Author: Gryphsis Academy
TL;DR
1. NFT lending is a financial product that occurs during the holding period of NFTs. Its core mechanism is to allow holders to use idle NFTs as collateral to borrow short-term funds without selling NFTs, obtain liquidity in exchange for cryptocurrency or fiat currency, and earn income while enjoying NFT rights, improving the efficiency of fund utilization.
2. In NFT lending agreements, there are mainly two forms: collateral lending and unsecured lending.
- Key Information on Pendle, the Latest LSDfI Project Launched by Binance
- Nostr: How to overcome the digital dilemma of social graphs?
- Analyzing the new digital currency standard “currency tied to purpose”: what are its characteristics and use cases?
1) Collateral agreement:
-
Peer-to-Peer P2P, suitable for bear markets with liquidity shortages, is not afraid of extreme market conditions affecting the security of the platform.
-
Point-to-Pool Peer to Pool, suitable for bull markets with sufficient liquidity.
-
Hybrid, has higher operation convenience on the basis of the standard point-to-pool model.
-
Collateralized Debt Position (CDP) is a good choice for those who seek some liquidity from blue-chip NFTs without paying high interest rates.
2) Unsecured agreement:
-
Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL), suitable for NFT market users who have purchase intention but temporarily lack the ability to purchase in full.
-
Flash Loan
3. The profit model of NFT lending business mainly comes from the loan interest paid by users for collateral lending. If there are flash loan and other functional businesses, it will also bring corresponding functional service fees.
4. The main risks of NFT lending include:
-
NFT collateral valuation fluctuation risk (bad debt risk)
-
High concentration of target users of the business
-
Potential overall track business volume growth space is limited due to the limited increase in high-quality asset targets
5. It is estimated that within 3 years, the overall market value of NFT estimated by neutral hypothesis will reach about $60 billion, and the TVL of NFT lending will reach about $18 billion, which can meet the lending demand of about $9 billion. The overall revenue of the NFT lending industry is expected to reach $1.3 billion.
1. Industry Pattern
In the past few years, two areas in the crypto industry have developed rapidly, one is decentralized finance that experienced the DeFi Summer in 2020, and the other is the NFT Boom in 2021.
The overall market size of NFT on Ethereum has grown from $61 million at the beginning of 2021 to a peak of around $32 billion after just over two years of development, even though the overall market value has dropped significantly, the market size is still around $7.5 billion, with industry growth exceeding 120 times.
Ethereum NFT market size and transaction volume source: NFTGo.io (2023.5.31)
Nowadays, NFT-Fi, as a track that combines NFT and DeFi, has also rapidly developed from a niche field to an indispensable part of the crypto world.
The significance of NFT securitization is to help users expand and enhance their consensus and demand for NFT in a financial deepening way. Its industry structure can be vertically divided into three layers:
1) Direct trading: that is, through trading markets, aggregators, AMMs, etc. to exchange with cryptocurrency.
Representative projects: Opensea, Blur
2) Indirect trading: i.e. providing NFT mortgage lending, financing, custody and other services.
Representative projects: BendDAO, BlockingraSBlockingce
NFT lending is a financial product of NFT that occurs during the holding period. Its core mechanism is to allow holders to borrow short-term funds by pledging idle NFTs without selling them, obtain liquidity in exchange for cryptocurrencies or fiat currencies, and obtain returns while enjoying the rights of holding NFTs, thereby improving the efficiency of fund utilization.
As a solution to the NFT liquidity problem, the demand for this innovative market is becoming greater and greater. NFT liquidity solutions with smooth user experience and sustainable transaction models will soon stand out in the entire NFT-Fi.
3. Industry barriers
The industry barrier of NFT lending business is the feasibility of realizing the core business model, which mainly includes:
1) How to effectively match the system mechanism of NFT lending demand users
Since NFTs are unique by definition, users usually need professional knowledge of specific assets and related financial knowledge to link NFT assets with lending businesses. How to design a reasonable business model that is attractive to both lenders and borrowers is the basis for ultimately achieving effective matching of user needs.
2) Reasonable pricing mechanism for NFT assets
A key related component of NFT lending business is pricing. How to provide the system with a reasonable quotation quickly and relatively accurately when estimating the value of NFT assets, calculating LTV (Loan To Value ratio), and during the liquidation period is the most important link in the operation of NFT lending business. Especially when the number of users in the protocol increases and the business demand occurring in the same period of time increases, the system quotation mechanism and efficiency for tracing and updating data will directly affect the customer experience of the entire protocol.
4. Competition pattern
Currently, NFT lending business is divided into two forms: collateralized lending and unsecured lending .
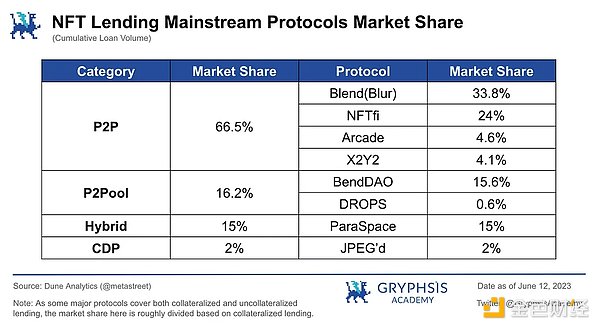
From the two charts above, it can be seen that the point-to-point and point-to-pool protocols dominate the entire NFT lending market.
It is worth noting that after Blur launched Blend in May, thanks to Blur’s head position in the NFT trading market and its user volume advantage, Blend quickly occupied the top position of the mainstream lending protocol, and its trading volume was far greater than the sum of several other protocols for several weeks. Currently, its cumulative lending business volume has jumped to the top of the industry.
