
Recently, the US Congress is voting on multiple cryptocurrency-related bills. These bills can greatly enhance the clarity of industry regulation. If these bills are successfully passed, they may become milestones in the regulatory legalization of the digital asset industry. The cryptocurrency market may be going through the most important legislative period in the history of the US Congress. This article will summarize the key contents, market impact, and potential for passage of the following bills.
- H.R.4763 — Financial Innovation and Technology for the 21st Century Act
- H.R.4766 — Clarity for LianGuaiyment Stablecoins Act of 2023
- H.R.4841 — Keep Your Coins Act of 2023
- H.R.1747 — Blockchain Regulatory Certainty Act
- S.2355 — A bill to clarify the applicability of sanctions and anti-money laundering compliance obligations to United States persons in the decentralized finance technology sector and virtual currency kiosk operators, and for other purposes. (THE CRYPTO-ASSET NATIONAL SECURITY ENHANCEMENT AND ENFORCEMENT (CANSEE) ACT)
- H.R.2670 — National Defense Authorization Act for Fiscal Year 2024
Note: “H.R.” stands for House of Representatives, indicating that the bill is proposed by a member of the House of Representatives. “S” stands for Senate, indicating that the bill is proposed by a senator.
1. US Legislative Process
First, we need to have a general understanding of the legislative process in the United States to better understand the contradictions and potential opportunities for the passage of bills. The United States is a country with separation of powers, where legislative power belongs to Congress, executive power belongs to the President, and judicial power belongs to the Supreme Court. Congress is composed of senators and representatives elected directly by the people, with each member representing their constituency. The specific composition of the 118th Congress of the United States is as follows:
- UNIBOT is gaining popularity. How to prevent phishing and fraud related to Telegram bots?
- MIT How did Worldcoin acquire 500,000 early test users?
- Recent Overview of POW Projects Dynex, Microvision Chain, Neurai
- Senate: 48 Democrats; 3 Independents (operating with the Democratic caucus); 49 Republicans
- House of Representatives: 212 Democrats; 222 Republicans
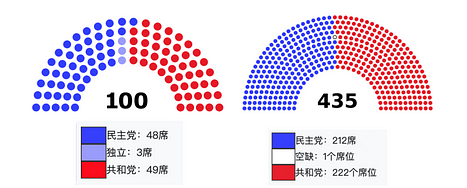
Therefore, the ruling Democratic Party maintains a majority in the Senate, while the majority party in the House of Representatives is the Republican Party.
According to the rules of procedure of the US House and Senate, there are four types of resolutions: simple resolution, concurrent resolution, joint resolution, and bill. Among them, the bill is the most common and most frequently used form of legislation. Except for tax bills and omnibus bills, which must be proposed by the House of Representatives, bills are proposed by one chamber, reviewed and passed by the other chamber, and submitted to the President for signature and become national laws after being passed and unified in text by both chambers. The process requires the following procedures:
1. Drafting the bill
The idea for a bill can come from an industry representative organization or individual citizen. Only senators or representatives can formally propose legislative bills. The drafter will seek co-sponsors among fellow members to increase the weight of the proposal.
2. Proposal
During the session of the Congress, the proposing members fill out the proposal title and main content in a fixed format and sign it. The members then submit the proposal to the “proposal box” to complete the submission process. Senators can either hand in the proposal to the Senate Secretary or read the proposal title and present the content in a plenary session, with the permission of the session presider, to complete the submission process.
3. Committee Review
The Congress will forward the proposal to a specialized committee for research, debate, hearings, and improvement. Once the proposal is submitted to the committee, it enters a complex, lengthy, and ever-changing deliberation process. The committee review process is a process of reaching consensus based on various forces competing and compromising. After obtaining the committee’s approval, the proposal will be sent to the plenary session for debate and voting.
4. Plenary Session Review
The House of Representatives and the Senate have significant differences in the plenary session review process. The House of Representatives emphasizes “the minority submits to the majority”, while the Senate highlights “consultation, compromise, and cooperation” between the majority party and the minority party.
House of Representatives: For important proposals that reflect the interests of the majority party, the Rules Committee can adopt “closed rules” during the deliberation process, which means that the proposal does not accept amendments or substitutes. For other proposals, the Rules Committee can adopt “open rules”, allowing members to propose relevant amendments or substitutes during the deliberation process.
