
Editor | Chainchen@Web3CN.Pro
Table of Contents
1. Abstract
- Starting from native inclination, explore the specialization of major chains.
- LianGuai Daily | Animoca Brands invests $30 million in Hi; Eco, supported by a16z, launches encrypted wallet Beam
- Project Research | Stacks – Expanding the New Chapter of Bitcoin Smart Contracts and DApps
2. Project Introduction
3. Project Architecture
4. Project Applications
5. Team Background
6. Fundraising Information
7. Development Achievements
8. Economic Model
9. Advantages and Risks
1. Abstract
This research report delves into the Stacks project, an innovative blockchain technology that aims to achieve high decentralization and scalability without increasing additional environmental impact by linking itself to the Bitcoin chain through its unique consensus mechanism, Proof of Transfer (POX). By providing smart contract functionality, Stacks enables Bitcoin to become a fully programmable asset, thereby offering broader applications for decentralized applications (dApps).
This report provides a detailed overview of the main components of Stacks, including how it leverages the state and security of Bitcoin, as well as the features and advantages of creating smart contracts using the Clarity language. Additionally, the report will discuss the workings of the Proof of Transfer (POX) consensus mechanism and how it utilizes Bitcoin’s proof-of-work mechanism.
2. Project Introduction
Stacks is a blockchain project that links itself to the Bitcoin blockchain. Its goal is to provide a platform that shares security with the Bitcoin chain and allows for settlement of transactions on the Bitcoin chain. By extending the functionality of Bitcoin, Stacks turns Bitcoin into a fully programmable asset, unlocking trillions of dollars of passive Bitcoin capital and providing broader applications for decentralized applications.
The Stacks project links to Bitcoin through its unique consensus mechanism, Proof of Transfer (POX). PoX allows the Stacks chain to leverage the security of the Bitcoin chain while also enabling Stacks token holders to earn Bitcoin rewards through “Stacking” behavior. This mechanism enhances the usability and scalability of Bitcoin by adding new features such as smart contracts and fast transactions on top of Bitcoin’s security foundation.
The vision of Stacks is to establish a fully decentralized network and application ecosystem based on Bitcoin. By providing new tools and technologies such as smart contracts and fast transactions, the Stacks project aims to drive further development of Bitcoin and its ecosystem, ultimately achieving a more secure, fair, and open Web3.
3. Project Architecture
The Stacks project links itself to the Bitcoin chain through its unique consensus mechanism, Proof of Transfer (PoX). This allows Stacks to leverage the state and security of the Bitcoin chain, providing a more secure and reliable platform for decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. On this platform, all transactions are settled on the Bitcoin chain, thus leveraging the robust security of Bitcoin.
The smart contract layer of Stacks has the following innovative features:
S (Secured): Stacks transactions are ultimately confirmed by Bitcoin for finality.
After approximately 100 Bitcoin blocks or about one day of confirmation, transactions that occur on the Stacks layer are protected by the full hashing power of Bitcoin. This means that to reverse these transactions, an attacker would need enough computational power to reorganize the Bitcoin chain. Stacks transactions settle on the Bitcoin blockchain and have the finality of Bitcoin. Additionally, the Stacks layer fully forks Bitcoin, meaning any forks on the Bitcoin chain, such as soft forks or hard forks, are reflected on the Stacks chain. This ensures that the Stacks chain can evolve with the development of the Bitcoin chain without conflicting with it.
T (Trust-minimized): Trust-minimized Bitcoin anchoring mechanism; writable Bitcoin
Stacks introduces a new decentralized and non-custodial Bitcoin-anchored asset called sBTC. This allows smart contracts to operate with Bitcoin-anchored assets in a faster and cheaper manner without compromising security. Furthermore, this enables contracts on the Stacks layer to write to Bitcoin without trust through anchoring transactions.
A (Atomic): Bitcoin atomic swaps and assets owned by Bitcoin addresses
Atomic swaps and assets: Stacks already has atomic swaps with Bitcoin, allowing Bitcoin addresses to own and move assets defined on the Stacks layer. Examples of trustless atomic swaps between Bitcoin L1 and assets on the Stacks layer, such as magic swaps and dual swaps, have already been launched. Additionally, users can own assets from the Stacks layer, such as STX, stablecoins, and NFTs, on their Bitcoin addresses and transfer them using Bitcoin L1 transactions if desired.