5. Technical Implementation Paths and Their Advantages and Disadvantages
Based on the different types of NFT lending protocols mentioned in the previous chapter, they have their own characteristics.
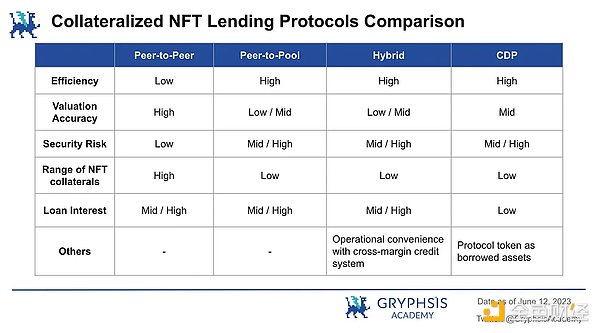
5.1 Collateral Lending
5.1.1 Point-to-point
The user valuation method is mainly used in point-to-point lending. The pricing of NFT is matched based on the price estimation given by the user. Users provide corresponding specific quotations based on the particularity of each individual NFT. It has the following characteristics:
-
Low efficiency: The pairing of both lenders and borrowers may take a long time.
-
Relatively accurate valuation: The value of NFTs with different attributes in the same series is different. Lenders and borrowers can negotiate and determine the valuation based on the attributes of a single NFT, rather than using the floor price of the entire NFT series as the only valuation standard.
-
High security: When an individual defaults, it will only affect the lenders and borrowers of that loan, and will not expand the risk exposure to other users on the platform.
-
Supports a wider range of NFT collateral: Since it is a point-to-point quotation, theoretically any NFT series can be used as collateral for lending.
Summary: The point-to-point model is more suitable for the bear market with low liquidity and is not afraid of extreme market conditions affecting the security of the platform.

5.1.2 Point-to-pool
The Time-Weighted Average Price method (TWAPs) is widely used in point-to-pool lending protocols. Oracles like Chainlink can obtain and publish a time-weighted average price of the sales price and floor price, creating a mixed price to assess the value of NFTs. Such a model can reduce the impact of abnormal events on prices by taking the average of multiple prices over a predetermined period of time, making it more difficult to manipulate prices maliciously.
Its main features are:
-
High efficiency: interact directly with the lending pool, borrow and lend at any time.
-
Less accurate valuation: the platform cannot make a detailed mortgage valuation for each NFT attribute, and can only determine the valuation based on the floor price of the series of NFTs. The loan amount that can be obtained for any attribute of NFT in the same series is the same.
-
Security risks: each loan on the platform will affect the interests of all depositors on the platform, and in extreme cases, a large number of liquidations of NFTs may trigger systemic risks.
-
Support for a small number of NFT collateral targets: for security reasons, only blue-chip NFTs with large trading volumes, good liquidity, and relatively stable prices are supported as collateral.
Summary: The Point-to-Pool model is more suitable for a bull market with abundant liquidity.
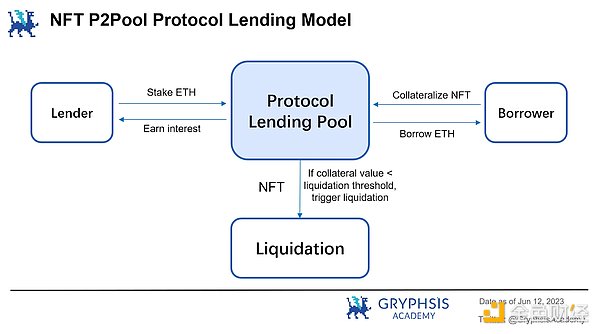
5.1.3 Hybrid
The underlying lending business of the hybrid protocol also adopts the Peer-to-Pool model. Users can borrow and lend NFTs in real time as borrowers and lenders. Its innovation lies in the creation of a cross-margin credit system instead of the isolated margin pool design used by existing platforms, which will allow users to provide loans with a credit limit for all collateral.
Here’s an example:
Suppose you own 61 BAYC and decide to mortgage 5 of them to borrow, and then buy another one. Using the existing lending protocols and their isolated margin model, you would need to borrow ETH with these 5 BAYC separately and then go to the market to buy new BAYC.
There are at least two disadvantages to this process:
1. In terms of user experience, users need to perform 5 different on-chain transactions and manage 5 separate borrowing and lending positions.
2. If any of your borrowing and lending positions are about to be liquidated, you must repay the loan immediately to avoid being auctioned off.
On the other hand, a hybrid protocol generates a credit line for you by collateralizing your NFT assets, and generates a health factor for your entire collateralized asset portfolio. As long as the health factor of your entire collateralized asset portfolio remains above 1, none of your NFTs will ever trigger a liquidation auction. To reduce risk, you can always choose to deposit more collateral (NFT or ERC-20 tokens) to maintain a high health factor.
This credit system is similar to a valuation system that evaluates the value of all your collateral, and automatically approves loans based on that evaluation. As long as your collateral is a supported collateral type of the credit system, you can borrow and lend based on their total value. This is a full leverage mode that adopts cross-margin.
It is easy to understand that this mode has higher operability than the standard point-to-pool mode.
5.1.4 Collateralized Debt Position (CDP)
After the user deposits NFTs as collateral into the vault, they can mint the corresponding protocol currency. The project protocol of the CDP allows the protocol currency debt position to reach a certain proportion of the collateral value and charge a certain annual interest rate.
