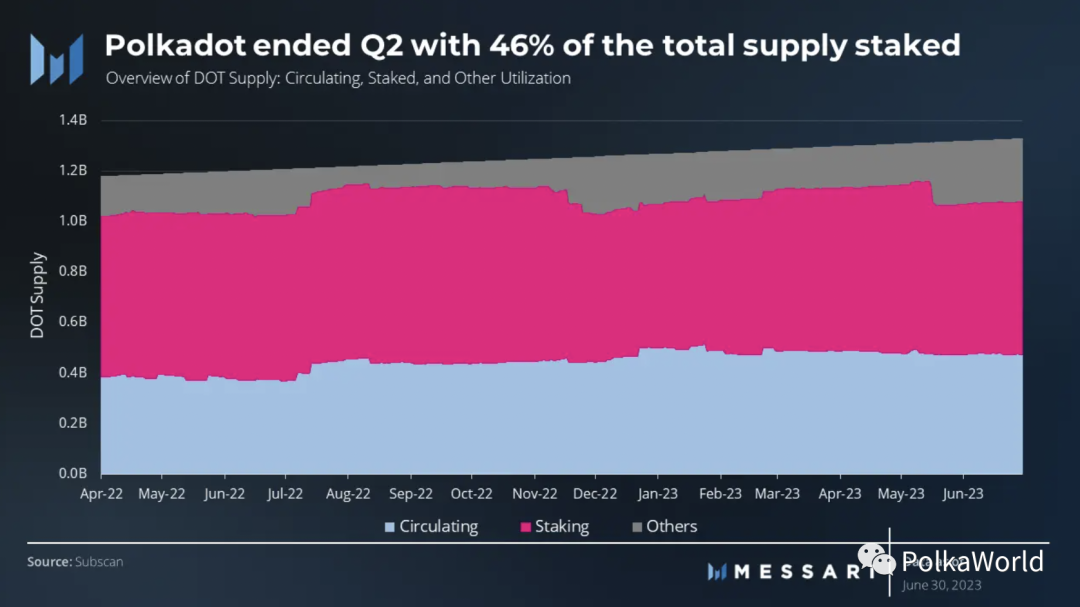
Polkadot’s staking rate was around 46% at the end of the second quarter, equivalent to 607 million DOT in total supply. Though slightly lower than the ideal staking rate, this lower proportion increases staking rewards to encourage increased staking participation. Polkadot has maintained a consistent staking rate close to the ideal staking rate.
OpenGov
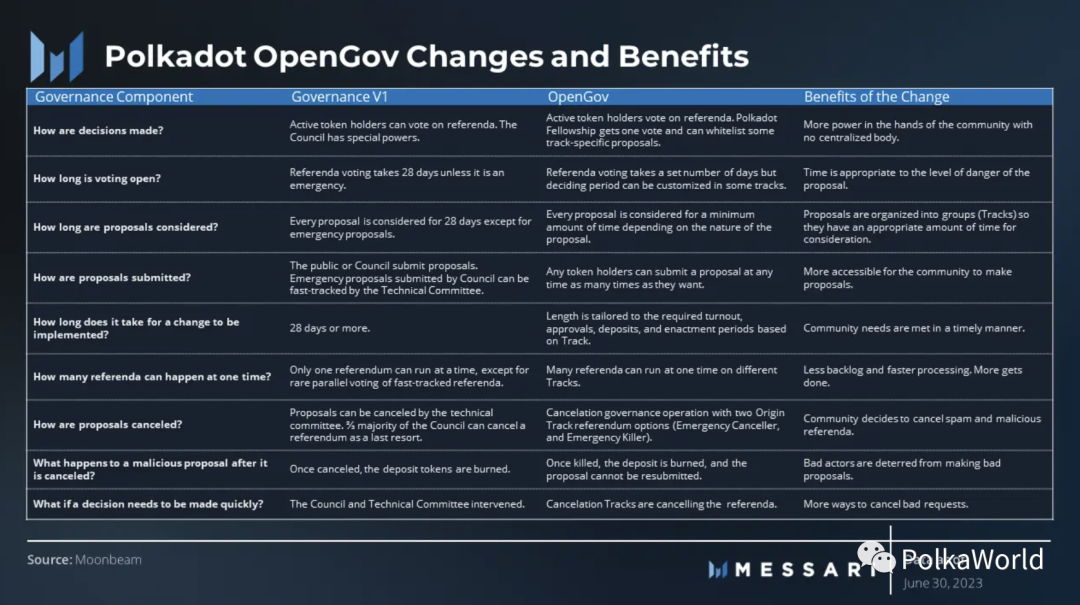
Polkadot’s new governance model, OpenGov, has officially launched, marking an important milestone after months of anticipation. In the OpenGov system, referendums go through a structured implementation cycle, including a lead-in period for submitting proposals, a decision period for voting and approval, and an enactment period for execution. OpenGov allows multiple referendums to take place simultaneously, speeding up the process of proposal approval. In the first six months of OpenGov’s operation on Kusama, the number of proposals increased by more than four times compared to the previous year.
In the OpenGov system, the council and technical committee have been replaced by the Fellowship, which serves as a developer DAO and ensures decentralization through community voting and power balancing. Additionally, the new model introduces representative flexibility, allowing users to delegate their voting rights based on the amount of tokens they believe in and commit to. These changes reflect Polkadot’s commitment to a more community-centric governance approach, promoting more democratic and efficient decision-making processes.
Conclusion Summary
Polkadot made significant progress in Q2 and continued to develop along its roadmap. The network achieved two key milestones on June 15 with the launch of OpenGov and XCM V3. While these releases occurred at the end of the quarter, they have significant potential to add value to the Polkadot network in the coming quarters. OpenGov introduces an advanced governance model, while XCM V3 enhances message formatting, paving the way for improved functionality and interoperability.
The fundamentals of the network remain strong, with significant increases in activity on parachains throughout the quarter. Acala and Moonbeam re-signed their slots, demonstrating their continued commitment to the Polkadot ecosystem. Additionally, Mythical Games’ move to Polkadot further emphasizes its growing appeal. With the first batch of parachain leases set to expire in October, it is expected that existing and new parachains will compete for limited slots, increasing the intensity of slot competition.
Looking ahead, the upcoming implementation of system parachains, asynchronous support, and parallel threads will further enhance the network’s functionality, scalability, and interoperability. Polkadot boasts one of the largest developer communities in the crypto industry and has already demonstrated its ability to deliver and release products according to its roadmap.
This report was commissioned by the Polkadot Treasury. All content is independently produced by the author and does not necessarily reflect the views of Messari, Inc. or the organization requesting the report. The commissioning organization does not affect editorial decisions or content. The author may hold cryptocurrencies mentioned in the report. This report is for informational purposes only and is not investment advice.
Original link: https://messari.io/report/state-of-polkadot-q2-2023
Translation by: PolkaWorld
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!