Author: Bessie Liu Source: blockworks Compilation: Shanooba, LianGuai
Blockchain infrastructure company Espresso Systems has released a testnet version of Espresso Sequencer, which is based on a forked version of Polygon zkEVM. The testnet, named “Doppio,” is already running internally within the company and will be opened to external nodes in the coming months. The Sequencer is responsible for sorting transactions from the mempool and then sending the information back to the virtual machine. Similar to validators on Layer-1 networks, they play a crucial role in running Layer-2 blockchain networks.
Currently, the Sequencer is still relatively centralized. Rollups run their own independent Sequencers and have their own execution environments – in the case of zero-knowledge (ZK) Rollups, they also have their own proof systems.
Jill Gunter, co-founder and head of strategy at Espresso, explained in an interview with Blockworks that existing Sequencers are relatively monolithic in operation. Gunter said, “In existing Rollup solutions, the Sequencer is just a component bundled with the rest of the Rollup software. There is no programmable, upgradable, or replaceable way.” Therefore, many Rollups today have experienced some degree of downtime, which Gunter believes has been downplayed in today’s Rollup environment. She said, “It’s not catastrophic because you can always force transactions back to [Layer-1]. But it can be costly and it creates what I call a soft censorship problem, where transactions are not prioritized.”
- Summer of Time Travel Protocol: Cryptography Technology Imagination from a Humanistic Perspective
- Technical interpretation of the Starknet upgrade: A user-friendly update that kills Pending
- Buidler DAO: “Plain” ZK Series (Part 1): Construction and Case Studies of zk-SNARK
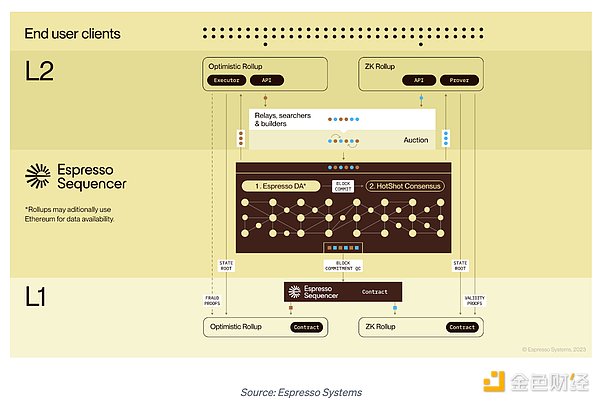
How does Espresso’s decentralized Sequencer work?
Espresso has designed its own proprietary proof-of-stake system called HotShot, which will be used to optimize performance while maintaining decentralization and robustness, Gunter explained.
She said, “It’s a distributed consensus system that can be shared across different Rollups, so Rollups no longer need to bundle the Sequencer in their own software stack. They will use the Espresso [application programming interface] to invoke and submit transactions to the Espresso Sequencer.”
Espresso Sequencer has two main functions: first, it acts as an optional execution data availability, which means if a Rollup wants to have data availability as an additional feature, they can choose to use it. Second, it provides consensus on the order of transactions.
Gunter said, “The Espresso Sequencer can perform these two functions across multiple Rollups, and there are interesting situations that arise when you start cross-Rollup sorting.” She continued, “This could potentially lead to cross-Rollup MEV (maximizing transaction value) – which we think could be a source of income for participants in the Espresso network and [Layer-2].”
The team also plans to use ETH staking to ensure economic consistency with Ethereum Layer-1 and has already partnered with Eigenlayer. After launching the testnet on Polygon zkVM, Gunter noted that Espresso is also working with Caldera to establish integration between Espresso Sequencer and the OP stack. At the same time, agreements have been reached with teams such as Spire, Injective, and Catalyst AMM to support their priority integration with Espresso Sequencer.
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!