When the user’s debt/collateral ratio exceeds the liquidation threshold, DAO will execute liquidation. The DAO repays the debt and retains or auctions off the NFTs to establish its vault.
Users can purchase insurance against liquidation when borrowing, paying a specified percentage of the loan amount upfront, which is non-refundable. With insurance, users can choose to repay the debt themselves within a specified time after liquidation (with a penalty).
CDP loans are a good option for those seeking liquidity from their blue-chip NFTs without paying high interest rates.
5.2 Unsecured lending
5.2.1 Flash Loan (Down Payment Purchase)
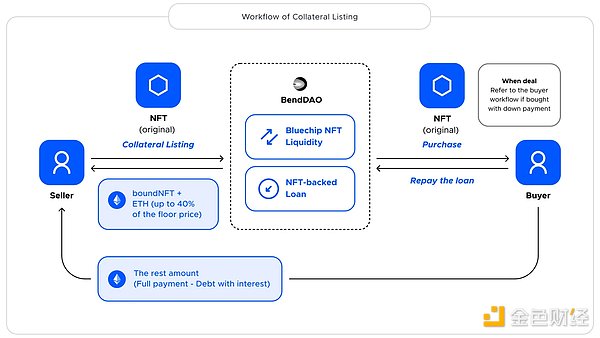
Lightning loan (Buy Now Pay Later) is a variant of traditional lending, where the user can pay a certain down payment on an NFT listed in the trading market and the remaining funds are provided by a third-party DeFi protocol that offers lightning loan services (such as Aave). When the user pays the down payment and the third-party obtains the remaining amount through a lightning loan, the buyer owns the NFT and at the same time mortgages and borrows from the NFT lending protocol. The funds lent by the protocol are returned to the lightning loan, and the interest calculation, repayment mechanism, and liquidation mechanism are all based on the provisions of the lending protocol. When the asking price is higher than the floor price of the NFT in the protocol, the down payment ratio will also increase accordingly. The fees usually include down payment fees and lightning loan service fees.The workflow is shown in the following diagram: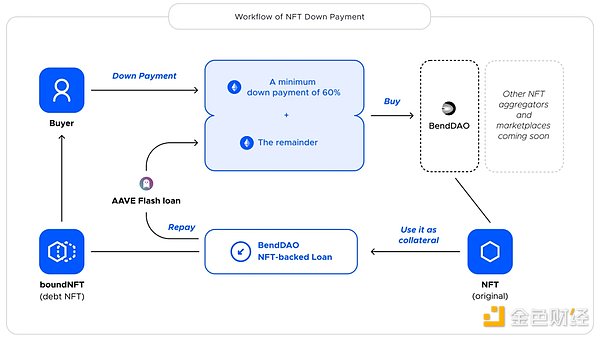 Source: BendDAOFrom the buyer’s perspective, the BNPL (Buy Now Pay Later) operation works as follows:1. Bob wants a Pudgy Penguin. First, he initiates a BNPL plan on the platform to buy any Penguin currently listed on Opensea, LooksRare, or X 2 Y 2.2. Then, the platform provides Bob with an installment plan that includes a pre-quoted interest rate, which he needs to repay within a three-month installment period. Regardless of the NFT price fluctuations, the installment payment will not change and will be fixed for three months.3. If Bob accepts the plan, he will receive ETH from the platform’s funding pool to purchase the NFT and be held in custody according to the platform’s smart contract.4. When Bob completes all his installment payments, the NFT will be transferred to his wallet, and he can have full ownership. (Note: If the price of the NFT appreciates during this period, Bob can pay the full amount of the BNPL plan in advance and sell the NFT.)5. Overdue payments will be considered a breach of contract, and the NFT will be kept in the corresponding platform Vault for liquidation.The BNPL function provides a “pawn” service that allows users to temporarily publish their NFTs as collateral in exchange for loans. Then, the loan is repaid along with the interest, which goes directly into the funding pool. To prevent plan breaches, the platform adopts various risk management measures, such as raising interest rates to regulate loans and prevent holding high-risk NFT products.
Source: BendDAOFrom the buyer’s perspective, the BNPL (Buy Now Pay Later) operation works as follows:1. Bob wants a Pudgy Penguin. First, he initiates a BNPL plan on the platform to buy any Penguin currently listed on Opensea, LooksRare, or X 2 Y 2.2. Then, the platform provides Bob with an installment plan that includes a pre-quoted interest rate, which he needs to repay within a three-month installment period. Regardless of the NFT price fluctuations, the installment payment will not change and will be fixed for three months.3. If Bob accepts the plan, he will receive ETH from the platform’s funding pool to purchase the NFT and be held in custody according to the platform’s smart contract.4. When Bob completes all his installment payments, the NFT will be transferred to his wallet, and he can have full ownership. (Note: If the price of the NFT appreciates during this period, Bob can pay the full amount of the BNPL plan in advance and sell the NFT.)5. Overdue payments will be considered a breach of contract, and the NFT will be kept in the corresponding platform Vault for liquidation.The BNPL function provides a “pawn” service that allows users to temporarily publish their NFTs as collateral in exchange for loans. Then, the loan is repaid along with the interest, which goes directly into the funding pool. To prevent plan breaches, the platform adopts various risk management measures, such as raising interest rates to regulate loans and prevent holding high-risk NFT products.
As can be seen, the business model of non-collateralized lending, whether it is flash loans (down payment purchase) or BNPL buy now pay later, actually places the mortgage behavior in the post-purchase order. Users can obtain NFTs with a smaller initial investment by paying a certain percentage of the down payment in advance and repay the corresponding loan within a designated time period. This is suitable for NFT market users who have a willingness to buy but temporarily lack the ability to buy in full.