C (Clarity): Clarity language for safer and determinative smart contracts
Stacks supports a secure and determinative smart contract language called Clarity. With Clarity, developers can know what a contract can and cannot do through mathematical determinism before executing the contract. Decentralized anchoring contracts will benefit from the security properties of the Clarity language. As of December 2022, there are already 5000+ Clarity contracts deployed on the Stacks layer. Clarity’s design also avoids the issue of “gas estimation,” which is a common problem in many other smart contract languages like Solidity. In Clarity, the execution cost of a transaction can be accurately known before the transaction occurs, avoiding transaction failures due to insufficient fees. On Stacks, the creation and management of Bitcoin-anchored assets like sBTC are achieved through a special smart contract called the decentralized anchoring contract. This contract utilizes the security and reliability of the Clarity language to ensure the safety and reliability of the process of creating and managing anchoring assets.
K (Knowledge): Bitcoin full-state knowledge proofs; readable Bitcoin
Stacks has a complete understanding of the Bitcoin state. It can read Bitcoin transactions and state changes without trust and execute smart contracts triggered by Bitcoin transactions. The ability to read Bitcoin helps to maintain consistency between decentralized anchored states and BTC locked on Bitcoin L1, etc. Stacks’ ability to read Bitcoin ensures that the decentralized anchored state (i.e., the state of sBTC) remains consistent with the BTC locked on Bitcoin L1. This is because whenever there is a transaction on the Bitcoin chain, Stacks can read these changes and update the state of sBTC accordingly. In this way, users can ensure that their sBTC remains synchronized with the BTC they have locked on the Bitcoin chain.
S (Scalable) scalability, fast transactions on the BTC settlement layer
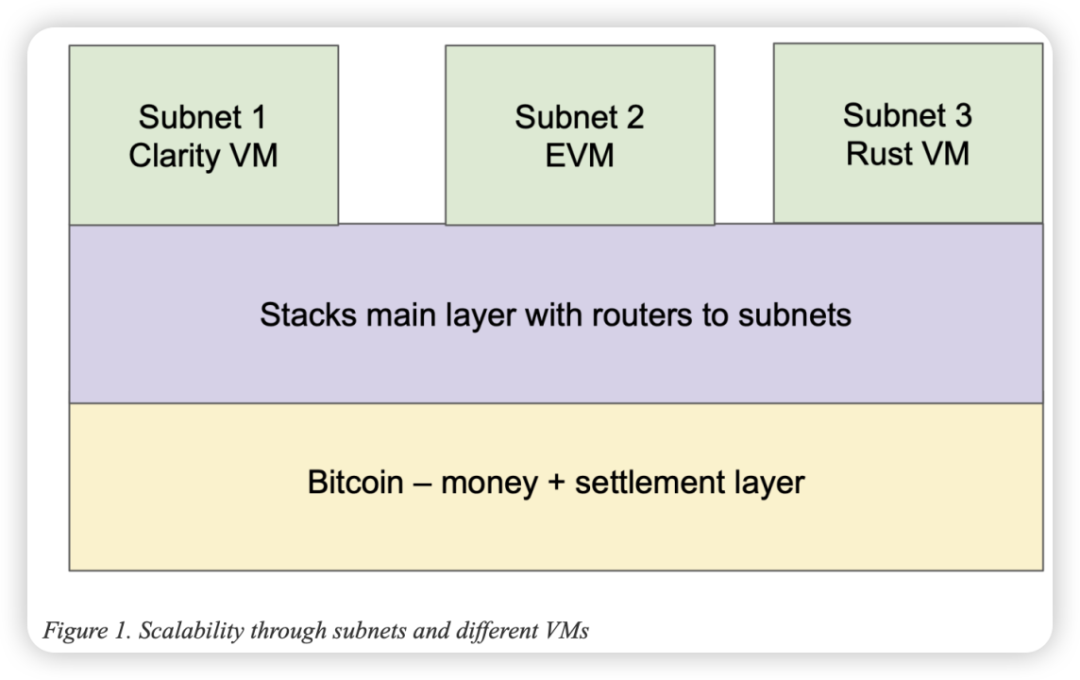
Stacks improves transaction processing speed by generating Stacks blocks faster between Bitcoin blocks. This means that transactions on the Stacks network can be completed and confirmed at a faster speed than Bitcoin. In addition, the subnet is a scalable layer of the Stacks network that can make different trade-offs between performance and decentralization. This means that subnets can be optimized based on their specific needs and priorities, such as faster transaction speeds or higher degrees of decentralization. Stacks’ subnets can support other programming languages and execution environments, such as Ethereum’s Solidity language and EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine). This means that smart contracts developed on the Ethereum network can run on the Stacks network, use Bitcoin-anchored assets, and settle on the Bitcoin chain. This greatly increases Stacks’ compatibility and application scope.
