Author:
Will Awang, Master of International Business Law in the United States, with ten years of legal practice experience, TMT industry serial entrepreneur, and investment and financing lawyer.
Diane Cheung, Master of Accounting from the University of Sydney and MEM from Peking University, with ten years of experience as a FinTech product manager and a practitioner of Web3.
The emergence of blockchain and cryptocurrency technology not only allows people to purchase NFT digital artworks, interact with players in the Metaverse, and make money in GameFi gameplay, but also provides the most essential decentralized peer-to-peer payment solutions. These fast and convenient Web3 payment solutions are changing our current payment methods and even the entire financial market.
Since LianGuaiyLianGuail launched the stablecoin LianGuaiyLianGuail USD in August, we have seen many industry giants announcing one after another to expand their business scope to Web3 payments or integrate Web3 payment channels. It feels like a full-scale attack on Web3 payment business. We can see MetaMask’s deposit and withdrawal aggregation solution, X’s (formerly Twitter) payment license application, VISA’s USDC settlement blockchain payment network, and a series of actions by industry giants in the blockchain industry.
As Web3 payments cover almost all infrastructure in the industry, including payment, stablecoins, wallets, custody, and transactions, understanding the wide range of use cases and potential advantages of Web3 payments is crucial for all participants in the Web3 ecosystem.
This article will briefly describe the concept and path of Web3 payments, and then from a business perspective and a legal compliance and regulatory perspective, explain why Web3 payments are expected to reshape the cryptocurrency market. I hope this article can be helpful in this regard and welcome discussions and exchanges. The full article is about 16,000 words long, and the expected reading time is 30 minutes.
TL; DR
- Traditional payments and Web3 payments are not separate but are moving in both directions. Fiat currency and cryptocurrencies interact continuously and gradually merge into stablecoins, central bank digital currencies, and other real-world use cases;
- Bitcoin was designed to achieve a decentralized peer-to-peer electronic cash payment system, and Web3 payments evolved from this. Currently, Web3 payments can be roughly divided into two categories: deposit and withdrawal payments, and cryptocurrency payments (on-chain and off-chain);
- LianGuaiyLianGuail, Coinbase, MetaMask, and other industry giants are gradually opening up/accessing Web3 payment businesses and scenarios, including wallets, custody, payments, transactions, and stablecoins, ultimately covering their entire ecosystem and forming their own closed-loop ecosystems;
- The Web3 payment infrastructure is gradually taking shape, connecting wallets, custody, and stablecoins. What is more important than this is how to build payment scenarios. Imagine how X (Twitter), Telegram, MetaMask, and LianGuaiyLianGuail will form their own large-scale crypto ecosystems. In this context, the existing structure of the cryptocurrency market will inevitably change;
- Compliance is the foundation of payment business. The complex cross-border and cross-scenario characteristics of Web3 payment business pose significant challenges to regulatory compliance. However, with the further clarification of crypto regulations, the adoption of cryptocurrencies is expected to increase, promoting the rapid development of the Web3 payment industry;
- From the perspective of the monetary system, the BIS believes that the key to the development of currencies after digitization is tokenization, which can significantly enhance the capabilities of currencies and financial systems. The future monetary system is expected to unleash new economic growth dynamics through tokenization;
- The biggest opportunity for cryptocurrencies may not be seen as cryptocurrencies themselves, but as a new set of payment methods. Some people believe that the killer application of Web3 has not yet arrived, but it may have quietly arrived: it is payments!
1. Overview of Web3 Payments
In simple terms, Web3 Payments refer to a payment method based on blockchain and cryptocurrency technology. However, due to the characteristics of blockchain and cryptocurrency, Web3 Payments encompass more than just payment.
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have multidimensional attributes. They are not only a form of payment, but also an innovative technology, a store of value, and a financial infrastructure. In transactions, they can also serve as a unit of account to represent value.
Traditional payments and Web3 payments are not mutually exclusive, but rather evolving in both directions. Fiat currencies and cryptocurrencies interact continuously and are gradually integrated into stablecoins, central bank digital currencies, and other real-world use cases. Web3 Payments are redefining our payment methods and financial systems.
1.1 Traditional Payments
Let’s first look at traditional payments. Payment is the act of transferring currency (or equivalents) or claims from a payer to a payee, completing the matching of information flow and fund flow. The essence of payment is the transfer of funds.
In a broad sense, payment includes both cash in paper form and electronic forms of currency. There are roughly four ways to transfer funds: cash payment, bank account transfer, debit card transfer, and credit card payment. For the latter three forms of electronic payment, fund transfers need to be facilitated by centralized financial systems such as banks. If banks cannot directly process the payment, the involvement of third-party payment institutions is required.
Depending on the currency used for payment, there are domestic payments and cross-border payments. As Web3 Payments are conducted on the blockchain, they can achieve dual functionality in terms of cross-currency (fiat currency vs cryptocurrency) and cross-border transactions, making them a type of cross-border payment.
There are many participants in the cross-border payment industry chain, including customers, commercial banks, third-party account/acquiring payment institutions, clearing institutions, and merchants. The entire industry chain can be roughly divided into three levels: the first level consists of users and merchants, who are the origins and endpoints of the payment; the second level consists of payment service providers such as banks and third-party payments; the third level consists of cross-border payment networks, which are the underlying support for cross-border payments, such as SWIFT and SEPA.
The following diagram illustrates the architecture of cross-border payments:
(Source: How new entrants are redefining cross-border payments)
Based on the type of cross-border payment service provider, it can be divided into interbank telegraphic transfer, specialized remittance companies, bank card clearing institutions, and third-party payment institutions. The following examples compare Web3 Payments based on blockchain settlement.
1.1.1 Interbank Cross-Border Payments
(Source: SWIFT gpi- Future of Cross-Border Payments)
Early cross-border payments were mainly conducted through banks, such as the earliest appearance of bank telegraphic transfers, which were mainly used for cross-border payments between banks, import and export trades, and other cross-border payments. This payment method requires a complex banking network and may take several days or even weeks to complete. This process may involve the exchange of multiple currencies and the fees are relatively high.
Traditional bank cross-border payments mainly rely on the SWIFT network. SWIFT does not hold funds or manage accounts for users, but provides communication information networks and exchanges standardized financial messages. SWIFT can be understood as a network that connects almost all major banks worldwide, and banks use the same language to complete foreign exchange transactions. However, the disadvantage of SWIFT is that if a payment goes through multiple intermediary banks or encounters anti-money laundering checks, it is easy to experience delays or even payment failures, and there are also issues such as exchange rate losses.
As shown in the above figure, when a commercial account relationship is established between the receiving bank and the remitting bank, the funds paid by the user will be transferred directly through the bank’s commercial account to complete the payment, and the bank will charge the corresponding fees; When there is no commercial account relationship between the receiving bank and the remitting bank, it needs to be completed through an intermediary bank. The intermediary bank will charge additional fees, and the time for the payment to arrive will also be extended as the number of transaction parties increases.
Bank cross-border payments belong to heavily regulated businesses, and the regulatory policies in different countries and regions are not the same, which also imposes certain limitations on cross-border payments. In addition, most bank cross-border payments have strict KYC/AML requirements, which need to be completed after the user opens an account, so the cost is relatively high.
1.1.2 International card organizations
Similar to SWIFT, international card organizations are also the main networks for traditional cross-border payments, but they focus more on the acquiring scenarios of merchant collections (debiting the buyer’s account). The acquiring methods are diverse, and the exchange process is completed directly during the payment process, settling the local currency for merchants.
Card organizations are international regional payment information processing networks. There are currently six major card organization networks worldwide: VISA, Mastercard, China UnionPay, American Express, JCB, and Discover. Cross-border payments processed through international card organizations usually take T+1 day or longer to complete, which means it takes at least T+1 day to reach the merchant’s account. International card organization payments also require licenses to operate and are subject to different regulatory policies in various countries.
1.1.3 Third-party cross-border payments
With the development of e-commerce and network technology, electronic transfers have become a popular cross-border payment method. This cross-border payment method is generally provided by non-bank institutions (such as Alipay, LianGuaiyLianGuail, etc.) as third-party payment institutions that provide all or part of the fund transfer services. These third-party payment institutions play an important role in cross-border e-commerce retail, remittances, import and export business, and overseas mobile payments.