Therefore, the characteristics of such lending models are:
-
Reasonable capital utilization rate, which can reduce user financial pressure by making a smaller initial investment ahead of time to purchase behavior.
-
Require a reliable credit evaluation system to assess the risk of each transaction.
-
The risk control model needs to be tested, especially in the early stage of the product. It is crucial to effectively control risks and maintain business health when the number of users increases dramatically in the future.
6. Profit Model
Generally speaking, the income sources of NFT lending protocols mainly include: (1) loan interest paid by users for collateralized loans, (2) loan handling fees brought by flash loans and other functional businesses, and (3) transaction market fees.
The profit model of the NFT lending business in the protocol mainly comes from loan interest and loan handling fees, and the transaction market fees are not related to the lending business.
The distribution of project income may vary depending on the project agreement. There may be different proportions of distribution between the project treasury and token holders/users.
7. Industry Valuation
Using the top-down valuation method and analogizing the DeFi lending market size for estimation. The growth logic is mainly that the NFT market size will continue to grow with the development of the entire Web 3 industry. As a track that is still in the early stage of development, NFT lending still has a considerable overall growth space.
7.1 Valuation Assumptions
The encryption market has periodicity and is currently in a cyclical bear market. The overall size of the NFT industry will fluctuate with the market cycle. The penetration rate (locked-in assets TVL) of NFT lending will rise relatively quickly.

(a) Annual growth rate of industry market value
Referring to the development of Defi lending market for about 4 years from 2019 to now, it can be seen that in the first two years of the rapid development of the industry, and under the condition that the market environment is relatively healthy, due to the small market base, the overall market size will grow rapidly by tens of times. However, in 2022, due to the overall weak market, the overall market value will experience a sharp decline. The trend of changes in the NFT market over the past two years is similar to that. Since the beginning of this year, the overall Defi market value has recovered on the basis of 2022. If the slow recovery continues, it is expected to recover last year’s decline after a whole year.
Therefore, it is assumed that the overall industry market value of the NFT industry will increase by 60% this year. Referring to the bull-bear cycle, assuming that 24 is also a stable period, the growth rate is the same as that of 23, and 25 is a period of bull market outbreak, which is 3 times the growth rate of the stable period.
The above assumptions are taken as neutral assumptions. The conservative assumption takes 50% of the neutral assumption’s annual growth rate, and the aggressive assumption gives a high expectation based on the neutral assumption.
(b) NFT lending TVL ratio
Referring to the penetration rate of lending business in the overall Defi market TVL lock-in rate in the past 3 years in the range of 25%~30%, the NFT lending TVL is expected to reach a similar ratio in 25 years, taking 30% as the neutral assumption. Taking 25% as the conservative assumption and 40% as the aggressive assumption.
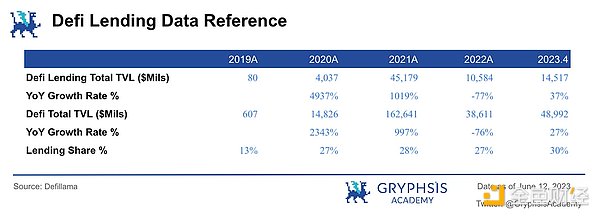
(c) NFT collateral LTV
After comprehensively analyzing the LTV data of several mainstream NFT lending protocols, 50% is taken as the LTV assumption for valuation.
(d) Borrowing interest rate APR
Referring to the annualized interest rate of Defi lending and the current NFT lending, 15% is taken as the APR interest rate assumption for NFT borrowing.
7.2 Market valuation forecast
In the next 3 years, if the neutral assumption in the valuation model is used as the basis for estimation, that is, the overall market value of the NFT industry will steadily increase in 23/24 years (annual growth rate of 60%), and it may enter a bull market cycle in 25 years with a significant increase (annual growth rate of 200%). NFT lending TVL accounts for 30% of the overall industry market value. LTV = 50%, borrowing APR = 15%.
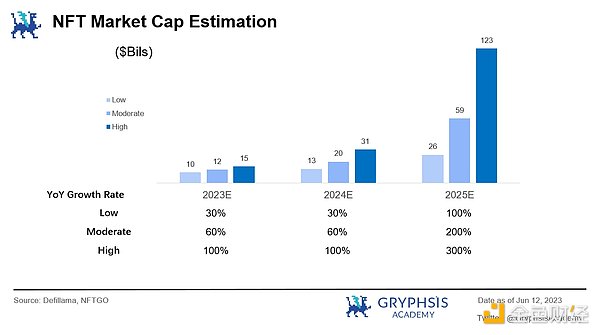
According to the assumptions above, it is expected that within 3 years, the overall market value of NFTs could reach about $60 billion and the TVL of NFT lending could reach about $18 billion, with a potential lending demand of about $9 billion (estimated based on an average LTV of 50%). The overall operating income of the NFT lending industry is expected to reach $1.3 billion, which is nearly 10 billion yuan (estimated based on an average annualized lending rate of 15%).
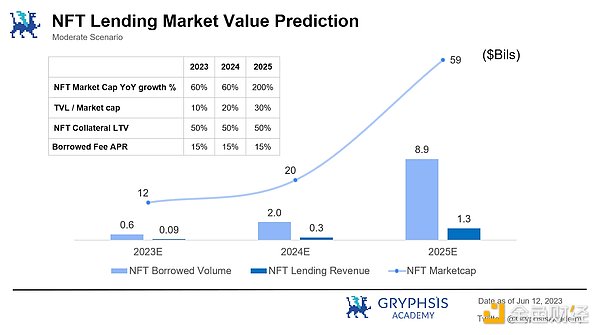
Note: The operating income here only considers the absolute majority of lending interest income in the industry, referring to historical lending data from several major NFT lending platforms (with interest rates mostly concentrated in the range of 15% to 30%) and combined with the evolution trend of Defi lending rates, taking 15% as the average annualized lending rate assumption for NFT lending.