Proof of Transfer (PoX) consensus mechanism
Proof of Transfer (PoX) is a core component of the Stacks project. It is a new consensus mechanism that utilizes Bitcoin’s proof-of-work (PoW) to achieve high decentralization and scalability. In PoX, Stacks chain nodes participate in block creation by “burning” Bitcoin. This means that nodes send Bitcoin to an inaccessible address to prove that they have contributed to the security of the network. Then, these nodes have the possibility of being selected as the nodes to create new blocks, thereby receiving Stacks tokens as rewards.
The Stacks layer relies on STX and BTC for its novel consensus mechanism called Proof of Transfer (PoX), which leverages both the Stacks and Bitcoin layers. PoX is conceptually similar to Bitcoin’s proof-of-work (PoW) consensus: just like Bitcoin PoW miners spend electricity and receive BTC rewards, Stacks PoX miners spend (mined) BTC and receive STX rewards. Like PoW, PoX uses Nakamoto-style single leader election: PoX miners simply bid by spending BTC, and they have a leader with a random probability based on the bidding weight. Leader election takes place on the Bitcoin chain, and new blocks are written on the Stacks layer. In this way, PoX reuses the work already done by Bitcoin miners and does not consume any significant additional electricity: it only requires running a normal laptop/computer for Stacks nodes to bid with BTC.
Another part of PoX is “Stacking,” which allows holders of Stacks tokens to participate in the security of the network. If holders choose to “Stack” their tokens, they will be regularly rewarded with Bitcoin. This is a unique mechanism that allows participants in the Stacks chain to directly receive Bitcoin as a reward, further enhancing the connection between the Stacks network and Bitcoin.
Stacks is an intelligent contract Bitcoin layer that is deeply and continuously connected to the Bitcoin chain, unlike sidechains such as RSK and Liquid. The Stacks layer allows applications and smart contracts to use Bitcoin (BTC) as their asset or currency and settle their transactions on the Bitcoin main chain. The goal of the Stacks layer is to expand the Bitcoin economy by transforming BTC from a passive asset to a productive asset and enabling various decentralized applications. Like sidechains such as RSK and Liquid, the Stacks layer has its own global ledger and execution environment to support smart contracts and prevent the Bitcoin blockchain from being burdened by additional transactions. However, the Stacks layer is unique because it has most of the desirable Bitcoin smart contract properties. It also provides high-performance mechanisms such as fast blocks, decentralized anchoring, and subnets.
4. Project Applications
Utilizing Bitcoin as a fully programmable asset
Stacks provides Bitcoin with new functionalities and use cases. By leveraging Stacks, Bitcoin can be used as a fully programmable asset in decentralized applications and smart contracts. This innovative application allows Bitcoin to be widely used in various decentralized financial products and services, such as lending, insurance, prediction markets, etc.
Using the Stacks layer, developers can build any application they can build on other smart contract platforms like Ethereum, Solana, Avalanche, etc., but using BTC as their asset/currency and settling their transactions on the Bitcoin blockchain. They will be able to do this on the Clarity VM or using subnets on Solidity or other language EVMs or other virtual machines. Users can also directly exchange BTC from the Bitcoin chain for stablecoins and NFTs.