Senate: Whether a proposal can enter the voting process after being approved by the committee depends on the support of 60 senators. The Senate has few restrictions on members’ debates. As long as they do not violate the rules of procedure, senators can speak freely on any issue without time limits. The Senate can only vote after all senators have finished speaking, which gives rise to a special operating method called filibuster. Senators can use filibustering, through lengthy speeches, to prevent the Senate from voting on the proposal under discussion. Senators can propose amendments or substitutes of any form and content for any part of the proposal, providing space and conditions for the leaders of both parties to negotiate and seek compromise.
5. Unified Text of Both Houses
Prior to the submission of the bill to the President for signature, the two houses must negotiate and unify the text of the bill.
6. Presidential Signature
Presidential Approval: The bill is approved and becomes law.
Presidential Veto: The bill is returned to Congress with an explanation of the reasons for the veto. Congress can accept the President’s opinion, modify the bill or joint resolution accordingly, and then send it back to the President for signature. Alternatively, Congress can overturn the veto by a two-thirds vote in both the House of Representatives and the Senate, and the bill will become law.
Presidential Inaction: If Congress is in session, the bill becomes law automatically after 10 days without a response from the President. If Congress adjourns within 10 days after submitting the bill to the President, the bill will not become law.
Recent Cryptocurrency-related Bills
1. The Financial Innovation and Technology for the 21st Century Act (Fit21)
Sponsors
The 212-page bill was jointly drafted by Republican members of the House Agriculture Committee and the House Financial Services Committee. It was first released in early June and its co-sponsors include Glenn Thompson, Chairman of the House Agriculture Committee (Republican from Pennsylvania), French Hill, Representative from Arkansas (Republican), and Dusty Johnson (RS.D), with Hill leading the inaugural Digital Asset, Financial Technology, and Inclusive Subcommittee, and Johnson leading the Commodity Markets, Digital Assets, and Rural Development Subcommittee.
Some may wonder why the House Agriculture Committee is interested in cryptocurrencies. The reason is that one of the committee’s responsibilities is to oversee commodities, and historically most commodities have been agricultural products such as corn, soybeans, and wheat. In 1974, the federal government established the Commodities Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) to regulate commodity futures trading, and the Agriculture Committee still authorizes the CFTC and handles futures transactions. The Agriculture Committee stated in a statement that it is interested in all types of commodity markets, including commodities that emerge through new technologies, such as cryptocurrencies and cryptocurrency futures trading.
Content and Impact
The bill clarifies the regulatory roles of the Commodities Futures Trading Commission (CFTC) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) in cryptocurrencies, giving the CFTC jurisdiction over digital commodities, including exchanges, brokers, and dealers related to digital commodities. According to the bill summary released by the co-sponsors, about 70% of cryptocurrencies are better suited to be classified as commodities rather than securities, meaning that 70% of tokens should be regulated by the CFTC, and it points out that tokens cannot be classified as securities based solely on investment contracts. The following is the definition of digital commodities in the bill, which states that digital assets are considered digital commodities based on their decentralization and the functionality of associated networks.

Market participants must comply with new and more comprehensive disclosure requirements, and intermediaries can register with the SEC or CFTC depending on whether the underlying asset is a digital commodity. If both are involved, registration with both the SEC and CFTC is required (DUAL REGISTRATION).
The bill defines digital assets as “any fungible digital representation of value,” thus explicitly excluding NFTs. At the same time, the bill also lists “ancillary activities” that are not subject to the bill, including critical blockchain support and operational services and actions such as “compiling network transactions,” “providing computation work,” “providing user interfaces,” “developing, releasing, building, managing, maintaining, or otherwise distributing blockchain systems,” etc.
The bill represents a good first step in appropriately regulating the digital asset industry and responds to the need for regulatory clarity in the digital asset field.
Process
On July 27th, the House Financial Services Committee passed the bill; on July 28th, the House Agriculture Committee passed the bill; the legislation will now be sent to the House for a full vote.
The bill faces obstacles from the Democratic Party, as many believe that the SEC should play a bigger role than what the bill currently allocates. Democratic Representative Maxine Waters from California has expressed that she never thought the CFTC should be given such strong support; Hilary Allen, a professor at American University Washington College of Law, criticized the bill as Republicans trying to please cryptocurrency exchanges, Wall Street, and Silicon Valley venture capitalists. It remains uncertain whether the bill will pass in the Democrat-controlled Senate.