8. Introduction of Major Companies/Protocol Products
This chapter introduces the main company products under the mortgage lending model.
8.1 Peer-to-Peer
8.1.1 NFTfi
NFTfi.com is a mature auction-based P2P NFT lending platform, where the bidding and interest rate calculation are jointly determined by the funding provider and the NFT collateral provider, and it is a leading platform in P2P lending business.
Since its launch in 2020, it has accumulated more than 45,000 loans, with a lending amount of about $450 million (as of the end of May 2023). Since April 2022, the monthly ETH lending volume has been maintained at more than 10,000 coins, and the peak monthly volume reached nearly 18,000 coins in January 2023. From March to May 2022, the monthly revenue exceeded $1 million, reaching a peak of over $1.5 million in May.
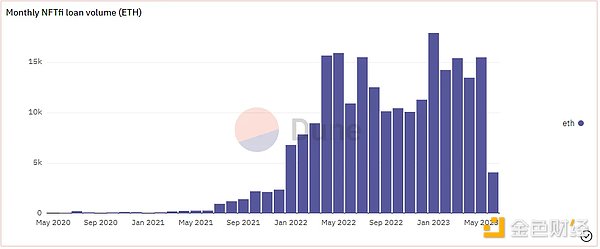
Source: Dune Analytics@rchen 8 (June 12, 2023)
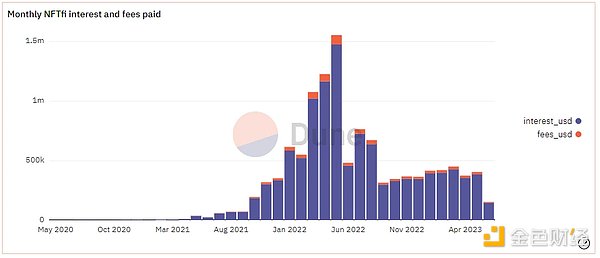
Source: Dune Analytics@rchen 8 (June 12, 2023)
8.1.2 Arcade
Arcade is also a peer-to-peer platform that provides a liquidity lending market for NFTs. Its predecessor was Blockingwn.fi. The project is built on top of the Blockingwn protocol, which is an infrastructure layer for NFT liquidity that includes a set of smart contracts deployed on the Ethereum blockchain that can securitize non-fungible assets. NFT holders can apply for loans using one or more of their assets as collateral through the Arcade application. They then request a loan with specified terms.

Source: Arcade (2023.6.12)
The platform creates a packaged NFT (or wNFT) using smart contracts, representing the borrower’s loan collateral when applying for a loan. The wNFT is locked in an escrow smart contract that records when the principal funds are sent to the borrower and repaid to the lender.
As of June 12, Arcade has accumulated over 2,000 loans, lending out about $100 million in lending funds, and the monthly lending volume has remained above 5,000 ETH for the past six months. The cumulative loan interest income exceeds $1.3 million.
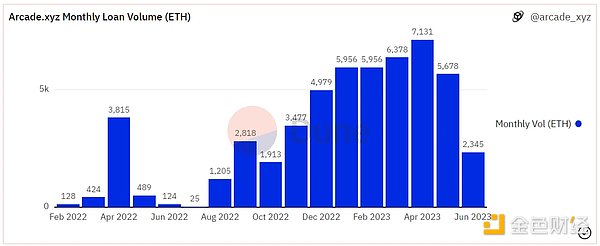
Source: Dune Analytics@arcade_xyz (2023.6.12)
8.1.3 Blur (Blend)
Blur, the top NFT trading platform, launched the Blend P2P NFT lending protocol and its associated feature of buying NFTs with loans in May in collaboration with Blockingradigm.
The core features of Blend are:
-
Peer-to-peer, perpetual lending, no expiration date, no need for an oracle
-
The lender sets the amount and APY that can be lent and publishes the offer, and the borrower chooses the offer
-
When the lender exits, the borrower needs to repay the loan within 30 hours or borrow new funds, otherwise it will be liquidated
-
The borrower can repay at any time
-
Supports buy now, pay later, i.e. down payment + loan to buy NFTs

Source: Blur
The core advantage of Blend is to unify non-essential elements, reduce system complexity, and migrate lending relationships flexibly within the system, price risks and returns through market games, and maximize user satisfaction.
Compared with the traditional peer-to-peer model, Blend unifies the term element of the three borrowing elements, collateral ratio, interest rate, and term, into a perpetual flexible model, greatly improving the liquidity of the borrower.
Blend unifies the borrower’s exit and liquidation, and the oracle is the service for deciding the liquidation timing. Blend unifies the exit option and gives it to the borrower to handle flexibly.
Blend unifies non-essential elements in the traditional peer-to-peer lending model, improves efficiency, and is fully integrated with the Blur trading module, which has greatly improved at the product level. After launching on the market, it has been recognized by the market in the short term, and the lending transaction volume has rapidly increased. In early May, the loan volume has exceeded NFTfi.
Since its launch in early May, Blend has achieved nearly 50,000 loan transactions and loan amounts exceeding US$700 million in just over a month. The cumulative number of users is nearly 20,000. Since June, the business scale has further expanded compared to May, and the daily number of lending transactions has remained at around 2,000, and the daily loan amount has steadily exceeded US$20 million, with a peak of US$34 million on June 6.

