On June 13th, Uniswap released the Uniswap V4 version code draft, which caused strong shock in the industry and also became a hot topic in the news in recent weeks. As the largest decentralized trading platform, Uniswap has long held over 50% of the on-chain trading share, and its trading volume is more than three times that of its second largest competitor. The launch of Uniswap V4 will further consolidate its position as the largest DeFi DEX.In Uniswap’s “Our Vision for Uniswap v4” and “Uniswap v4 Core WhiteBlockingper” (white paper), Uniswap Labs introduced Hooks that can customize AMMs, Singletons that change account frameworks and order logic, and Flash accounting and Native ETH that can greatly reduce gas fees. These innovative features will bring greater freedom, better liquidity, lower fees, and more choices to DEXs. At the same time, it injects a catalyst into DEXs, which have long been in a weak position in the competition with CEXs, and accelerates the pace of DEXs catching up with CEXs, which will have a profound impact on the future development of DeFi.Uniswap leads the development of the entire DeFi industry with innovation. One of the reasons why the upgrade of Uniswap V4 has attracted the attention of many institutions is that the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission’s (SEC) lawsuit against the world’s largest CEX, Binance, has made industry institutions begin to worry about the future development of CEXs, and DEXs with decentralization and anti-auditability undoubtedly receive more favor. In addition, the most important point is that as the industry leader, each version of Uniswap’s release has led the development direction of DEXs, and has been imitated by successors, which has also driven the prosperity and development of the entire DeFi. Let’s review each historical version of Uniswap.Uniswap V1 is the first official version, launched in November 2018. It provides trading between ERC-20 tokens and ETH, and introduces the automatic market maker model for the first time, automatically adjusting token prices and liquidity, making token transactions faster, simpler, and lower cost. This approach has also inspired many later decentralized exchanges and laid the foundation for the development of the entire DeFi ecosystem. During the same period, SushiSwap, Curve Finance, and Bancor all borrowed from Uniswap V1’s approach.Uniswap V2 was launched in May 2020, further providing support for trading between ERC-20 tokens and introducing liquidity mining mechanisms, increasing the liquidity of trading pairs by rewarding liquidity providers. With the liquidity empowerment of V2, projects that emerged during the same period include Yearn.finance, AAVE, Compound, and Chainlink, among others.
Uniswap V3 was launched in May 2021 and introduced centralized liquidity and price limit order (PLC) functionality. Centralized liquidity allows market makers to more efficiently manage funds, increasing their profits and efficiency. PLC allows users to set upper and lower bounds on trade prices according to their needs, allowing for finer control over trades. During the same period, Concentrated Liquidity and BarnBridge also achieved higher efficiency and returns by using Uniswap V3’s centralized liquidity and PLC functionality.
Uniswap V4 is the upcoming new version, and although the specific launch time has not been announced, according to information released by the project party, this UniswapV4 version will be different from V1-V3 in the past, and will not be a technical innovation from 0 to 1, but a comprehensive subversion of DeFi’s infrastructure. For example, V4 will provide token pools that can be created and managed independently, AMMs that can add new functions through “hooks,” and a large contract framework to replace the previous Factory/Pool model, among other innovations. These innovations will further strengthen Uniswap’s characteristics as a decentralized trading platform and bring new changes and opportunities to the entire DeFi ecosystem.
Uniswap V4: Four Innovative Mechanisms to Build True DeFi Infrastructure
- Inventory of the top 10 potential projects recently invested by venture capital firms.
- Understanding the current development of MakerDAO: Expected profit increase, repurchase rules may be adjusted to capture the value of the protocol
- Adventure Gold DAO launches new L2 network Loot Chain: Can it bring development advantages for the Loot community and AGLD?
Uniswap, as an important participant and leader in the DeFi industry, has played a crucial role in promoting industry progress and improvement. This Uniswap V4 will create an efficient, flexible, and low-cost infrastructure truly suitable for DeFi by introducing innovative mechanisms such as Hooks, Singleton, and Flash accounting, providing users with a better trading experience and more opportunities. Let’s take a closer look at these new features of Uniswap V4.
Hooks
One of the key innovations of Uniswap v4 is the introduction of “hooks,” an external contract created and defined by developers to create and define transaction logic. Through Hooks, developers can call external contracts to execute specified operations at specific points in the lifecycle of the liquidity pool, such as creating limit orders before trading, adjusting transaction fee levels after changes in liquidity pool positions, and so on.
With the ability to add plugins through Hooks, Uniswap V4 becomes a customizable liquidity pool platform. This customizable feature is not possible for centralized exchanges. Developers can freely develop new features on top of this, thus meeting various trading scenarios and making liquidity more deeply bound to the project’s own development. In addition, this customizable feature can also stimulate the imagination and creativity of developers and communities, further increasing the network effect of Uniswap V4, making it the underlying infrastructure of the entire DeFi ecosystem.
-
Internalization of MEV profit distribution to LPs
In traditional AMM exchanges, MEV profits are usually captured by miners or other participants, while liquidity providers can only earn revenue from trading fees and mining rewards. By internalizing MEV profit distribution back to LPs, liquidity providers can directly benefit from MEV profits, thereby increasing their revenue sources and levels.
