Background
Blockchain technology is an innovative distributed ledger technology that enables decentralized, transparent, and tamper-proof data storage and exchange. The potential applications of blockchain technology are wide-ranging, from finance, social media, the Internet of Things, to identity authentication, digital rights, and more. These fields can all benefit from the advantages of blockchain technology.
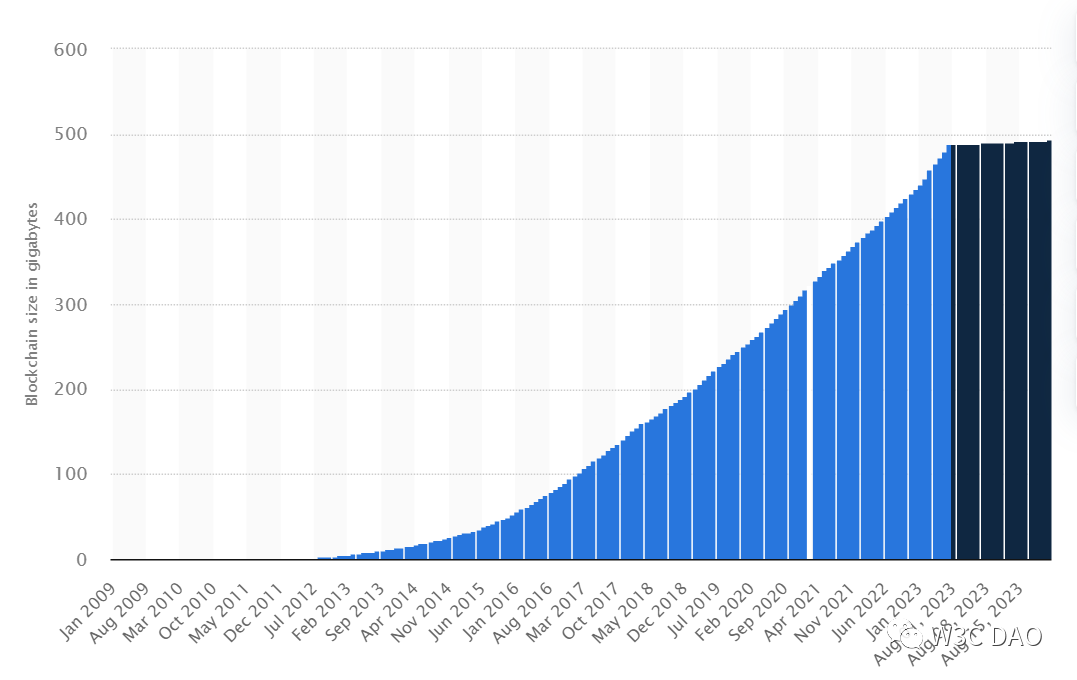
However, blockchain technology also faces challenges and limitations, one of which is scalability. Since blockchain needs to store all transaction data on each node to ensure data consistency and security, the size of the blockchain expands with usage, increasing the computational resources and storage space required for node operation.
As a simple example, the Bitcoin blockchain currently exceeds 400 GB, and the Ethereum blockchain exceeds 600 GB. This means that ordinary users find it difficult to participate in the blockchain network and can only rely on centralized service providers to access blockchain data and services. This not only undermines the decentralized spirit of blockchain but also reduces the security and reliability of the blockchain.
- Selected Weekly | Mixin Hacked for 200 Million USD; Crypto Practitioners Donate 50 Million RMB to Shenzhen University, Attracting Attention; Celestia Launches Airdrop Plan and Economic Model.
- An In-depth Explanation of Celestia Airdrop and Economic Model How Will the Future Project Airdrop Evolve?
- TON Rebirth A Brief History of Creation, Technological Advancement, and Future Outlook
To address scalability issues, some blockchain projects have adopted a layered architecture, transferring some computational and storage tasks from the main chain (Layer 1) to side chains (Layer 2) or other networks. However, this approach also has drawbacks, such as increased system complexity, reduced data integrity and interoperability, and more.