Source: Dune Analytics@ goyem (2023.6.12)

Source: Dune Analytics@impossiblefinance (2023.6.12)
8.2 Point-to-Pool
8.2.1 BendDAO
The point-to-pool model is led by BendDAO. BendDAO is the industry’s first NFT lending protocol with the “point-to-pool” model, mainly serving blue-chip NFT holders. The borrower (point) can quickly borrow funds in ETH from the protocol pool (pool) by pledging blue-chip NFTs in the pool, and the depositor (point) provides Ethereum to the fund pool (pool) to obtain interest calculated in ETH, and both the borrower and lender will receive BEND mining rewards. When the pledged NFT price falls to a certain level, liquidation will be triggered. Currently, BendDAO supports 10 mainstream blue-chip NFTs for collateralized borrowing.

Source: BendDAO
BendDAO Interface:
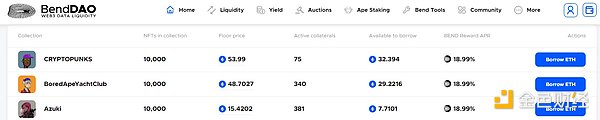
Source: BendDAO
BendDAO’s blue-chip NFT collateral amount:

Source: Dune Analytics@cgq 0123 (June 12, 2023)
The floor price data of NFTs is obtained by the Bend oracle. The Bend oracle is developed by the BendDAO team in collaboration with Chainlink. The raw data of the oracle comes from the floor price of Opensea, X2Y2, and LooksRare. The data will be filtered according to the trading volume of each platform to calculate the low price. TWAP (Time-Weighted Average Price) is used to ensure that the data is not manipulated.
Source: BendDAO
Since its launch in March 2022, the protocol has been continuously updated and iterated, and the team has continued to develop new businesses to serve market demand. Currently, in addition to the main lending business, BendDAO has also launched an embedded trading market, supporting new functions such as “flash loans” and “collateral orders”, as well as “peer-to-peer” lending and “Bend Ape Staking” asset pairing functions for Yuga Labs pledging.
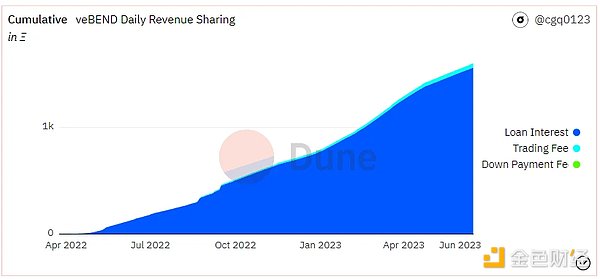
Source: Dune Analytics@cgq 0123 (June 12, 2023)
The protocol fees of BendDAO come from (1) loan interest and (2) flash loan function fees (paid by the buyer, rate is 1%). There are also transaction market fees (paid by the seller, rate is 2%), but they are not related to the lending business. Among them, the part of the protocol income that is included in the treasury is (1) 30% of the interest paid by the borrower and (2) 50% of the flash loan fee.
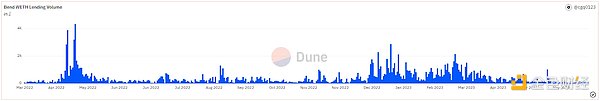
Source: Dune Analytics@cgq 0123 (June 12, 2023)
As of June 12, BendDAO has lent out over 170,000 ETH, with a peak daily lending volume of 4,340 ETH in May 2022. The total project revenue is 1,669 ETH, of which loan interest income accounts for approximately 94%. As a point-to-pool project, BAYC/MAYC/Cryptopunks are the three main blue-chip collateral targets, currently accounting for over 70% of the collateral amount. Since the beginning of this year, the project’s loan annualized interest rate APR has remained in the range of 25-30%, with daily interest income of approximately 3-6 ETH.
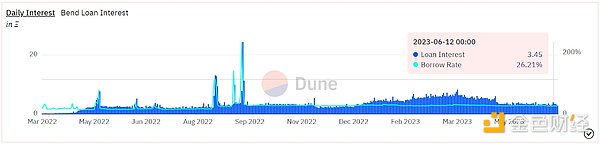
Source: Dune Analytics@cgq 0123 (2023.6.12)
8.2.2 DROPS
DROPS operates a currency market similar to Compound, where users can collateralize an NFT investment portfolio to borrow USDC and ETH. The NFTs are priced by a Chainlink oracle that adjusts based on outliers and the average over a period of time.
Like Compound and Aave, DROPS uses a piecewise interest function that targets a specific utilization rate, with borrowers paying significantly higher rates when there is not enough funding available for withdrawals.
To limit liquidity provider risk, DROPS separates the protocol into isolated pools, each with its own NFT collection. This is similar to how Fuse operates on Rari Capital, and ensures that borrowers get to choose the collection they are satisfied with.