Third-party cross-border payments require access to international card organizations or banks for clearing and settlement to complete the payment. The currency exchange process in cross-border payments is also mainly completed through banks. Third-party payments usually have custodial functions, which means that the funds of the payment can be deposited in the third-party payment account and transferred to the seller’s account after the transaction is confirmed.
(Source: Acquiring Banks vs Issuing Banks in Credit Card Processing)
In the above image, in a cross-border e-commerce scenario, the user side is the starting point for fund transfer. The third-party payment institution connects the user’s bank account with the issuing bank’s credit card/debit card. After the user makes a purchase, the user’s funds are transferred to the payment channel and settled with the card organization. After the settlement, the third-party payment institution transfers the funds to the merchant. In offline shopping scenarios, an acquiring agent is needed to connect the merchant with the third-party payment institution.
Traditional payment methods have been developed for a long time and currently cover most application scenarios with a wide range of functions. However, cross-border payments face practical problems such as high costs, slow speed, limited access, and lack of transparency. According to a survey by the Federal Reserve, users’ pain points mainly focus on two aspects: firstly, the payment speed needs to be improved, and the current payment deadlines do not meet user needs. Users expect to have 24/7/365 payment services. Secondly, there is a strong demand for periodic real-time payment scenarios.
1.2 Web3 Payments
Although current payment methods are rapidly digitizing, the fund transfer process is cumbersome and involves many participants, resulting in high friction costs. The improvement of payment experience has been constrained by intermediaries, banks, technology companies, and other parties.
Bitcoin was designed to achieve a decentralized peer-to-peer electronic cash payment system from the very beginning. In 2008, Satoshi Nakamoto released the Bitcoin whitepaper against the backdrop of the global financial crisis, hoping to change the traditional bank-centric financial system and achieve decentralization of the entire financial system. Since the birth of Bitcoin on January 9, 2009, it has ushered in the large-scale application of cryptocurrencies.
Bitcoin payments allow direct transfer between users without the need for banks, clearinghouses, and third-party institutions such as electronic payment platforms. This avoids high fees and cumbersome transmission processes, and any user with a device connected to the Internet can use it without permission.
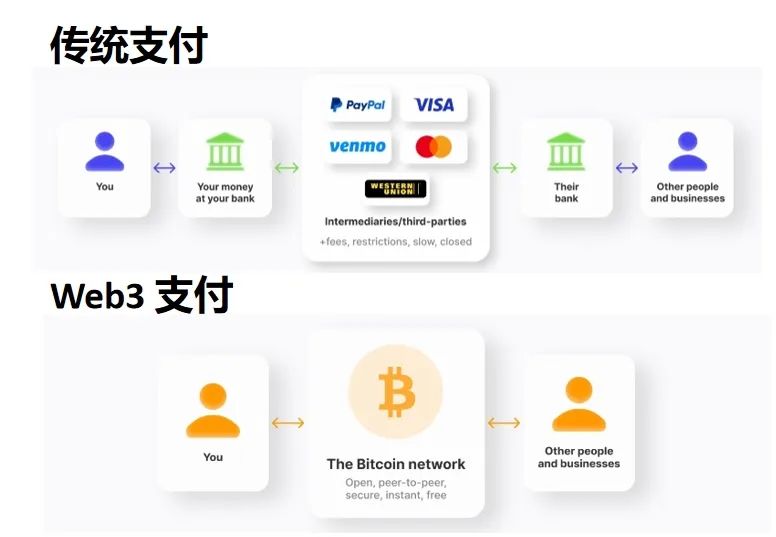
(Source: How Crypto Payment Solutions Have Changed the Market)
Similar to the Bitcoin payment network, cryptocurrency payments rely on the blockchain network as the backbone infrastructure, allowing cryptocurrencies to be transferred directly between the sender and receiver without any third party, with speed, convenience, and extremely low costs.
As the acceptance of cryptocurrencies continues to increase, it is inevitable for cryptocurrencies to interact with fiat currencies in the real world. In this case, institutions that provide deposit and withdrawal services play the role of banks that provide foreign exchange services in cross-border payments, facilitating the exchange between cryptocurrencies and fiat currencies.
Currently, there are two main payment methods in Web3: (1) On Ramp & Off Ramp payment, which refers to the exchange between cryptocurrency and fiat currency; (2) Cryptocurrency payment, which includes (2.1) payment with native assets on the cryptocurrency chain, such as the interaction between two addresses on the blockchain or between cryptocurrency and on-chain assets (e.g., purchasing NFT with cryptocurrency, swapping between different cryptocurrencies); and (2.2) traditional entity payment with cryptocurrency off the blockchain, which refers to the payment when using cryptocurrency as an equivalent to purchase other goods/services;
Web3 payment connects fiat currency and cryptocurrency through On Ramp & Off Ramp payment, and enables the circulation of cryptocurrency assets through cryptocurrency payment, forming a complete payment loop.
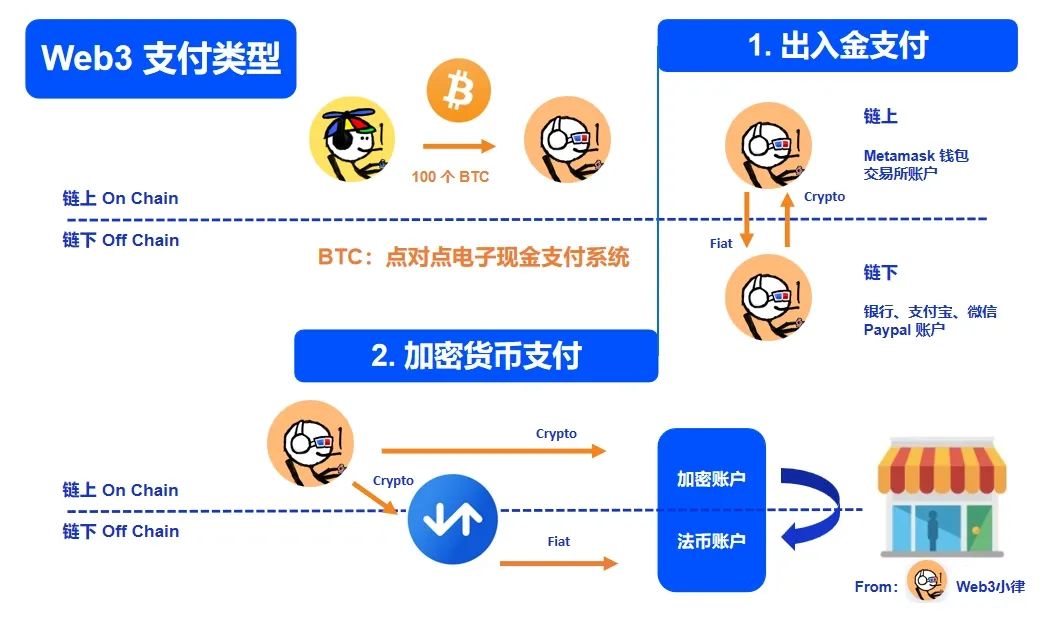
Since cryptocurrency payment is conducted on the blockchain, it is not subject to geographical restrictions. The regulation of cryptocurrency payment by various jurisdictions is also gradually improving. However, On Ramp & Off Ramp payment itself involves fiat currency payment and will therefore be subject to existing financial regulations.
1.3 Advantages of Web3 Payment Compared to Traditional Payment
(Source: Can Web3 Wallets Become the Lever for Industry Transformation?)
Traditional payment is a payment method based on an account system, and the transfer of value is recorded in the accounts of intermediaries (such as banks and third-party payment companies). Due to the large number of participants, the process of fund transfer is very cumbersome and the friction cost is significant, resulting in higher costs.
In contrast, Web3 payment is a payment system based on a value-based or token-based system, where the transfer of value is stored by users themselves in the distributed ledger on the blockchain. Web3 payment is based on the blockchain network as the backbone infrastructure, allowing for the transfer of cryptocurrency between senders and receivers, and can address the issues of high costs, low efficiency in cross-border transfers, and high costs in traditional payment.