Therefore, it is necessary to find a blockchain solution that can achieve efficiency, lightweight, and scalability without sacrificing security and decentralization. Mina Protocol is born out of this vision.
Project Overview
Mina Protocol is a “succinct” blockchain based on zero-knowledge proof technology, aiming to provide efficient, secure, and privacy-preserving decentralized applications (DApps).

The biggest feature of Mina Protocol is that the blockchain size remains around 22 KB through recursive zero-knowledge proofs, regardless of the number of transactions or users in the network. This is because Mina Protocol does not need to store all transaction history data but only needs to store a zero-knowledge proof representing the current state.
As a result, even devices with relatively weak computational capabilities, such as smartphones, can synchronize and verify the Mina network. In contrast, Bitcoin and Ethereum require high-performance GPUs and terabyte-level storage disks to support node construction and mining. Mina has moved node mining to the more widely used mobile end, significantly improving node deployment simplicity and network decentralization compared to Bitcoin and Ethereum.

Zero-knowledge proof is a cryptographic technology that allows one person to prove to another person that a statement is true without revealing any other information. For example, a person can prove to another person that they have the private key to a certain account without revealing the private key itself. Mina Protocol utilizes the properties of zero-knowledge proof to transform the blockchain validation process from validating all data to validating a proof. This allows anyone to easily download and verify the entire blockchain without relying on third-party service providers. This makes Mina Protocol the lightest blockchain in the world and the only blockchain that can run as a full node on any device.
Consensus Mechanism
Mina uses the Ouroboros Samasika proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus algorithm, based on the improvement of PoS consensus. The network consensus is still achieved through proof-of-stake PoS, allowing anyone to participate proportionally according to the protocol. Block producers are selected for each round using a verifiable random function (VRF). Each block producer independently runs the VRF for each time slot, and if the output value they obtain is greater than a threshold proportional to their stake size, they have the opportunity to produce a block within the specified time slot.

Block producers can increase their chances of being selected to produce blocks by delegating tokens to another account’s block producer. When the delegated account stakes, the combined funds are used to evaluate the VRF threshold, thereby increasing the likelihood of being selected to produce blocks for the slot. The delegated funds are not usable, but can be canceled by re-delegating the stake back to the original account at any time.
The characteristic of Ouroboros Samasika is that there is no upper limit on the number of consensus validators. In general PoS algorithms, most of them are based on committee elections and can only accommodate a few hundred validators, as the complexity of network communication increases sharply with the number of validators, and nodes cannot bear the communication overhead. Ouroboros Samasika, on the other hand, is based on traditional PoS and has scalability on nodes.
Secondly, nodes can enter and exit dynamically. Most PoS consensus protocols have requirements for the online time of nodes and impose penalties on those who go offline, which greatly increases the threshold for running nodes and exposes the network to the risk of attacks. Ouroboros Samasika allows nodes to enter and exit freely.
At the same time, Mina’s nodes only need to rely on simple rules to determine which chain is valid, without relying on external information for guidance. Most PoS algorithms have problems with long-range attacks and nothing-at-stake, and require the introduction of “weak subjectivity” to determine the validity of the chain. Ouroboros Samasika mainly uses the “longest chain rule” to deal with short forks. In the face of historical attacks, when nodes are faced with long forks, special rules can be adopted, namely concise state digests. Since attackers find it difficult to compute enough zero-knowledge proofs in a short period of time, this ensures that the blockchain is difficult to fork.
zkApps
In addition to achieving the simplicity of blockchain, the Mina Protocol also provides an innovative decentralized application development platform called zkApps (Zero-Knowledge Applications).
zkApps is a type of smart contract based on zero-knowledge proofs that can achieve the following three functions:
Data privacy protection: zkApps allows users to prove their data to others or applications without revealing their actual data. For example, a user can prove their identity and credit score to a loan application without disclosing specific information. This way, users can protect their privacy while enjoying the convenience of decentralized services.