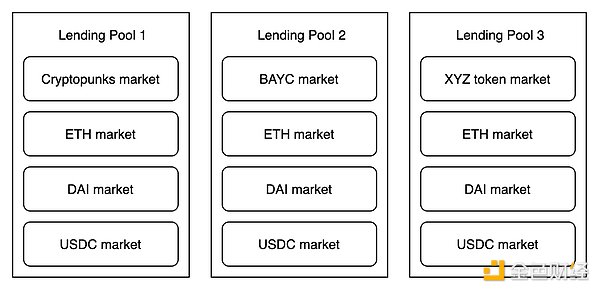
Source: DROPS
DROPS has currently accumulated over $11 million in borrowed funds (as of 6.12)
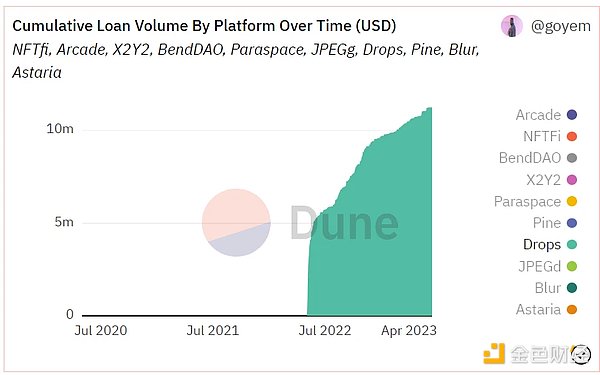
Source: Dune Analytics@metastreet / @goyem (2023.6.12)
8.3 Hybrid
8.3.1 BlockingraSBlockingce
BlockingraSBlockingce is an NFT lending protocol that uses a peer-to-pool model, allowing users to collateralize and borrow both NFTs and fungible tokens. BlockingraSBlockingce allows users to package assets of ERC-721 or ERC-20 tokens, collateralize and borrow against the package, using underutilized funds to further invest, improving the efficiency of users’ on-chain assets and earning profits.

Source: BlockingraSBlockingce
BlockingraSBlockingce’s innovative collateral lending model creates the first cross-margin credit system, as opposed to the isolated margin pool design used by existing platforms, which will allow users to offer loans against all collateral at a credit limit.

Source: BlockingraSBlockingce
By pledging your NFT assets through BlockingraSBlockingce, you’ll generate a credit line and a health factor for your entire collateralized asset portfolio. As long as the health factor of your entire collateralized asset portfolio stays above 1, none of your NFTs will ever trigger a liquidation auction.
This credit system is similar to a valuation system that evaluates the value of all of your collateral and automatically approves loans based on that evaluation. As long as they are supported collateral types by BlockingraSBlockingce, you can borrow against their total value.
This is adopting the cross-margin full-position leverage mode.
In addition, BlockingraSBlockingce has also designed a “Hybrid Dutch Auction” liquidation mechanism, a “Buy Now, Pay Later” feature under the credit system, high rarity NFTs now offer high credit limit loans, and borrowing to short feature to meet the needs of the current NFT market.
Since its official launch in December 2022, BlockingraSBlockingce’s business scale has grown rapidly, with growth rates significantly higher than the overall NFT lending market data. In the past six months, lending data has surpassed BendDAO across the board. The project’s cumulative lending funds have reached nearly $300 million (as of June 12, 2023), with more than 13,000 users. It reached a single-week lending peak of over $20 million in April of this year, and the lending capital scale has remained at around $5 million per week in the past month.
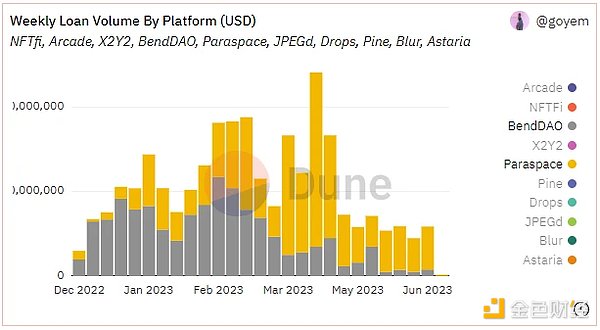
Source: Dune Analytics@goyem (June 12, 2023)
8.4 Collateralized Debt Position CDP
8.4.1 JPEG’d
JPEG’d is an improved lending protocol for NFT P 2 P pool, which adopts the MakerDAO’s CDP (Collateralized Debt Position) model in its lending mechanism. Protocol users pledge NFTs into the protocol, borrow stablecoins PUSd generated by NFTs collateral, and can borrow up to 32% of the floor price of PUSd. The first NFT allowed to be collateralized by JPEG’d is CryptoPunks, with an initial borrowing interest rate of 2% and a one-time borrowing fee of 0.5%. JPEG’d sets the LTV (Loan-to-Value) to 32%, and liquidation will be triggered when LTV reaches 33%.

Source: JPEG’d
Due to the large fluctuations in NFT floor prices, JPEG’d uses Chainlink as its data source, with the core being the time-weighted average price. It is worth mentioning that JPEG’d has designed a novel insurance mechanism. Users can choose to pay a 5% loan fee for insurance. Once liquidated, they can buy back the NFT after repaying the debt, accrued interest, and a 25% liquidation penalty. However, they must repay the debt within 72 hours, otherwise the NFT will belong to JPEG’d DAO.
JPEG’d also innovatively provides a platform-defined weighted valuation for designated blue-chip NFTs (CryptoPunks, BAYC, Azuki) rarity. For each specific attribute, after different weighting, the valuation will receive corresponding weight increase rewards. Currently, there are relatively few platforms in the market that provide valuations for rarity attributes.
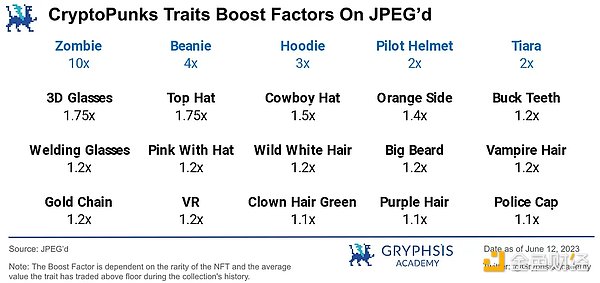
In addition, pETH generated from JPEG’d has a relatively good yield rate when pledged on Convex with ETH-pETH assets, with a peak of around 30~45% in early 2023.
