Definition of Vampire Attack
The concept of “vampire attack” in the cryptocurrency market is very simple. It refers to an attack where the attacker creates a protocol that is similar or identical to the target protocol, but with more profitable and attractive incentive mechanisms. The attacker aims to attract the target’s market share or users to their side, thus “sucking blood” from the target.
Let’s further understand this concept through two examples.
SushiSwap 🆚 Uniswap
SushiSwap can be considered the first and most famous “vampire” in the cryptocurrency market, with Uniswap as its target.
Weakness of Uniswap
Uniswap is an open-source decentralized exchange using the AMM (Automated Market Maker) model. During the DeFi Summer in 2020, Uniswap enjoyed the market’s momentum and with the launch of its V2 version, its Total Value Locked (TVL) grew from $70 million in June to $300 million by the end of August, becoming a leading player in the DEX (Decentralized Exchange) sector.
- Liquid Restaked Token (LRT) The Script of the New Ponzi Token Economy Era
- Singapore Token2049 leader’s view Payments and RWA become key tracks, ETFs and regulations spark heated discussions
- USDT pledge lock-up, accelerating the release by recruiting people, exposing the latest 3M derivative scam
However, Uniswap had a vulnerability on its development path. At that time, it did not have a governance token and did not change its incentive mechanism as the platform evolved (the reward for liquidity providers was only transaction fees). This was undoubtedly a weakness for the platform because liquidity providers supported the platform’s operation and bore impermanent loss but couldn’t benefit more from the platform’s rapid growth. At this time, a developer named “Chef Nomi” seized this weakness.
Innovation of SushiSwap
Nomi created SushiSwap, which was essentially a simple fork of Uniswap. Notably, SushiSwap introduced a crucial new feature: the combination of a governance token (SUSHI) and liquidity staking rewards.
As a governance token, SUSHI also functions as a platform token. In SushiSwap, 0.25% of the transaction fees in the pool are directly allocated to active liquidity providers, and 0.05% is converted into SUSHI and distributed to SUSHI holders (essentially a buyback). This means that liquidity providers not only receive a share of the platform’s transaction fees but also receive token rewards.
Here comes the key part: SushiSwap stipulated that SUSHI would only be rewarded to users who provide liquidity in the form of Uniswap LP tokens. In other words, it was an attempt to attract Uniswap users to participate in SUSHI mining together.
“Bloodsucking” Process
The staking contract and SUSHI distribution of SushiSwap started on August 28, 2020, with the initial rewards being very aggressive, with an annual interest rate of up to 1000%. With such incentives, users rushed to deposit assets into eligible pools on Uniswap (including pools such as USDC/ETH and SUSHI/ETH), in exchange for Uniswap V2 LP tokens, which were then quickly deposited into the SushiSwap contract.
After 100,000 blocks (approximately two weeks), SushiSwap launched liquidity migration, which involved transferring all Uniswap LP tokens to SushiSwap and exchanging the corresponding token pairs on Uniswap. The tokens were then used to initialize new SushiSwap liquidity pools. By the end of the migration, SushiSwap had accumulated approximately $800 million in tokens, accounting for about 55% of Uniswap’s liquidity at the time. Meanwhile, Uniswap’s TVL (Total Value Locked) plummeted by approximately $400 million.
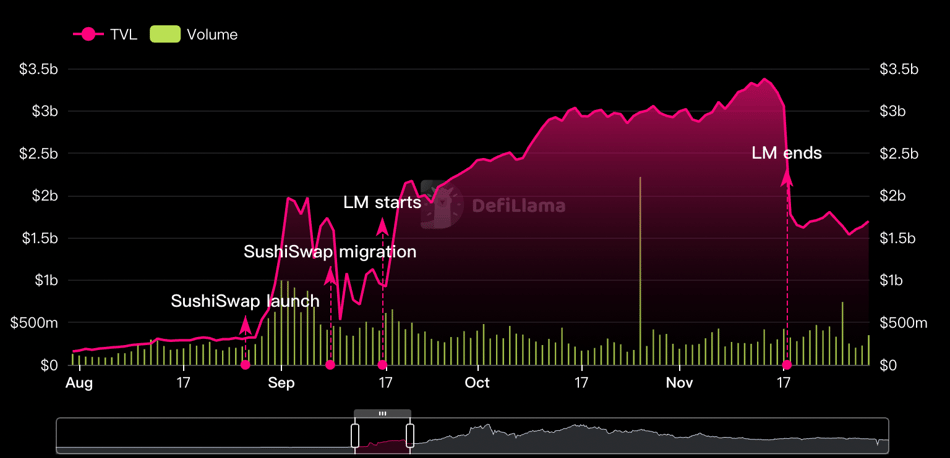
In retrospect, SushiSwap forked Uniswap’s architecture and introduced new incentive mechanisms to create an image that was “based on Uniswap but better than Uniswap.” Incentivized users flocked to SushiSwap and transferred their funds. Although Uniswap managed to withstand the competition and even launched its own token, UNI, SushiSwap was still successful. It quickly accumulated a large amount of liquidity through its vampire attack strategy and became one of the top DEXs (Decentralized Exchanges) in a short period of time.