Cross-chain interoperability: zkApps allows users to access data and services on other blockchains without leaving the Mina Protocol. For example, a user can use tokens or contracts on Ethereum through a zkApp on the Mina Protocol. This way, users can leverage the efficiency and security of the Mina Protocol while having access to the rich functionalities of other blockchains.
Real-time network connection: zkApps allows users to access any website and data on the internet without sacrificing security and decentralization. For example, a user can use a zkApp to retrieve real-time information such as weather forecasts or stock quotes on the Mina Protocol. This way, users can connect the blockchain with the real world and realize more application scenarios.
Highlights
As an innovative blockchain project, the Mina Protocol has the following highlights:
- Efficiency: The Mina Protocol achieves a constant blockchain size and improves verification speed through zero-knowledge proofs. This allows the Mina Protocol to run on any device and support more transactions and users.
- Security: The Mina Protocol ensures the security and stability of the blockchain network through a decentralized consensus mechanism (Ouroboros Samasika5). This allows the Mina Protocol to resist 51% attacks and guarantee data consistency and integrity.
- Privacy: The Mina Protocol achieves privacy protection and secure sharing of user data through zkApps technology. This allows users to control their own data and enjoy more decentralized services.
- Interoperability: The Mina Protocol achieves cross-chain and cross-network interoperability through zkApps technology. This allows users to access data and services on other blockchains and the internet, expanding more application scenarios.
Data
The on-chain data of the Mina Protocol is as follows:
- Block height: 294908
- Super nodes: 178
- Circulating token supply: 981,582,723
- Total transactions: 221,479
- Average transaction fee per transaction: $0.014
Team
The development team of the Mina Protocol is O(1) Labs, founded by Evan Shapiro and Izaak Meckler in 2017.
The O(1) Labs team currently consists of world-class cryptographers, engineers, doctors, and entrepreneurs who are dedicated to bringing the Mina Protocol to market. Here are introductions to some core members:
Evan Shapiro: CEO and Co-founder, formerly a software engineer at Jane Street Capital, responsible for developing high-performance trading systems.

Izaak Meckler: CTO and Co-founder, formerly a software engineer at Google Brain, responsible for developing machine learning systems. He holds a Ph.D. in Mathematics from the University of California, Berkeley.
Emre Tekisalp: COO, formerly the Director of Business Development at Coinbase, responsible for projects such as Coinbase Ventures and Coinbase Earn. He holds a Master’s degree in Management Science and Engineering from Stanford University.
Brad Cohn: CFO, formerly a Vice President of Investment Banking at Goldman Sachs, responsible for mergers and acquisitions and financing in the technology, media, and telecommunications sectors. He holds dual Bachelor’s degrees in Finance and Accounting from the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania.
Claire Kart: Chief Marketing Officer, formerly the Director of Product Marketing at Coinbase, responsible for market strategy and execution of products such as Coinbase Pro, Coinbase Prime, and Coinbase Custody. She holds a Master’s degree in English Literature from Columbia University.

In addition to the O(1) Labs team, Mina Protocol also has contributors from San Francisco and around the world participating in the project’s development, including cryptography experts, protocol designers, community managers, etc. They provide technical, community, and ecological support for Mina Protocol.
Funding History
Since its establishment in 2017, Mina Protocol has completed four rounds of funding, raising a total of approximately $48.15 million. Here is a summary of Mina Protocol’s funding history:
November 2017: Seed round raised $3.5 million, invested by DFG, Polychain Capital, Metastable Capital, Electric Capital, CoinFund, etc.
April 2018: Series A round raised $15 million, invested by Coinbase Ventures, Accomplice, LianGuaradigm, General Catalyst, etc.
October 2020: Strategic round raised $10.9 million, invested by Three Arrows Capital, Bixin Ventures, Collaborative Fund, Fenbushi Capital, HashKey Capital, etc.
March 2021: Community Token Sale (CTS) raised $18.75 million, hosted by the CoinList platform with over 40,000 participants.
These investors not only provide financial support to Mina Protocol but also assist in market promotion, ecological construction, and strategic cooperation. Mina Protocol’s funding history demonstrates its project’s advantages and potential, as well as its influence and recognition in the blockchain industry.

Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!