Currently, the project has accumulated borrowing funds of more than 36 million US dollars (data as of June 12, 2023). In January and February of this year, it reached a peak weekly borrowing of around 770,000 US dollars. The share of CDP-type NFT lending protocols in the entire market is relatively small.
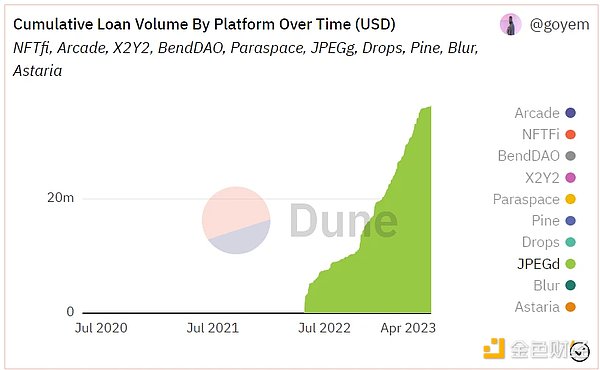
Source: Dune Analytics@goyem (June 12, 2023)
9. Risks and Prospects
Although the NFT lending track is developing rapidly, some major risks cannot be ignored:
1) NFT collateral valuation fluctuation risk (bad debt risk)
For lending projects, the worst-case scenario is that the liquidity of the capital pool will dry up, and borrowers who borrow against collateral assets will be unable to repay the debt.
For NFT lending protocols, it is particularly important to define high-quality NFT collateral targets. When the floor prices of the collateralized NFT series drop sharply, many borrowers may voluntarily abandon the NFT assets and choose to default on the loan. Under such circumstances, the NFT with collapsed prices may have no bidders.
(Review of historical events – BendDAO liquidity crisis: From August to September 2022, the floor price of blue-chip NFTs fell as a whole, and multiple collateral assets triggered liquidation without any bids, causing panic in the market and a large amount of ETH withdrawals from the liquidity pool, resulting in the depletion of liquidity in the pool. Loan and deposit interest rates skyrocketed, and the BendDAO protocol faced a potential collapse crisis. Later, the team initiated a proposal to modify some parameters to respond to the crisis. Over the next few days, funds in the protocol pool gradually recovered, the market sentiment eased, and the utilization rate of funds and loan interest rates returned to normal levels.)
2) High concentration of target users in business objectives
The target audience of NFT lending itself is not very broad. Although the industry is developing rapidly as a whole, data from some projects’ operations show that the head users account for a large proportion of the business, and the project has a certain dependence on the business volume of the target key customer group.
For example:
BendDAO protocol: As of June 12, 2023, the total loan amount was 178820 ETH, and the user Franklinisbored.eth, who ranked first in the total loan amount, borrowed a total of 45447 ETH, accounting for more than 25% of the total business volume.
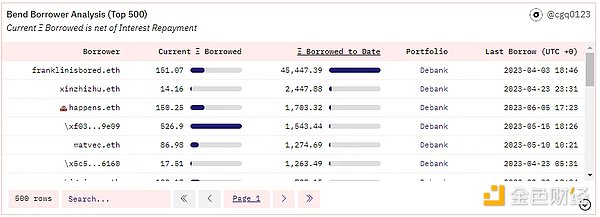
Source: Dune Analytics@cgq 0123 (June 12, 2023)
3) The growth space of the business volume in the track may be limited
In order to ensure the healthy development of the business of NFT lending projects, they often focus on selecting high-quality blue-chip NFT targets as collateral assets, which have strong price consensus and risk resistance. However, the types of blue-chip NFTs that meet these conditions are limited, and the NFT issuance of each project is fixed. In the current market environment, qualified NFT collateral assets require a long time of market testing and are difficult to predict and judge in advance. This may limit the overall market size and business growth space of the NFT lending market and may be a potential risk point.
As for the overall development of the NFT market, at present, subcategories including blue-chip PFP (Profile Picture), high-quality GameFi assets, and NFT assets with unique project empowerment will be an important part of the future industry development. As the industry matures, more and more users will accept and invest in the NFT field, and the connection between NFT and real life will become more diversified. The influence of NFT will continue to spread with various derivatives. As the overall market size of NFT grows, the opportunities for various sub-sectors of NFT will also increase. For NFT lending, the diversity of protocols can meet the needs of different users. When the overall lending protocol can achieve high activity and high popularity, it will be able to provide better bidirectional liquidity solutions for NFT and Defi users.
10. Conclusion
Currently, most users in the NFT market still focus on the markets and aggregators with the lowest barriers to entry, but these two areas have not fully demonstrated the greatest capital efficiency. As more and more users join the NFT field, how to use NFT financing to effectively improve the capital efficiency of the market and attract users’ attention may be a continuous breakthrough in the growth of Web 3 businesses.
NFT lending, as an important component of NFT financing, the improvement of oracle and liquidation mechanisms has gradually demonstrated the efficiency advantage of P2Pool in the competition with P2P. The update iteration between different products also makes the product form of this market increasingly mature. How to independently rate different NFTs, accurately price them, and establish liquidity are key issues in improving customer experience.
We believe that NFT liquidity solutions with reasonable and accurate pricing mechanisms, smooth user experience, sustainable transaction models and profit models, and complete risk control mechanisms will become an important cornerstone for the progress of the NFT-Fi industry.
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!