(Source: Blockchain & Crypto in LianGuaiyments: Transforming the Way Money Moves)
What are the advantages of Web3 payment compared to traditional payment?
Firstly, relying on blockchain technology can effectively reduce the trust costs between transaction parties, making payments more direct, fast, and secure. The functionality of smart contracts enables programmable payments and automated execution, improving the efficiency and trustworthiness of payments.
Secondly, cryptocurrency payment currently has a significant advantage over traditional payment in terms of timeliness, especially in cross-border payments. This feature will be an important driving force for the development of cryptocurrency payment and also a major force in upgrading traditional cross-border payment technologies.
In addition, based on the decentralized nature, Web3 payments simplify the process that relies on centralized clearing institutions, reduce friction costs, especially greatly improve cross-border payment efficiency, and accelerate clearing and settlement speed.
Various signs indicate that traditional cross-border payments and Web3 payments are not completely separated, and they are forming a two-way situation in various aspects. This is reflected in the application of blockchain technology in the traditional payment industry, in addition to the CBDC being practiced by many countries, major participants in traditional payments such as SWIFT, VISA, and LianGuaiyLianGuail are also exploring Web3 payment solutions. On the other hand, Web3 payment projects are actively cooperating with traditional financial institutions and third-party payment institutions, as well as exploring the accelerated application of compliant stablecoins.
Although Web3 payments still face challenges in technology, user acceptance, security compliance, etc., Web3 payments still have significant implications for the encryption industry and even the entire traditional finance.
2. Main Paths of Web3 Payments
Currently, Web3 payments can mainly be divided into two payment methods: (1) On Ramp & Off Ramp payments; (2) Cryptocurrency payments (including on-chain native scene payments and payments between off-chain traditional entities).
Web3 payments connect fiat currency and cryptocurrency through On Ramp & Off Ramp payments, and enable the circulation of cryptocurrency assets through cryptocurrency payments, thereby forming a complete payment loop.
Due to the small volume of native assets in the current encryption market and the limited payment scenarios, most of the payments discussed in the Web3 industry are related to the exchange between fiat currency and cryptocurrency.
2.1 On Ramp & Off Ramp Payments
On Ramp & Off Ramp is an important bridge that connects fiat currency and cryptocurrency, and can form a complete payment loop. In addition to OTC/P2P On Ramp & Off Ramp methods, other On Ramp & Off Ramp processes require the participation of third-party payment institutions.
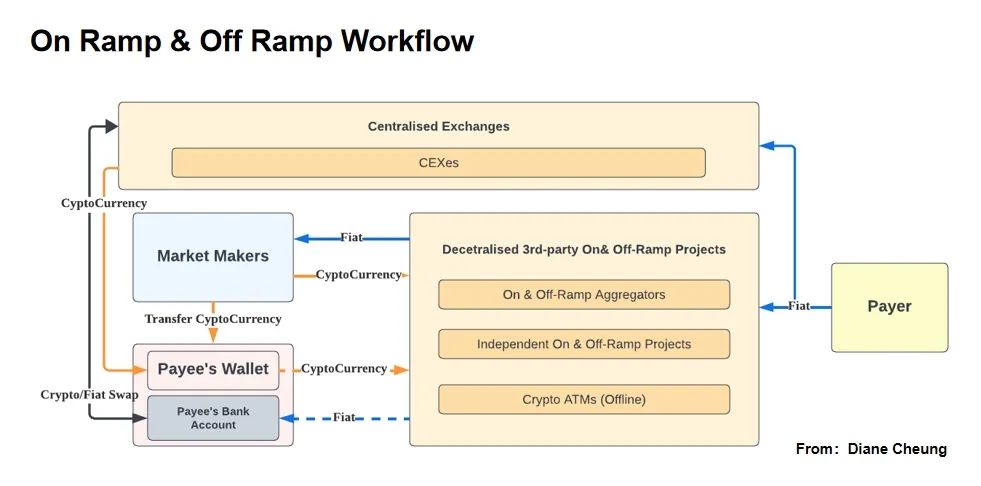
2.1.1 On Ramp & Off Ramp Payment Process
The fund flow behind On Ramp & Off Ramp payments: Users transfer fiat currency through payment channels to liquidity providers behind third-party payment institutions (Crypto Liquidity Providers), and liquidity providers are more like merchants in traditional third-party payment scenarios, transferring cryptocurrencies as “goods” to users’ addresses through the chain, while providing cryptocurrency liquidity to third-party payment institutions. The same applies to Off Ramp payments.
These liquidity providers are usually centralized exchanges (such as Coinbase Prime, Binance, Kraken) or stablecoin issuers (such as Tether and Circle), or crypto-friendly banks (such as the collapsed Silvergate bank and Signature bank). Liquidity providers are crucial in the On Ramp & Off Ramp process and play a role in bridging fiat currency and cryptocurrency.
2.1.2 Main On Ramp & Off Ramp Payment Methods
A. Centralized Exchange
Since centralized exchanges also have the nature of currency transfer, their functions are consistent with payment institutions. The application for related encrypted asset/payment licenses is the same as the license for payment institutions. Therefore, most centralized exchanges also have functions related to deposit and withdrawal payments.
In addition, centralized exchanges can also act as liquidity providers. Therefore, we see that most centralized exchanges have their own deposit and withdrawal payment sections. Users can directly purchase cryptocurrencies through debit cards/credit cards or bank transfers, such as Binance, Coinbase, XXX, etc.
Centralized exchanges provide a payment interface for the trading parties’ custodial wallets. The trading parties can choose to use different accounts in the same custodial wallet or non-custodial wallets as needed, with lower fees for the former as it does not involve gas fees.
In addition, in jurisdictions with stricter regulations, centralized exchanges need to connect to independent deposit and withdrawal payment institutions as underlying payment channels to facilitate user deposits and withdrawals. This operation also applies to decentralized exchanges. For example, Uniswap has connected independent deposit and withdrawal payment institutions such as MoonPay, LianPay, etc., to support user deposits and withdrawals.
B. Independent Deposit and Withdrawal Payment Institutions
Independent deposit and withdrawal payment institutions are payment institutions that have the function of cryptocurrency transfers (including cryptocurrency-friendly banks). They need to obtain relevant licenses for cryptocurrency/payment operations in their business operating locations.
Among them, MoonPay is the leading project for cryptocurrency deposits and withdrawals and is positioned as Web3’s LianPay. It has registered users of over 5 million. In terms of coverage, MoonPay supports cryptocurrency payments in over 160+ countries and regions, supports the exchange of over 80 cryptocurrencies and 30+ fiat currencies, and holds payment business licenses in most jurisdictions.
In terms of payment methods, MoonPay currently supports payment channels such as credit cards, debit cards, mobile payments, and account-to-account payments. Users can enter the on-chain address and the amount of the cryptocurrency and complete the payment. Coinbase provides liquidity supply for MoonPay, and with its comprehensive deposit and withdrawal functions and first-mover advantage, it quickly occupies the majority of the European and American markets where credit card usage is predominant, with a valuation of 3.5 billion USD.
In addition, we have seen that recently, the traditional payment giant LianPay, based on its powerful payment channels, has joined forces with stablecoin issuer LianGuaixos to launch PYUSD stablecoin, aiming to enter the Web3 payment market. Previously, Slivergate Bank, which had a fraudulent incident, and Signature Bank, which was forcibly closed, these cryptocurrency-friendly banks are actually important deposit and withdrawal payment channels.
C. Other Deposit and Withdrawal Payment Methods
Other deposit and withdrawal payment methods are basically payment products that integrate the above two payment methods as the foundation.
Aggregated payment products integrate multiple independent deposit and withdrawal payment methods, allowing users to obtain different rates and quotes for different independent deposit and withdrawal payments for payment. MetaMask is the most typical aggregated payment product, and other well-known leading projects include TransitSwap and KyberSwap.
