Rollup is currently the mainstream Layer2 scaling solution and has contributed to Ethereum’s pursuit of scalability. OptimisticRollup and ZKRollup, two Rollup solutions, have also been gradually validated by the market. After that, Layer2 scaling began to welcome multiple Rollup directions, and anyone can quickly start their Rollup by using an SDK and run applications on it with high performance and low cost. In the future of Layer2 scaling, Rollup will gradually occupy a dominant position, and the most important thing in this process is to simplify the way developers deploy various types of Rollups.
On June 26th, zkSync launched the modular open-source framework ZK Stack for building zk-powered applications. ZK Stack is a free, modular open-source framework designed to build custom ZK-supporting L2 and L3 (known as superchains) code-based on the zkSync Era. Before this, the Optimism team had already launched the scalability solution OP Stack, creating a shared, high-quality, fully open-source system for creating new Layer2 blockchains.
In this article, we will compare the differences between these two solutions, their respective advantages and disadvantages, and usage scenarios. In the increasingly competitive Layer2 market, who will break through and build a larger ecosystem interoperability?
OP Stack
- Status of encrypted VC financing in the first half of 2023 and projects with the highest fundraising in June.
- Framework Ventures Co-founder: The position of cryptocurrencies is much better than anyone thinks
- Godfish: Review and Outlook of Major Events in the Cryptocurrency Market in 2023
OP Stack is a standardized, shared, and open-source development stack that supports Optimism and is maintained by Optimism Collective. It has three design principles: practicality, simplicity, and scalability. As a public product of the Ethereum and Optimism ecosystems, OP Stack consists of many different software components that together make up the pillars of Optimism.
Features of OP Stack
OP Stack focuses primarily on creating a shared, high-quality, fully open-source system for creating new Layer2 blockchains. By coordinating shared standards, Optimism Collective can avoid rebuilding the same software in isolation. OP Stack can be seen as a software component that can help define specific layers of the Optimism ecosystem and can also serve as a role of modules in existing layers. Although the core of OP Stack is currently the infrastructure for running Layer2 blockchains, it theoretically can be extended to layers above the underlying blockchain, including tools such as block explorers, messaging mechanisms, and governance systems.
OP divides the blockchain into three layers: consensus layer, execution layer, and settlement layer. Then, it standardizes the three layers. In terms of specific architecture, OP Stack can be divided into six layers:
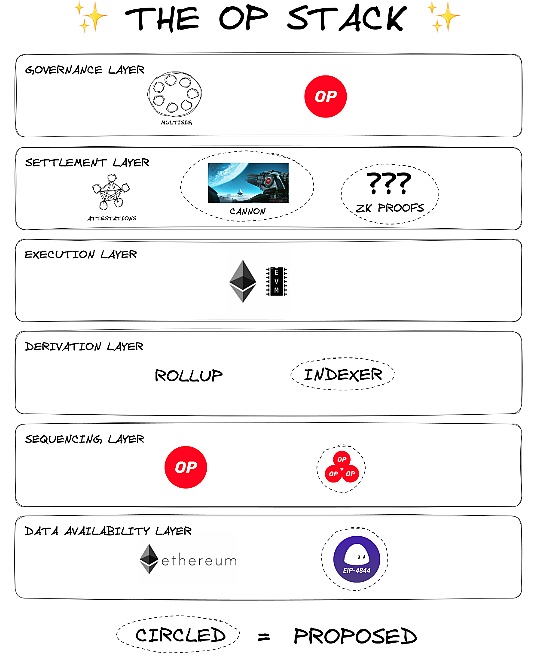
DA (Data Availability Layer): The Data Availability Layer defines the source of Layer 2 raw data based on the OP Stack. The OP Stack can use one or more data availability modules to obtain its input data. Ethereum DA is currently the most widely used data availability module in the OP stack, but more and more other chains can also be connected in the future.
Sequencing Layer: The sequencing layer determines how user transactions on the OP Stack chain are collected and published to the data availability layer module in use. In the default Rollup configuration of the OP Stack, sequencing is typically handled by a single dedicated sequencer. The rules defined in the derived layer often limit the ability of the sequencer to retain transactions beyond a specific time period. In the proposed future, sequencing will be modular so that chains can easily choose and change the mechanism that controls their current sequencer.