Unlocking passive Bitcoin capital
Stacks, through its smart contracts and decentralized applications, can unlock passive Bitcoin capital, allowing these capital to generate greater value. For example, by using Stacks, Bitcoin holders can put their Bitcoin into decentralized lending platforms to earn interest income. Additionally, Bitcoin holders can also use their Bitcoin for the security of the network by participating in the “Stacking” mechanism of Stacks and receive Bitcoin as a reward.
Providing fast transactions for Bitcoin
In addition to the above functionalities, Stacks also provides the ability for fast transactions for Bitcoin. Due to the design characteristics of Bitcoin, its transaction speed is slow, which may limit its applications in certain cases.
The Stacks Bitcoin layer provides additional functionality to achieve higher performance, as well as greater versatility and security. Although the performance mechanisms of the Stacks layer have been described above, the Stacks layer optimizes decentralization, similar to Bitcoin, rather than low latency or high network throughput: users in remote areas should be able to run full Stacks and Bitcoin nodes using ordinary laptops and home internet connections. However, the Stacks chain web layer can coordinate higher performance. The web also supports smart contracts and can make trade-offs between decentralization and performance that are different from the main Stacks chain or other webs. In addition, individual webs can support smart contracts in different programming languages and execution environments. Some webs may support Clarity and Clarity VM, with the advantage of security, while others may support Ethereum’s Solidity language and EVM compatibility, or compatibility with the Ethereum Virtual Machine, which have the advantages of easy integration and development, and can leverage all Ethereum smart contracts and tools. Through Stacks, users can conduct faster Bitcoin transactions, making Bitcoin widely used in daily transactions and micro-payments scenarios.
5. Team Background
Currently, Stacks is a project composed of multiple independent entities and communities. In the early stages, Stacks was mainly led by Blockstack PBC (now renamed Hiro Systems PBC, referred to as Hiro). Hiro has 66 team members, with Muneeb Ali as the founder. The key members of the project team have years of research and development experience in the field of distributed systems, including 6 PhDs in the field of distributed systems and 2 scientists who have received the US Presidential Career Award.
Muneeb Ali, Co-founder of Stacks and CEO of Hiro, is a computer PhD from Princeton University, focusing on researching full-stack solutions for building distributed applications.
Jude Nelson, Stacks Foundation Research Scientist and former Hiro Engineering Partner, obtained a PhD in Computer Science from Princeton University and was a core member of PlanetLab, which received the ACM Test of Time Award for implementing planetary-scale experiments and deployments.
Aaron Blankstein, Engineer, joined the Blockstack engineering team after obtaining his PhD in 2017.
Mike Freedman, Technical Advisor to Hiro, is a distributed systems professor at Princeton University.
Albert Wenger, Hiro Director and Managing Partner at Union Square Ventures (USV). Prior to joining USV, Albert was the President of del.icio.us until the company was sold to Yahoo. He is also an angel investor and has invested in Etsy and Tumblr.
6. Financing Information
The token fundraising sales amount to 609.2 million tokens, with a total fundraising amount of approximately $75.6 million. The founder and team reward amount is 253.1 million tokens. By the end of 2019, 441 million STX tokens will be unlocked, of which 36% will be held by employees, founders, and Series A investors, and 52% will be held by Reg D investors.
7. Achievements
Currently, some well-known projects on the Stacks network are:
Wallets:
- Hiro Wallet is the most commonly used open-source wallet on the Stacks chain, which helps users store, receive, or send assets on the Stacks network. It supports Ordinals but has not yet integrated the Lightning Network.
- Xverse is an non-custodial wallet that supports users to store, receive, or send assets on the Stacks blockchain. It supports Ordinals and has added biometric authentication to improve wallet security and convenience, but has not yet integrated the Lightning Network.
- GoSats is a Bitcoin wallet developed by an Indian team that focuses on the Indian community. Its vision is to have every shopper, consumer, and saver use BTC. It has also launched GosSats Visa cards, loyalty programs, and more.
DEFI:
- ALEX is a decentralized exchange (Dex) built on the Stacks chain, supported by the non-profit organization ALEX Lab Foundation. Users can trade, stake, provide liquidity, cross-chain, and participate in functions including lotteries and IDOs on this platform.