Cryptocurrency retail terminals ATM and POS. With the development of the cryptocurrency industry, in addition to online payments, cryptocurrency physical retail terminals have also emerged. Cryptocurrency ATMs are used to purchase cryptocurrencies directly with cash offline. ATM providers purchase liquidity from third-party suppliers and pay it to users. The characteristic of this type of payment is its anonymity. Users do not need to provide identity verification or only need very little personal information to purchase cryptocurrencies. However, the disadvantage is that the transaction fees are extremely high (5% to 20%). Bitcoin Depot is a leading project in this field.
Cryptocurrency payment POS is another channel for offline cryptocurrency payments. Users can pay with cryptocurrencies through POS machines, and merchants receive fiat currencies directly. This type of payment also requires a license application, but the withdrawal fee rate is lower compared to ATMs. LianGuaiy is one of the projects that provide such solutions.
(Source: Crypto | Money is evolving)
Overall, there are many ways for users to choose from in Web3 payments. However, when it comes to deposits and withdrawals involving the conversion between fiat currencies and cryptocurrencies, the operators generally need to apply for operating licenses according to the regions. The fees generated by payments vary slightly due to different payment method business models.
In addition to deposit and withdrawal payments, some centralized exchanges and payment institutions have collaborated with card organizations such as Visa and Mastercard to issue debit cards and credit cards, which have both deposit and withdrawal payments and cryptocurrency payment attributes.
2.2 Cryptocurrency Payments
With the increasing acceptance of cryptocurrencies, Web3 payments are also entering traditional markets such as e-commerce (for online shopping), gig economy (for contracts and freelancers), cross-border remittances, travel bookings, and online games (for in-game item exchanges), etc. It uses cryptocurrencies for online consumption and remittances, instead of relying on outdated infrastructure of traditional banks or third-party payment institutions.
Currently, cryptocurrency payments can be mainly divided into two categories: payments between offline traditional entities and payments in native on-chain scenarios.
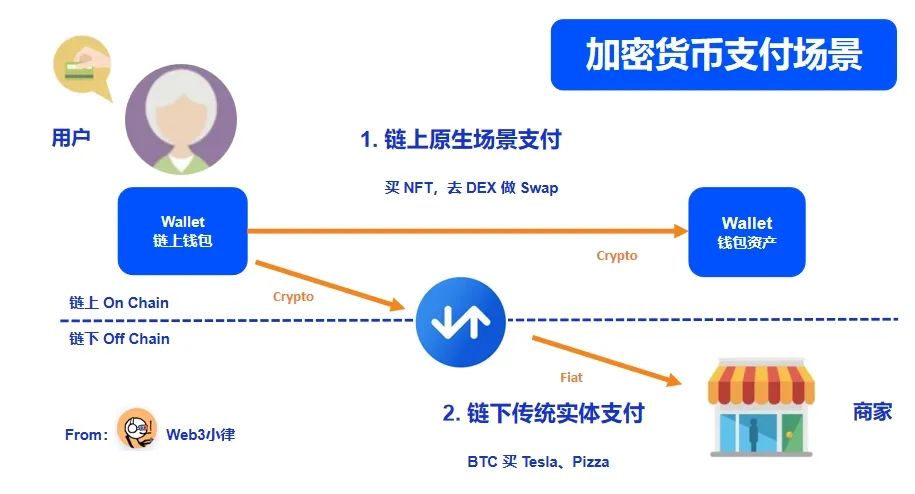
2.2.1 Cryptocurrency Payments – Payments to Offline Traditional Entities
According to a report by PYNMTS and BitLianGuaiy in 2022, the report surveyed more than 2,330 online merchants with annual sales exceeding $250 million. Approximately 85% of large retailers (with annual revenue exceeding $1 billion) currently offer cryptocurrency as a payment method. Among all surveyed merchants, half of them accept cryptocurrency payments, and among the merchants that have not yet accepted cryptocurrency payments, 42% are planning to do so. The report also found that most merchants use non-native cryptocurrency wallets to support cryptocurrency payments, such as LianGuaiyLianGuail and Venmo.
In order to meet the growing Web3 payment needs of customers, leading payment giants such as Mastercard, Visa, LianGuaiyLianGuail, Stripe, and Venmo have partnered with cryptocurrency companies to provide millions of users with cryptocurrencies as a means of payment. Most major retailers, such as Overstock, Microsoft, Expedia, and Starbucks, have also integrated cryptocurrency payments, allowing their customers to directly purchase digital and physical goods using cryptocurrencies. Other major companies include popular streaming company Twitch, Norwegian Air, Etsy, and Burger King.
(Source: How Crypto Payment Solutions Have Changed the Market)
As for traditional payments between off-chain physical entities, we simulate a scenario where a user consumes cryptocurrency and the merchant receives fiat currency. In terms of fund flow, the cryptocurrency is first converted into fiat currency through deposit and withdrawal methods by a third-party payment institution, and then used to make fiat currency payments to the merchant.
The most common solution currently is the issuance of cryptocurrency bank cards. Centralized exchanges or wallet companies often cooperate with card organizations such as Visa and Mastercard to issue cryptocurrency debit/credit cards. Users can use these cards for online or offline transactions as long as they hold cryptocurrencies in their platform accounts. However, during actual payments, the issuing company will convert the cryptocurrency into the local fiat currency through the withdrawal payment channel before paying the merchant. We can see that the centralized exchange Crypto.com has issued the Crypto.com Visa Card debit card in partnership with Visa. In addition to the functionality of fiat currency payments, it also provides users with the functionality of on-chain cryptocurrency payments.
2.2.2 Cryptocurrency Payments – On-chain Native Payment Scenarios
As for on-chain native payment scenarios, users pay with cryptocurrencies and merchants also accept cryptocurrencies. This method cannot simply be understood as a point-to-point payment transfer based on blockchain technology, but also needs to take into account the trust issues encountered in real-world payment scenarios, which requires the use of third-party payments.
Take an online shopping case as an example. In the case of solving the trust issue (trust chain between friends), transactions can be realized through blockchain point-to-point transfers, with user payment, merchant shipment, and user receipt. However, in an online platform without a trust basis, who can guarantee that the merchant will ship the goods after the transfer, and that the received goods match the actual ones?
Similarly, we can achieve point-to-point transfers with relatives and friends through the blockchain network, but what should we do if the counterparty is a stranger? Therefore, an account system needs to be linked to the settlement system on the blockchain to realize offline goods circulation and on-chain payment settlement.
Therefore, third-party payment institutions that provide cryptocurrency payment products are needed to solve the above problems. This includes the encrypted payment protocol, payment core system, front-end product interaction, and corresponding support modules shown in the above diagram. We can see the exploration of Ripple and Stellar in this regard.
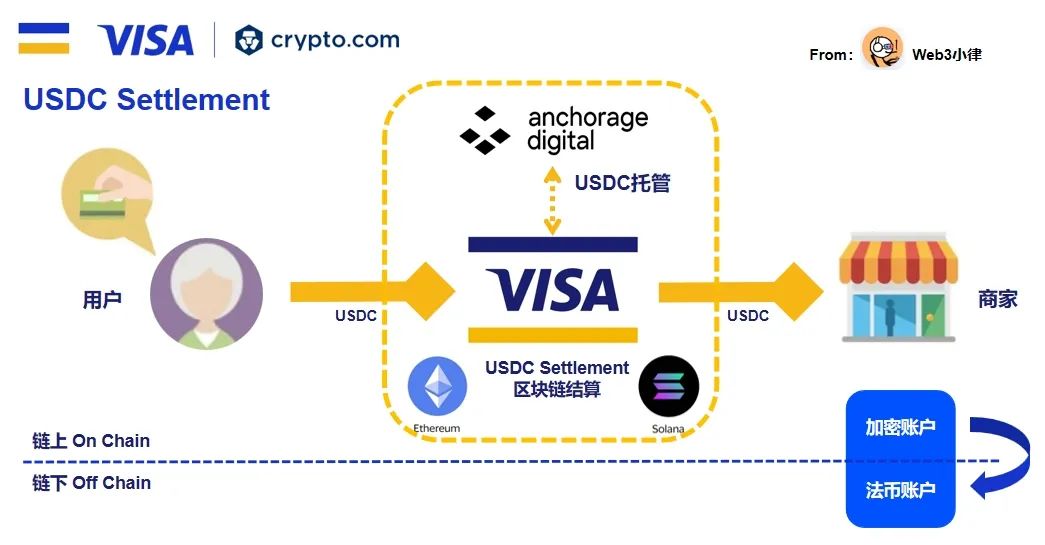
Visa recently provided a settlement solution based on the stablecoin USDC, which is applied in the case of Crypto.com. In the scenario where users spend cryptocurrency and merchants collect fiat currency, Crypto.com needs to convert the cryptocurrency paid by users into fiat currency and then pay it to merchants through traditional payment channels. Settlement through traditional payment channels means an increase in participants, transaction costs, complexity, and limits Crypto.com’s ability to settle outside of banking hours.