Derivation Layer: The Derivation Layer defines how to process raw data in the Data Availability Layer to form processed input, which is sent to the Execution Layer via the standard Ethereum engine API.
Execution Layer: The Execution Layer defines the state structure within the OP Stack system, abstracting EVM modification or providing an entry point to a completely different underlying VM.
Settlement Layer: Used to verify the current transaction result. After being confirmed by Layer2, the confirmation information will be sent to the target blockchain for final settlement to obtain data validity.
Governance Layer: The Governance Layer refers to the common set of tools and processes used to manage system configuration, upgrades, and design decisions.
The goal of OP is to upgrade to a super chain through this architecture. OP Stack deconstructs the various components needed to build a Layer2 chain and packages them as separate modules. Developers can combine the most suitable modules to create their own Layer2, making it easier and more efficient for developers to implement proprietary chains.
Bedrock Upgrade
The completion of the Bedrock upgrade represents the complete modular rewriting of the core components of the OP mainnet Rollup architecture, the launch of the first formal version of OP Stack, and the next major version of the Optimism network, further narrowing the gap between Optimism and Layer1 Ethereum. The Bedrock version will support the use of multiple proof schemes and multiple clients to attract different developers and projects. In addition, it will also follow different routes to keep up with the technical decentralization while maintaining the decentralization of the governance structure. This provides a key advantage for future OP to achieve a super chain:
-
Reduce network fees: optimized data compression strategies can eliminate Gas Fees related to EVM execution when submitting data to L1, reducing about 10% of additional fees;
-
Reduce deposit waiting time: support for Layer1 restructuring is introduced in the node software, and deposits are expected to be confirmed within 3 minutes;
-
Improve proof modularity: the proof system is separately abstracted from the OP Stack, and can choose fault-tolerant proofs or Zk-Snark and other validity proof mechanisms;
-
Improve node performance: by executing multiple transactions at once in a single Rollup block, 15G of data can be reduced annually.
-
Improve Ethereum equivalence: multiple deviations from Ethereum in previous versions have been removed, and support for EIP-1559, chain restructuring, and other Ethereum functions on Layer1 has been added.
After completing the upgrade of Bedrock, Optimism’s Layer2 Rollup was not only improved but also upgraded to a superchain, taking the next big scalability improvement of OP Stack to introduce the concept of superchains: a chain network of shared bridging, decentralized governance, upgrades, communication layers, and more, all built on top of OP Stack. The launch of the superchain will merge the Optimism mainnet with other chains into a unified OP chain network, marking an important step towards bringing scalable and decentralized computing to the world.
OP Stack simplifies the process of creating Layer2 blockchains and supports all of Optimism’s software. As Optimism develops, OP Stack will also develop. Coinbase is preparing to launch Base Layer2 later this year, which will be developed based on OP Stack, and BNB Chain has announced that its opBNB testnet is built on OP Stack. OP Stack currently appears in the form of software behind the Optimism mainnet and will eventually appear in the form of the Optimism superchain and its governance.
ZK Stack
ZK Stack is a free modular open-source framework designed to build custom ZK-supporting L2 and L3 chains (called superchains) based on the zkSync Era code. The core of ZK Stack provides two key functions: sovereignty and seamless connectivity. Developers have full rights to the code and unrestricted autonomy to customize and shape every aspect of the chain. Superchains operate independently, relying only on the Ethereum Layer1 to ensure their activity and security, while the superbridge network facilitates interconnection of each superchain, achieving trustless, fast, and cheap interoperability. Overall, ZK Stack has three characteristics: open source, composability, and modularity.

Features of ZK Stack
-
Free: ZK Stack is developed under the fully-permissive MIT/ABlockingche open-source license to ensure its availability for free.
-
Composable: Superchains built using ZK Stack can be seamlessly connected in trustless networks, with low latency and shared liquidity.
-
Modular: Customize and shape every aspect of the superchain, from the choice of sorter and data availability mode to defining unique token economies.