- Stackswap claims to be the first fully functional Dex on the Bitcoin chain. It allows users to trade assets, provide liquidity, stake, cross-chain, participate in LaunchLianGuaid, and deal with NFTs. It has also issued STSWToken.
- UWU is a lending protocol based on the UWU Cash stablecoin on the Stacks chain. It is designed by nickole.btc from BitAcademy and is currently in the testing phase. Users can join the community and fill out a form to qualify for testing.
Liquidity Staking:
- Planbetter is a liquidity staking protocol on the Stack chain. Over 88,000 Stackers have staked 280 million STX, accumulating 25.42 BTC in rewards.
NFT:
- Gamma is an NFT marketplace built for Bitcoin NFTs and has integrated with Stacks and Ordinals.
- Boom is a native NFT platform on the Stacks chain and has introduced a new type of NFT called Boomboxes. It allows users to delegate stake their STX and receive an NFT as a reward for the locked portion automatically.
- TradePort is a multi-chain aggregation NFT marketplace that currently supports Stacks and Near chains, with plans to expand to Aptos and Sui.
8. Economic Model
The initial supply is 1.32 billion. And there will be a certain inflation rate for issuance every year. It is estimated that it will reach 1.842 billion by 2050 (v1 was 2.052 billion).
STX is the registered digital asset on Stack 2.0 (such as usernames, software licenses, podcasts, or other digital products) and the fee required to deploy and run smart contracts. It is similar to gas fees in the Ethereum network, and operations on the network will consume STX. At the same time, STX can be used to pay transaction fees and serves as an incentive for miners to run mining nodes and developers to develop DApps.
The main attribute of STX is to work with Stack 2.0 to operate, regulate, and balance various mechanisms. The long-term value of STX depends mainly on the growth of the Stacks network and the demand for Clarity smart contracts.
In Stack 2.0, the primary way to obtain STX is through participation in the PoX consensus mechanism, by submitting BTC to receive STX or by staking STX to receive BTC. During each locked reward cycle of STX, Bitcoin transferred by miners will be received as part of the transfer proof. Once the locked cycle is completed, STX will be unlocked and can be freely used or staked again.
Nine, Advantages and Risks
Advantages
-
Bitcoin’s smart contract capability: Stacks provides Bitcoin with the ability to have smart contracts and dApps, which could attract a large number of users and developers. This could trigger the development of a new ecosystem for developers and users, thereby increasing the use and value of Bitcoin.
-
New applications and use cases: Stacks allows Bitcoin to be used as the underlying asset for smart contracts, which could open up a range of new applications and use cases, such as decentralized finance (DeFi) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs).
-
Contribution to the Bitcoin economy: By enabling Bitcoin to participate in smart contracts and dApps, Stacks could have a positive impact on the Bitcoin economy. This could increase the demand for Bitcoin and therefore increase its value. At the same time, by bringing transaction fees to the Bitcoin network, Stacks may also help maintain the long-term security of the Bitcoin network.
Risks
-
Technological development and adoption: While Stacks enhances Bitcoin with smart contract and dApp capabilities, the development and adoption of this technology still face challenges. Although the Clarity language is secure, not all developers are familiar with it. Additionally, while subnets provide higher performance and greater versatility, implementing and maintaining these subnets may bring technical and governance challenges.
-
Network effects and user adoption: Stacks needs to attract a large number of users and developers to realize its potential. This will take time and require overcoming the challenges of network effects, as existing platforms (such as Ethereum) may have already attracted a large number of users and developers.
-
Regulatory risks: Some features of Stacks, such as STX mining and Stacking, may be subject to regulatory restrictions in certain jurisdictions. Additionally, the global regulatory environment for cryptocurrencies and smart contracts is constantly evolving, which may have an impact on Stacks.
Overall, despite facing some challenges, the future of Stacks looks promising. If these challenges can be successfully addressed, Stacks could have a profound impact on Bitcoin and the entire cryptocurrency ecosystem.
References
https://www.chaincatcher.com/article/2060385
https://www.odaily.news/post/5187830
Stacks: A Bitcoin Layer for Smart Contracts
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!