With Visa’s USDC settlement solution, the currency exchange in and out of transactions as well as traditional payment steps are directly eliminated, achieving real-time, global settlement 24/7/365 through blockchain. This flexible settlement method, which does not require currency exchange in and out of transactions, opens up new business scenarios for Crypto.com, such as cryptocurrency payment gateways for merchants and blockchain-based cross-border payments.
Visa’s USDC settlement solution can also be used for cross-border remittances. The current cross-border remittance market, worth nearly $10 trillion, is plagued by high-cost traditional payment methods, with traditional payment methods charging up to 8% of the transaction total to the sender. Web3 cross-border remittance products like Strike’s Send Globally, which utilize Bitcoin’s lightning network, provide an affordable alternative to traditional cross-border remittances, with fees ranging from 0.01% to 0.1% of the transaction amount.
This settlement method, combined with the application of stablecoins, can reduce traditional cross-border payment costs by 80%. This means that for a $500 remittance, the transaction costs for on-chain cryptocurrency payments and currency exchange in and out of payments are only $4.8, much lower than the average cost of around $20 for cross-border remittances. In 2022, cross-border remittances to migrant workers amounted to nearly $800 million, and Web3-based payments could save the industry $40 to $64 billion in costs each year.
III. Industry Giants’ Layout of Web3 Payments
Industry giants are gradually opening up/accessing Web3 payment businesses and scenarios around their core businesses such as transactions, payments, communications, and social networking, including wallets, custody, payments, transactions, and stablecoins, ultimately covering their entire ecosystem and forming a logical loop. The following outlines the layouts of LianGuaiyLianGuail, Coinbase, and MetaMask in this regard.
3.1 Payment Company LianGuaiyLianGuail’s Layout of Web3 Payments – Payment, Wallet Custody, and Stablecoins
In the previous article “Payment Giant LianGuaiyLianGuail’s Stablecoin Expected to Lead the Cryptocurrency Industry”, we introduced LianGuaiyLianGuail’s PYUSD stablecoin launched on August 7, 2023. As the only supported stablecoin in LianGuaiyLianGuail’s ecosystem, it will be used to connect LianGuaiyLianGuail’s existing 431 million users, providing a seamless bridge between fiat currency and cryptocurrency for consumers, merchants, and developers in Web2.
3.1.1 Implementation Path of Deposit and Withdrawal Transactions
By reviewing the user agreement of LianGuaiyLianGuail CryptoCurrency, we can see that PYUSD stablecoin plays an important role as a bridge between Web2&3 payments, LianGuaiyLianGuail accounts, and encrypted custody wallet accounts.
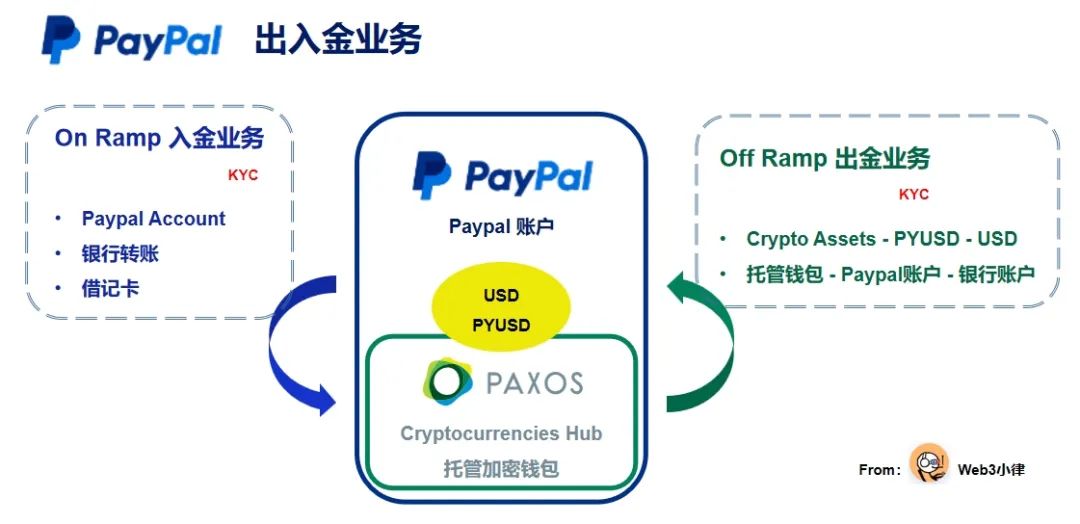
As shown in the above figure, LianGuaiyLianGuail uses PYUSD stablecoin as a bridge for exchange between fiat currency and cryptocurrency. Whether it is in the deposit, withdrawal, or encrypted payment business, it is completed through the USD – PYUSD – Crypto Asset link, and vice versa. For example, in the scenario of using cryptocurrency to pay for merchant services, the first step is to sell Crypto Asset as PYUSD/USD, and then it will be used to make payments to the merchant’s PYUSD/USD.
Fiat currency payment business uses LianGuaiyLianGuail accounts, while for cryptocurrency, LianGuaiyLianGuail creates a Cryptocurrencies Hub encrypted wallet under the LianGuaiyLianGuail account to implement it. This wallet will be hosted by the PYUSD issuer LianGuaixos, which means that users hand over their assets (private keys). The LianGuaiyLianGuail user agreement clearly states: “You will not hold the digital Crypto Assets themselves in your Crypto Asset balance / You do not own any specific, identifiable, Crypto Asset.”
Therefore, we can see that LianGuaiyLianGuail has completed the framework layout for Web3 payments by connecting the payment channels between fiat currency and cryptocurrency, issuing stablecoins as a medium of exchange, and building the LianGuaiyLianGuail account wallet system, forming a logical closed loop within its own ecosystem.
Based on this, LianGuaiyLianGuail can also combine its advantages in the payment industry to provide support for deposit functions to external encrypted wallets such as MetaMask and Ledger, as well as centralized exchanges such as Kraken. At the same time, in the withdrawal function announced by LianGuaiyLianGuail on September 12th, it can also support wallets, DApps, and NFT marketplaces.
With the channels, tools, and infrastructure in place, the key is how to guide LianGuaiyLianGuail’s existing 431 million users to enter Web3 and lead Web3 towards mass adoption.
(Source: Buy and Sell Cryptocurrency | LianGuaiyLianGuail US)
3.1.2 Traditional Payment Companies Preparing for Action
We can see that the path taken by LianGuaiyLianGuail is more suitable for traditional payment companies to replicate. Traditional payment companies like Stripe and Square have already been involved in deposit and withdrawal transactions. For example, Stripe announced the provision of cryptocurrency deposit services in December 2022, and Cash App, a subsidiary of Block (Square’s parent company), not only provides basic functionality for peer-to-peer payments but also offers BTC trading services.
Traditional payment companies have already implemented compliance processes and obtained qualifications for local payment businesses. When they will start Web3 payments and how they will conduct Web3 payments is only a matter of time and pace. On the other hand, new entrants like X (formerly Twitter) are actively applying for money transmission licenses (MTL) in various states in the United States to meet the requirements of compliant payments.