-
Ultra-low cost: Due to the simplicity of ZK proofs, certain transaction types (such as oracle updates) are 1,000 times cheaper on ZK Stack than on other aggregation platforms. In addition to ZK rollup mode, ZK Stack can also use the extremely affordable zkPorter account for optional expansion for appropriate use cases.
-
Proven: zkSync Era is the most widely used ZK rollup on Ethereum, and the considerable TVL and transaction volume of transactions prove it. With this record, ZK Stack is a safe choice in terms of security and reliability.
-
Future-oriented: ZK rollups are the future of Ethereum scalability. To fully unleash the potential of ZK superpowers, build the right architecture from the start.
Upgrade of ZK Stack
The upgrade of ZK Stack is also a major upgrade for the zkSync core team. From zkSync Era to zkstack, the team’s perspective has gradually expanded from building ZK technology to helping many teams understand ZK Stack and contribute to it. With the launch of more sidechains, the number of core contributors will increase, and the community will become the true owner of the zkSync network, especially when building custom sidechains. If you are building a general DeFi dapp or NFT project, deploying it on existing sidechains such as zkSync Era will be a simpler process, allowing it to sync and combine with other protocols in the ecosystem.
In addition, ZK Stack allows you to build your own sovereign sidechains without sacrificing interoperability and composability. This will greatly improve the scalability of ZK Stack. Each sidechain seamlessly integrates into its infinitely scalable ecosystem, supported by shared provers and fractal scaling, nurturing a complete liquidity network. In this ecosystem, users can quickly transfer assets in a trustless manner without incurring additional costs. Smart contracts will make cross-chain asynchronous calls, and the sidechains themselves will have sovereignty, enabling them to join alternative ecosystems and take their on-chain assets with them when they choose to leave.
Next, the ZK Stack team will modify the codebase to make it easier to check out, configure, and deploy ZK Stack instances, with the ultimate goal of one-click deployment.
OP Stack VS ZK Stack
The launch of ZK Stack is more about opening up a new situation of multi-chain interaction than competing with OP Stack.
From a technical perspective, ZK Stack’s sidechain maximizes the reuse of Ethereum’s security and consensus methods and can directly rely on Ethereum’s security. Compared with OP’s interactive fraud proof, ZK proof directly verifies state changes without waiting for underlying state changes in Ethereum, simplifying design and avoiding duplicate investment, and improving inter-chain interaction efficiency. In comparison, OP Stack still has significant limitations in asynchronous cross-chain calls: its state changes require waiting for underlying verification in Ethereum, and fraud proofs also require confirmation.
In addition, unlike OP stack, which focuses on the transformation of the Layer2 market, ZK stack wants to include both Layer2 and Layer3 markets. Although both want to achieve a multi-chain empire through inter-chain interoperability, the Layer3 and multi-chain networks built by ZK Stack attempt to develop highly customized expansion.
From an ecological perspective, OP Stack has a first-mover advantage. Shortly after its launch, OP Stack gained support from many projects. In February of this year, Coinbase announced the launch of the multi-chain Layer2 platform Base, built on OP Stack, and will build a super chain with Optimism Collective. In addition, OP Stack also received support from BNB Chain. On the evening of June 19th, BSC announced the launch of a new expansion solution: opBNB, which is based on the Bedrock version of OP Stack and is compatible with EVM. In addition, many application development teams, such as NFT trading market Zora and the client Magi launched by a16z Crypto, have also started to choose OP Stack to develop application chains.
In contrast, zkSync’s own Layer2 has not been fully established, and there have been compatibility and downtime issues with ZkRoullup, and most of the ecology is dominated by domestic projects, with less support from well-known companies and projects. In this regard, the urgency of building Layer3 by zkSync cannot convince the market’s recognition.
Summary
In terms of blockchain scalability, super chains and super scalability are worth paying attention to, but from the current development perspective, the projects are still in the early stage. It is unknown whether OP Stack with ecological advantages or ZK Stack with technical advantages can occupy the market, but despite the differences in technology, details, and perspectives, they all have the goal of infinite scalability. A new round of multi-chain and scalability narrative of Ethereum is gradually unfolding.
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!