LooksRare 🆚 OpenSea
Last year, a vampire attack occurred in the NFT market, initiated by LooksRare against OpenSea.
OpenSea’s Weaknesses
OpenSea is a comprehensive NFT trading platform where users can buy and sell various forms of NFTs, including crypto artworks, game items, virtual real estate, domains, financial products, and more. The platform supports ERC-721 and ERC-1155 formats of NFTs. The secondary transaction fee on the platform is 2.5%, while the maximum fee for primary minting can reach 10%.
As a dominant player in the NFT trading platform space, OpenSea has garnered the majority of the market share but has also received negative feedback from many users. The criticisms include inconsistent payment methods (users often need to convert between ETH and WETH to complete different types of purchases), high transaction fees, and most importantly, the high centralization and reliance on traditional capital in OpenSea’s organizational structure. It lacks sufficient decentralization and Web 3.0 features.
LooksRare’s Innovations
LooksRare was launched in January 2022 as another NFT trading platform. It learned from OpenSea’s experience and implemented several innovations, including:
- Allowing mixed payments in ETH and WETH. On the LooksRare platform, both can be used for bidding and payment;
- Supporting series offers. This design optimizes the buyer experience for those who focus more on the NFT series theme rather than the specific details of each individual piece, as they don’t have to list each item separately;
- Most importantly, upgrading the fee and incentive mechanism. LooksRare charges a 2% transaction fee for all trades and distributes this fee income to the stakers of LooksRare’s native token. The platform aims to challenge OpenSea’s dominance in the NFT space by allocating transaction fees to the community.
Does this operation look familiar? This is the core idea of the vampire strategy: target the weaknesses of a top project, then provide the right solutions to attract and retain users.
“Vampire” Process
The specific vampire process of LooksRare is even more straightforward.
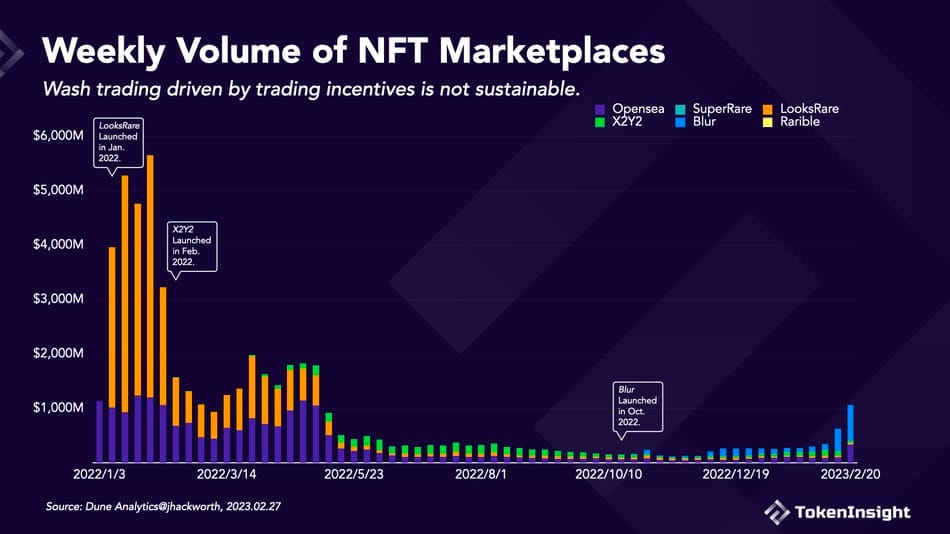
By using a filtering system, it identifies the major NFT traders on OpenSea (those with a cumulative trading volume of more than 3 ETH in the past six months) and directly includes these traders in its native token LOOKS airdrop whitelist. However, if these traders want to claim LOOKS, they must first conduct a transaction of 1 NFT on LooksRare.

This vampire approach directly converts many OpenSea users into LooksRare traders, causing LooksRare’s market value to soar to $1 billion and LOOKS price to rise to around $7, with a peak of $7.1.
Summary
For project teams, vampire attacks can be a devastating blow, bringing volatility risks to the market. However, from the perspective of the entire crypto market, this intense competition between projects may also be a good thing – it stirs up the market. In this regard, vampire attacks not only offer possibilities for improving user experience, but also help alleviate the centralized risks of monopolistic projects dominating users and market share.
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!