3.2 Web3 Payment Layout of Exchange Coinbase – Trading, Custody, and Payments
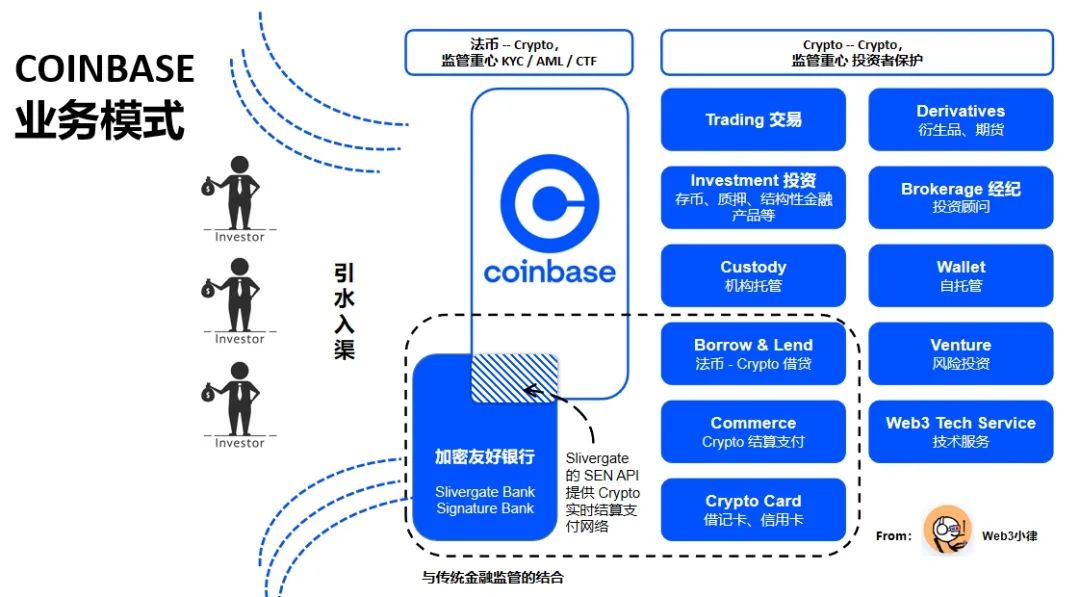
As the most compliant centralized exchange in the world, Coinbase’s many compliance paths are worth learning from. We see that Coinbase, through its layout of Web3 payments, can form a logical closed loop in its own ecosystem, including deposit and withdrawal payment channels, Commerce merchant payment solutions, stablecoin trading media (USDC), custodial wallets for cryptocurrencies, non-custodial wallets, and the core trading functionality of the exchange itself.
3.2.1 Trading as the Core, Payments as the Auxiliary
Although the purpose of centralized exchanges obtaining payment licenses is mainly for the compliance of their own trading business, the acquisition of these licenses also opens up deposit and withdrawal services and payment channels. Due to regulatory uncertainties, excessive reliance on third-party deposit and withdrawal payment channels, such as the previously bankrupted Slivergate Bank and Signature Bank, which was forcibly liquidated by regulators, may bring business instability. Therefore, we see that many exchanges have their own payment business sections, such as Binance Pay, Coinbase Pay, XXX Pay, etc.
In the Licenses & Disclosures section, we see that Coinbase has obtained money transmission licenses (MTL) in most states in the United States. In particular, Coinbase obtained a Bitcoin license (BitLicense) from the New York State Department of Financial Services (NYDFS) in 2017, becoming the first regulated Bitcoin exchange in the United States, able to provide buying, selling, receiving, and storing Bitcoin services to users in New York State.
Outside of the United States, Coinbase is actively expanding in overseas markets and has successively obtained EMI licenses in the UK, VASP licenses in Ireland and Germany, and DPT licenses in Singapore. As a result, Coinbase, with its trading business as an entry point, gradually covers trading business and payment channels in numerous jurisdictions around the world.
(Source: Coinbase Commerce)
In addition to obtaining compliance licenses, Coinbase has also launched an enterprise-level encrypted payment service called Coinbase Commerce. This is a merchant payment solution based on blockchain technology that helps online businesses accept cryptocurrency payments. The service allows merchants to accept mainstream cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin, Bitcoin Cash, DAI, and Ethereum as payment. The purpose of Coinbase Commerce is to help businesses quickly and flexibly conduct operations with global customers.
According to a report on August 21st, Coinbase is acquiring a partial stake in Circle Internet Financial, which means that Coinbase and Circle will have greater strategic and economic consistency in the future development of the encrypted financial system to counter competitors such as USDT and PYUSD. At the same time, Coinbase will also be able to expand the application scenarios of USDC, not limited to cryptocurrency trading, but also potentially extend to areas such as forex and cross-border transfers through Web3 payments. Therefore, USDC = USD Coinbase.
3.2.2 Custody Business and Non-Custodial Wallet
Coinbase Custody Trust Company, LLC, regulated by the New York State Department of Financial Services, is the main company providing custody services for Coinbase. We see that in the current competition for Bitcoin spot ETF applications, in addition to Blackrock and Coinbase confirming their cooperation on Bitcoin spot ETF, it also includes applications from Fidelity, VanEck, 21 Shares under ArkInvest, Valkyrie, and Invesco, all of which have designated Coinbase as their partner. Once the SEC approves these institutional applications, the large assets under management of these asset management companies will be custodied on Coinbase.
According to data from CoinGecko, in an analysis included in the ETF document submitted by Blackrock, Nasdaq estimates that 56% of the $129 billion Bitcoin trading volume in the United States is conducted on Coinbase. In the future, with the development of Bitcoin spot ETF, this proportion is expected to further expand. Coinbase will also benefit greatly from this and become the biggest winner in this competition.
As for the non-custodial wallet Coinbase Wallet, since users independently control assets (private keys) and interact directly with payment systems, Coinbase Wallet itself will not be defined as an MSB by FinCEN, similar to MetaMask.

Therefore, we see that Coinbase, based on its compliance advantages in its trading business, has established a logical closed loop in its own ecosystem by connecting deposit and withdrawal payment channels, stablecoin trading medium (USDC), encrypted asset custody wallets and non-custodial Wallet, as well as the trading function of the core exchange itself.
The key is that Web3 payment services complement Coinbase’s main business of exchanges and contribute to profits.
3.3 MetaMask’s Web3 Payment Layout – Wallet and Aggregation
We see that MetaMask has continuously introduced new features in the past year, and the current MetaMask Portfolio DApp has aggregated functions such as Sell, Buy, Stake, Dashboard, Bridge, and Swap, helping users manage assets conveniently and achieve unified on-chain asset operations. At the same time, MetaMask recently launched the Snaps version, integrating third-party public chain plugins.
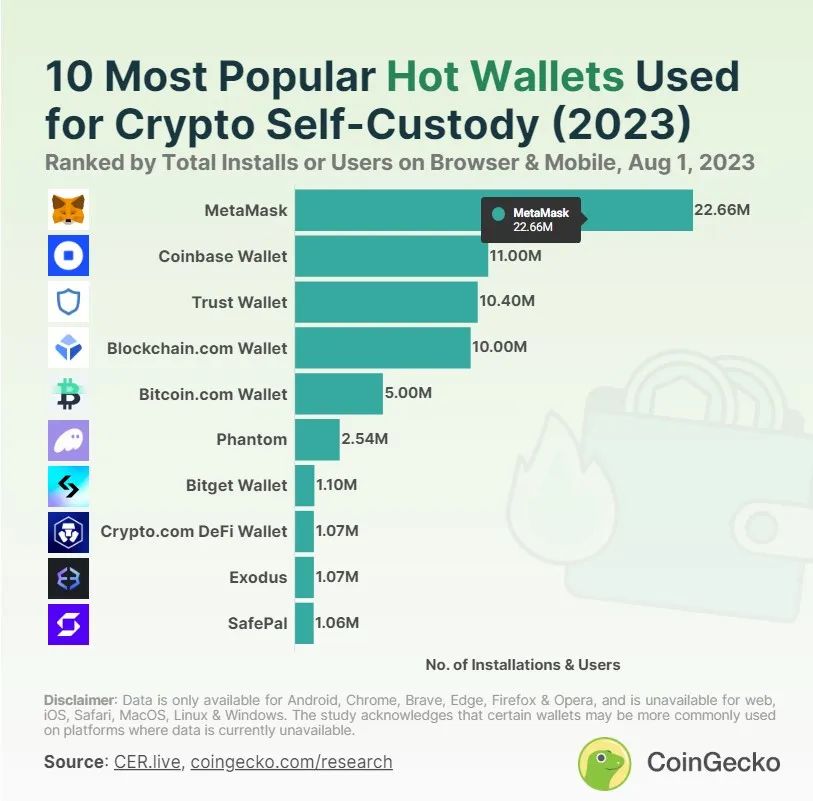
MetaMask’s natural advantage lies in its nearly 30 million monthly active users. According to data disclosed by Consensys, MetaMask has a total of 100 million users, associated with 17,000 DApps, and a daily interaction volume of 244,000 times. According to CoinGecko’s report, as of August this year, MetaMask has been downloaded 22.66 million times.