Singleton
Singleton is a new contract architecture of Uniswap V4. In previous versions, each liquidity pool corresponds to a contract. When adding a new liquidity pool, a new contract needs to be deployed, which not only increases the deployment cost for developers, but also causes transactions to cross multiple contracts, leading to increased gas fees and longer transaction times. In the Singleton architecture, all liquidity pools are stored in one contract, which greatly reduces the cost of creating liquidity pools and gas fees, and improves transaction efficiency.
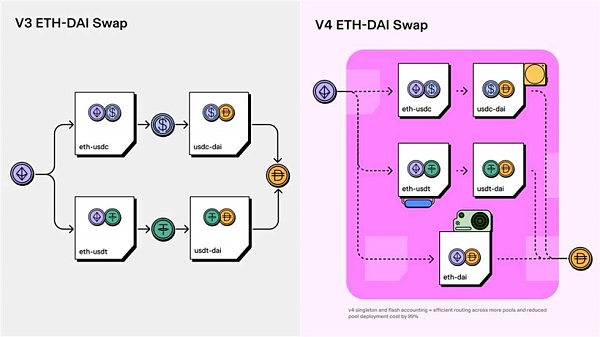
The advantages of Singleton architecture are mainly as follows:
-
Reduce costs: Since all liquidity pools are stored in the same contract, developers do not need to deploy separate contracts for each liquidity pool, thereby reducing development and maintenance costs.
-
Improve efficiency: The Singleton architecture implements multi-hop transactions, and users only need to call the contract once to complete all exchanges, which greatly improves transaction efficiency and reduces gas fees.
-
Scalability: Singleton architecture can easily add new features and capabilities, leaving more possibilities for future innovations, making Uniswap V4 more scalable and flexible.
-
Simplify liquidity position management: In the Singleton architecture, liquidity positions are no longer encapsulated using tokenization, but are managed using addresses, which can more simply and efficiently manage liquidity position data.
Flash Accounting
Flash Accounting is a new accounting method introduced on top of the Singleton contract architecture. In previous versions, all relevant position balances need to be calculated for each transaction, which consumes a lot of gas and leads to high transaction costs. The Flash Accounting system can calculate transaction fees based solely on net balances (i.e. changes in balances), thereby reducing gas consumption.
Specifically, the FlashAccounting system takes advantage of the fact that all liquidity pools in Uniswap V4 are managed by a single contract. When a user makes a transaction, the Flash Accounting system queries the net balance of the current pool (i.e., the difference between the buy and sell volumes) and calculates the transaction fee based on the user’s net balance in the transaction. Because only the net balance is calculated, the Flash Accounting system can avoid calculating the balance of all related positions, reducing the amount of gas required for computation.
In addition to reducing gas consumption, the FlashAccounting system can improve cross-pool routing efficiency and further reduce the cost of transacting across multiple pools. This feature, combined with hook contracts, becomes very useful and supports more complex integrations and innovations, which can greatly increase the number of pools.
Native ETH
In Uniswap V4, Native ETH refers to the direct trading between Ethereum’s native token (ETH) and other tokens during a transaction. In previous versions, if someone wanted to trade between ETH and other tokens, they had to convert ETH to the WETH token first, which required multiple transactions and gas fees, resulting in high transaction costs and low efficiency.
In Uniswap V4, the concept of Native ETH is introduced, making it possible to trade directly between ETH and other tokens without first converting to WETH. This can greatly reduce transaction costs and time. At the same time, Native ETH can also improve liquidity, attracting more liquidity providers to enter the Uniswap V4 ecosystem and provide better liquidity and prices for traders.
Specifically, Uniswap V4 adds an ETH pool to the core contract that is only used for direct trading between ETH and other tokens. When a user makes a transaction between ETH and other tokens, the system automatically compares the transaction volume with the amount of ETH in the pool and calculates the corresponding amount of other tokens based on the ratio. This way, users can trade directly between ETH and other tokens in Uniswap V4 without the hassle of the conversion process. Therefore, the introduction of Native ETH makes Uniswap V4 more convenient and efficient, providing users with a better trading experience and further strengthening Uniswap’s liquidity and competitiveness.
Uniswap V4 may become an opportunity to solve the DEX dilemma
In the digital asset trading market, CEX and DEX are the two main exchange models. Due to long-term problems such as insufficient liquidity, poor user experience, high trading fees and costs, DEX has been unable to compete with CEX and has long occupied only a small part of the digital asset trading market. With the rapid development of DeFi, the development dilemma of DEX has also attracted more and more attention. In this context, the release of Uniswap V4 may become an opportunity to solve the DEX dilemma. With innovative solutions, Uniswap V4 plans to improve the situation of DEX from four aspects. If successful, it will lead more institutions to join in and work together to solve the dilemma of DEX.
Although there is still a large gap between DEX and CEX in terms of user experience, cost and security, this gap is gradually narrowing with the continuous updates and improvements of the Uniswap version. It is believed that in the near future, Uniswap V4 will occupy a more important position in the competition between DEX and CEX, become the liquidity growth flywheel of the DeFi industry, and lead the development direction of the entire industry.
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!