2. Clarity for Payment Stablecoins Act
Initiator
The Clarity for Payment Stablecoins Act was proposed by Rep. Patrick McHenry, the Chairman of the House Financial Services Committee. It is the latest version of a series of stablecoin legislative drafts he has been involved in since last year. The bill aims to provide a regulatory framework for stablecoins and protect consumers by establishing unified standards for stablecoin issuance.
Main Content and Impact
The bill introduces requirements for capital, liquidity, and risk management, mandating licensed stablecoin issuers to hold reserves to support the issuance of stablecoins, publicly disclose the composition of their reserves on a monthly basis, disclose their redemption policies, and establish timely redemption procedures. The held reserves cannot be pledged, rehypothecated, or reused unless it is for creating liquidity to meet redemption requests. Overseas issuers must seek registration to operate in the country.
Although it may increase compliance costs, the bill is beneficial for the further development of stablecoins and DeFi. It also has a positive impact on RWAs, as projects involving on-chain assets such as fiat currencies and government bonds can be conducted legally and compliantly, paving the way for the large-scale development of RWAs. Coinbase’s Chief Legal Officer, Paul Grewal, stated on social media that the Clarity for Payment Stablecoins Act provides important protection for U.S. investors.
Process
On July 28th, the U.S. House Financial Services Committee passed the U.S. Stablecoin Regulation Act, the Clarity for Payment Stablecoins Act, with a vote of 34 to 16. The bill also faces obstacles from the Democratic Party. Democratic Representative Stephen Lynch from Massachusetts suggested postponing the vote until September, stating that Democrats did not have enough opportunity to express their thoughts. Maxine Waters, a Democratic representative from California, believes that the bill may lead to adverse competition in licenses and stated that neither the Federal Reserve nor the U.S. Treasury supports the current state of the bill.
3. Keep Your Coins Act of 2023
This bill aims to protect consumers’ rights to store Bitcoin in self-custody wallets, ensuring the freedom and privacy of individual users in managing their own crypto assets. It emphasizes giving individuals complete control over their digital assets and may have a significant impact on the cryptocurrency landscape through principles of decentralization and financial autonomy.
On July 28th, the “Keep Your Coins Act” was passed by the House Financial Services Committee and will be submitted for a House vote in the future.
4. Blockchain Regulatory Certainty Act
Sponsors
On March 23, 2023, U.S. Representatives Tom Emmer and Darren Soto introduced the “Blockchain Regulatory Certainty Act” to Congress. Tom Emmer, the sponsor and Majority Party Whip of the House, is considered to be one of the most supportive legislators for the crypto industry. He has previously supported the “SEC Stability Act” submitted by Representative Warren Davidson, which called for restructuring the U.S. SEC and dismissing its chairman, Gary Gensler. On May 18th, Tom Emmer and Darren Soto also introduced the bipartisan “Securities Clarity Act,” but there have been no further updates on this act.
Main Content and Impact
This bill aims to clarify the regulatory obligations of non-custodial blockchain developers and service providers and introduces “safe harbor” provisions for them. It argues that blockchain developers who do not custody consumer funds and non-custodial service providers (including miners, validators, and wallet providers) should not be considered as money transmitters and should not be subject to the same level of regulation as cryptocurrency exchanges that provide custody services. As long as these entities do not have control over the digital assets held by users on their platforms, they will not be classified as money transmitters or financial institutions requiring licenses or registrations, and will be exempt from specific licensing requirements.
Progress
On July 27th, the “Blockchain Regulatory Certainty Act” was passed by the House Financial Services Committee.
5. The Crypto-Asset National Security Enhancement and Enforcement (CANSEE) Act

Sponsors
Introduced on July 18th by Senator Jack Reed, and co-sponsored by Senators Mark Warner (Democrat from Virginia), Mike Rounds, and Mitt Romney (Republicans from Utah), the CANSEE Act is a bipartisan bill focused on money laundering and sanction compliance. Jack Reed has named this bill “The Crypto-Asset National Security Enhancement and Enforcement (CANSEE) Act” on his personal website.