In the foreseeable future, it can be seen that MetaMask will aggregate into a super wallet traffic entrance, allocate wallet traffic, and distribute it to various DApps. The operational business imagination space is huge.
3.3.1 Launch of “Sell” to enable deposit and withdrawal functionality
On September 5th, MetaMask launched its latest feature “Sell”, which allows users to convert cryptocurrencies into fiat currency through MetaMask Portfolio and send funds to bank accounts. For compliance purposes, this feature is currently only available in the United States, the United Kingdom, and certain regions in Europe, and only supports the exchange of US dollars, euros, and pounds. MetaMask stated that initially, it only supports ETH on the Ethereum mainnet and plans to expand to other native tokens on Layer 2 networks in the short term.
(Source: MetaMask Portfolio)
After selecting the region, users enter the amount of ETH to be sold and choose a quote from multiple service providers, and connect their bank account. According to official information, MetaMask has established partnerships with cryptocurrency withdrawal service providers such as MoonLianGuaiy, Sardine, and Transak. However, currently only MoonLianGuaiy and Transak provide services for this feature, and KYC verification is required.
The “Sell” withdrawal feature was launched five months after the introduction of the “Buy” deposit feature on MetaMask, which allows users to deposit funds using bank accounts, LianGuaiyLianGuail, debit cards, and credit cards.
Non-custodial wallets like MetaMask, which allow users to independently control assets (private keys) and interact directly with payment systems, only provide communication or network access services to support currency transfer services, and are not regulated under FinCEN as MSBs. MoonLianGuaiy, which provides payment channels for MetaMask, is classified as an MSB.
3.3.2 Independent third-party payment company MoonLianGuaiy
MoonLianGuaiy is currently the leading project for cryptocurrency deposits and withdrawals, with over 5 million registered users. In terms of coverage, MoonLianGuaiy supports cryptocurrency payments in over 160 countries and regions, and the exchange of over 80 cryptocurrencies and more than 30 fiat currencies. In terms of payment methods, MoonLianGuaiy currently supports payment channels such as credit cards and debit cards, mobile payments, and account-to-account payments. Uniswap has also included MoonLianGuaiy as one of its deposit channels.
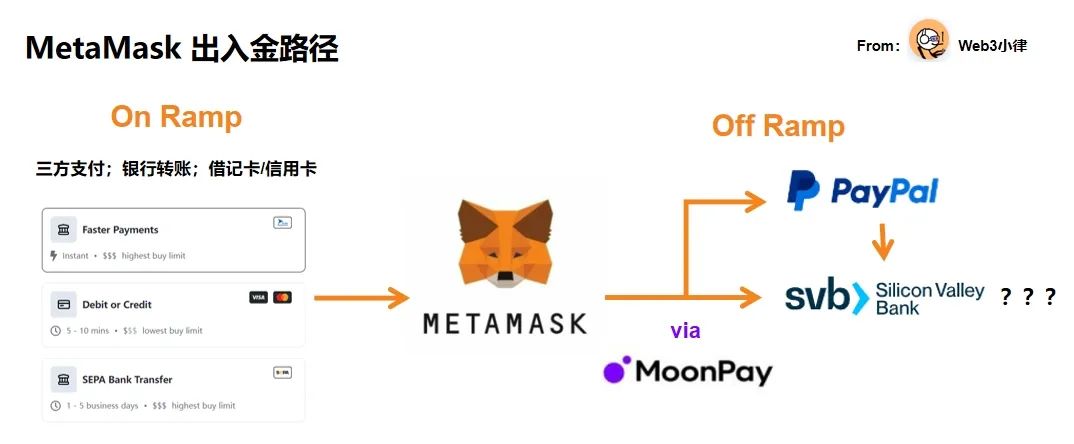
After aggregating these independent third-party payment companies such as MoonLianGuaiy, MetaMask is able to achieve deposit and withdrawal payment channels, non-custodial wallets, and various transaction functions (Swap, Bridge, Stake, etc.) aggregated on its portfolio page. This basically forms a logical closed loop.
3.3.3 Snaps Version
On September 13th, MetaMask released its Snaps version, which supports wallet integration with non-EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) chains including Solana, Sui, Aptos, Cosmos, and Starknet. Currently, there are 34 Snaps in the testing phase. In simple terms, MetaMask has open-sourced some of its functionalities to allow third-party developers to extend the MetaMask wallet in ways they want, aiming to provide users with a more personalized or diversified transaction experience.
In the past, when users wanted to interact with different public chains, they needed to download corresponding wallet plugins, which not only provided a poor user experience but also indirectly increased security risks. Now, MetaMask has opened up a set of Snaps API access specifications, allowing third-party public chain wallet providers to overcome technical difficulties and integrate with MetaMask. MetaMask is only responsible for auditing the integrations, while other development work is done by third-party developers.
As a result, users only need to download the MetaMask wallet and install third-party public chain plugins to freely navigate different public chain networks, with a higher level of security. This is a very clever ecological integration move, once again consolidating its leading position in plugin wallets.
MetaMask’s natural advantage lies in its nearly 30 million monthly active users. In the foreseeable future, MetaMask is expected to aggregate into a super wallet traffic entrance, allocating wallet traffic to various DApps. There is a great potential for operational business imagination.
IV. Regulatory Compliance of Web3 Payments
Due to the openness and innovation of encrypted assets, it is difficult to define their attributes uniformly. Currently, most jurisdictions do not have a complete regulatory framework specifically for encrypted assets. In practice, regulatory compliance for Web3 payments not only requires compliance with cross-border payment and currency transfer businesses but also compliance with encrypted asset businesses. In addition, considering the inherent global circulation of encrypted assets, Web3 payments will face exceptionally complex global regulatory challenges in multiple legal domains, which is also a huge challenge for regulatory jurisdictions.
Nevertheless, we can still see some jurisdictions actively exploring Web3 payments. For example, Switzerland, a crypto-friendly country, has clearly defined “payment tokens”; similarly, Singapore has a definition of “payment tokens” and recently released a stablecoin regulatory framework; the EU’s MiCA legislation also has a clear definition of “electronic money tokens”. The continuous clarification of these regulatory definitions will give cryptocurrencies a legally valid status, further promoting the development of the Web3 payment industry and leading the Web3 industry towards mass adoption.
Compliance is the foundation for traditional giants, so when they engage in Web3 payment businesses, they initially only limit their operations to certain regions. For example, MetaMask’s Sell-Out service (supported by MoonPay) is currently only available in the United States, the United Kingdom, and parts of Europe, and MoonPay’s stablecoin is currently limited to US users. Although Web3 payment businesses can only be conducted after meeting compliance requirements such as licenses and qualifications, this is also a major barrier for project parties participating in Web3 payment projects.
Web3 payments involve multiple aspects of legal compliance, such as encryption assets, payments, asset custody, stablecoins, and anti-money laundering/counter-terrorism financing. It is exceptionally complex. The following will provide a brief overview of the legal regulations related to Web3 payments in major jurisdictions, and how the giants are constructing legal compliance barriers.
4.1 United States
The main regulatory agency in the United States for Web3 payments is the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (FinCEN), which is under the U.S. Department of the Treasury. FinCEN is primarily responsible for supervising and implementing work related to anti-money laundering (AML), combating the financing of terrorism (CFT), and customer due diligence (KYC). It also collects and analyzes financial transaction information, tracks suspicious individuals and activities through mandatory disclosures by financial institutions.
FinCEN’s authority comes from the Bank Secrecy Act (BSA), which considers cryptocurrencies as “currency”. In 2019, FinCEN published guidance titled “Application of FinCEN’s Regulations to Certain Business Models Involving Convertible Virtual Currencies”, which provided regulations related to cryptocurrency payment.