Main Content and Impact
This bill aims to prevent money laundering and sanction evasion in DeFi and modernize the main anti-money laundering agency of the Treasury Department. It requires DeFi protocols to comply with the same anti-money laundering and related economic sanctions rules as other financial institutions, including maintaining an anti-money laundering program, conducting due diligence on their customers, and reporting suspicious transactions to the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN). The bill requires the controllers of DeFi protocols to ensure the effectiveness of the anti-money laundering program. If the protocol does not have identifiable controllers, the responsibility will fall on the individuals who invested more than $25 million in the development of the protocol. For example, if a sanctioned individual, such as a Russian oligarch, uses DeFi services to evade US sanctions, the individuals who control the project or invested more than $25 million in its development (in the absence of identifiable controllers) will be held responsible for assisting in such violations.
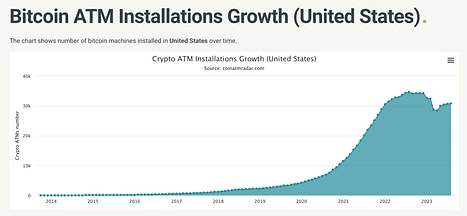
Currently, there are approximately 30,600 cryptocurrency ATMs in the United States. This bill imposes requirements on cryptocurrency ATM operators to comply with KYC laws to ensure that they do not become conduits for money laundering and other illegal activities. The bill will have an impact on the development of DeFi in the United States.
Process
This bill is the result of bipartisan cooperation, especially with its goal of strengthening national security, which gives it a better chance of receiving a full vote in the House. It has not yet entered the committee voting stage.
6. Fiscal Year 2024 National Defense Authorization Act (NDAA)
The National Defense Authorization Act is an annual bill proposed by the US Congress that redefines the military budget for the following year. The House of Representatives and the Senate have respectively proposed the Fiscal Year 2024 National Defense Authorization Act, H.R. 2670 and S. 2226.
On July 28, 2023, the US Senate passed the Fiscal Year 2024 National Defense Authorization Act, which includes amendments to strengthen regulation of cryptocurrency transaction financial institutions, mixers, and “enhanced anonymity” cryptocurrencies. The amendments were proposed by a bipartisan group of senators, including Kirsten Gillibrand (D-NY), Cynthia Lummis (R-WY), Elizabeth Warren (D-MA), and Roger Marshall (R-KS).
This amendment is based on the 2023 Lummis-Gillibrand Responsible Financial Innovation Act (S.4356) and the Digital Asset Anti-Money Laundering Act introduced by Warren and Marshall in 2022. It aims to strengthen anti-money laundering and counter-terrorism regulations for cryptocurrencies and combat anonymous cryptocurrency transactions. It requires the Treasury Secretary to establish review standards for cryptographic assets to help evaluators better assess risks and ensure compliance with money laundering and sanction laws. It also requires the Treasury Department to conduct research on “combating anonymous cryptocurrency transactions,” particularly with regard to mixers. The passage of the bill will enhance the United States’ efforts in combating cryptocurrency money laundering. Both houses now need to negotiate based on a unified version that can be passed by both houses.
Regarding the Lummis-Gillibrand Responsible Financial Innovation Act (S.4356) mentioned above, it was reintroduced by Senators Cynthia Lummis (Republican, Wyoming) and Kirsten Gillibrand (Democrat, New York). Cynthia Lummis, known as the “crypto queen” of the Senate, is a supporter of cryptocurrencies. The bill was once considered the most comprehensive and bipartisan cryptocurrency bill in the history of the Senate. The collapse of FTX put the bill on hold, and there have been no new developments since November 2022.

References:
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/38721
https://financialservices.house.gov/
http://www.npc.gov.cn/zgrdw/npc/zt/qt/xzdbtcf/2011-06/13/content_2054549.htm
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/118th_United_States_Congres
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/National_Defense_Authorization_Act_for_Fiscal_Year_2024
https://www.coindesk.com/policy/2023/07/28/us-senate-passes-886b-military-spending-bill-with-crypto-aml-provision/
https://www.congress.gov/bill/117th-congress/senate-bill/4356/all-actions
https://www.binance.com/en-AU/feed/post/874084
https://www.reed.senate.gov/news/releases/bipartisan-us-senators-unveil-crypto-anti-money-laundering-bill-to-stop-illicit-transfers
https://iq.wiki/wiki/clarity-for-payment-stablecoins-act-of-2023
https://iq.wiki/wiki/financial-innovation-and-technology-for-the-21st-century-act
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!