The 2019 guidance defines “money transmission” as the act of receiving currency (or the value of other substitute currency) from one party and sending all or part of it to another party. The “substitute currency” in this definition includes money orders, stored value cards, and cryptocurrencies. In most cases, any company engaged in money transmission business will meet the definition of a Money Service Business (MSB) under the BSA. They need to comply with the BSA and FinCEN’s relevant regulations and fulfill compliance obligations.
A rough summary of the 2019 guidance for determining whether a company is an MSB:
Control of user assets (private keys): Centralized exchanges and custodial wallet providers that offer services to U.S. users and can control user assets (private keys) are considered MSBs. Non-hosted wallets like MetaMask and decentralized exchanges (DEX) that only provide matching services and allow users to independently control assets (private keys) and directly interact with payment systems, or only provide communication or network access services to support money transmission services, are not considered MSBs.
Nature of business money transmission: Payment companies that provide services to U.S. users, such as MoonLianGuaiy, LianGuaiyLianGuail, Stripe, and Square, are engaged in money transmission business and are considered MSBs.
Companies classified as MSBs not only need to comply with the BSA and FinCEN’s relevant regulations and fulfill compliance obligations but also obtain money transmission licenses (MTL) from each state in accordance with each state’s money transmission laws. Obtaining an MSB license in the United States is relatively easy, but it takes about two years and millions of dollars in legal consulting fees to obtain an MTL license in each state in the United States.
Among them, BitLicense is a cryptocurrency license created by the New York State Department of Financial Services based on the New York State Financial Services Law. It is used to regulate cryptocurrency institutions and related limited purpose trust companies in the state. Licensed entities must comply with BitLicense’s compliance regulatory framework, including consumer protection, AML compliance, and cybersecurity guidelines. Entities that have previously obtained BitLicense include XRP II, Circle Internet Financial, Gemini Trust Company, itBit Trust Company, etc.
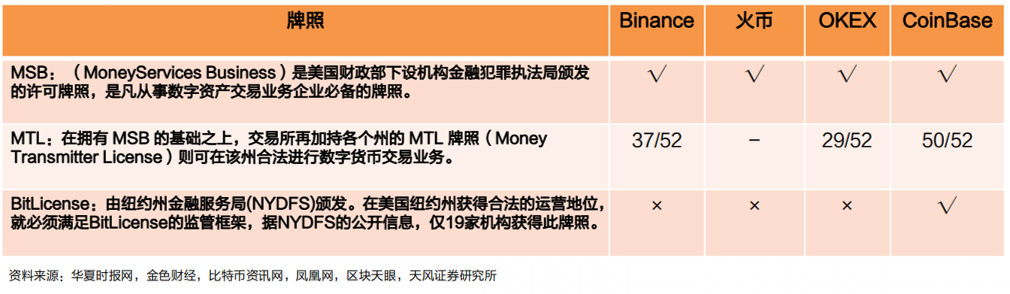
This is also what we saw in the news that X (the original Twitter) is actively applying for money transmission licenses (MTL) in various states in the United States. X (the original Twitter) wants to become like WeChat, which inevitably involves WeChat’s payment system. For payment companies that have already obtained licenses in various states, this will be a core barrier for them to operate Web3 payment business in the United States.
4.2 United Kingdom
Companies that want to conduct Web3 payment business in the United Kingdom need to obtain an electronic money institution (EMI) license issued by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) of the United Kingdom. We saw that Coinbase obtained an EMI license in 2018 and conducted encrypted business in the European Union region.
Interestingly, decentralized lending platform Aave, headquartered in London, also obtained an EMI license in 2020. It is reported that this is a compliance guarantee made by Aave to attract more users to enter DeFi, and it may also be due to the strict consumer protection compliance requirements in the United Kingdom.
Before Brexit, holders of EMI licenses in the United Kingdom were not subject to restrictions on time or areas of activity in the European Economic Area (EEA) and could provide any form of service. After Brexit, more companies have turned their attention to more neutral and friendly Ireland.
4.3 Ireland/European Union
In 2021, Ireland introduced a registration system for virtual asset service providers (VASPs), which is reviewed by the Central Bank of Ireland to ensure that companies can meet AML/CTF requirements. After Coinbase obtained the EMI license authorized by the Central Bank of Ireland, Coinbase Ireland Limited obtained the VASP license in Ireland in 2022, which enables Coinbase to issue electronic currency, provide electronic payment services, and process electronic payments for third parties.
Similarly, after obtaining the EMI license in the United Kingdom, MoonLianGuaiy obtained the VASP registration of the Central Bank of Ireland in 2023. Its CEO said, “We believe that registering VASP in Ireland first and ultimately applying for registration based on the EU MiCA will provide the company with a huge competitive advantage for compliance and entry into the EU market.”
The European Union’s Markets in Crypto-Assets Regulation (MiCA) has been passed by the European Parliament and is expected to take effect in 2024. In general, MiCA applies to all entities involved in the issuance of crypto-assets and the provision of crypto-asset-related services in the European Union: (1) various types of crypto-asset issuers, including E-Money Tokens, Asset-Referenced Tokens, and other Tokens; (2) various types of crypto-asset services and service providers, including wallet custody services, deposit and withdrawal services, exchange services, asset management services, investment advisory services, etc.
MiCA fills the gaps in the existing EU financial regulatory framework and, once implemented, will create a unified regulatory framework for crypto-assets within the EU, directly forming a large crypto-asset market that radiates to 27 countries and 450 million people in the European Union. Since registering a VASP license in one EU member state allows businesses to operate throughout the EU, Lithuania, which has the most lenient cryptocurrency regulation policy in the EU, has attracted many centralized exchanges and payment institutions to register and settle there.
4.4 Hong Kong
With the implementation of the Hong Kong VASP system, all centralized cryptocurrency exchanges operating in Hong Kong or actively promoting their services to Hong Kong investors, regardless of whether they provide security token trading services or not, will need to obtain a license from the Hong Kong Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) and be regulated by it.
At the same time, the VASP system imposes requirements on the operation of centralized exchanges to “safeguard customer assets”, which means that platform operators are required to hold customer funds and customer cryptocurrencies in trust through a wholly-owned subsidiary (TCSP trust license). This means that a TCSP license is required for independent custody of investor assets to avoid self-dealing.
The full name of the TCSP license is Trust or Company Service Providers. Since traditional banks can only hold fiat currency assets, custody of cryptocurrencies can currently only be placed in trust accounts, which also gives the TCSP trust license new business scenarios.
The Hong Kong High Court has previously ruled in the case of Re Gatecoin Ltd [2023] HKCFI 914 that cryptocurrencies are “property” and can be held on trust. Therefore, any company engaged in cryptocurrency custody business needs to apply for a TCSP license. Exchanges such as OSL, Hashkey Group, and Gate.io all have their own TCSP trust companies. In addition, wallet infrastructure and digital asset custody service provider Liminal has recently obtained a TCSP license.
Under the Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorist Financing Ordinance, any entity operating or intending to operate a money service in Hong Kong must apply for a Monetary Service Operator (MSO) license from the Hong Kong Customs and Excise Department. For Web3 payment businesses, if a company’s related cryptocurrency business in Hong Kong includes currency exchange services or remittance services, the relevant service providers need to obtain an MSO license issued by the Hong Kong Customs and Excise Department.
4.5 Singapore
The Monetary Authority of Singapore (MAS) is Singapore’s central bank and integrated financial regulatory authority, responsible for regulating the Web3 industry. Referring to MAS’s “A Guide to Digital Token Offerings” published in May 2020, it is clear that security tokens and payment tokens are regulated by two specific regulations, while utility tokens are not subject to regulation.
For payment tokens, under the Payment Services Act that came into effect in January 2020, providing digital payment token (DPT) services in Singapore includes direct transaction services for DPTs (such as buying, selling, fiat currency exchange, token-to-token exchange) and services that facilitate DPT transactions (such as exchanges, custodian institutions, wallet services, etc.).
The application difficulty for this license is relatively high, and in recent years there has been a cautious attitude towards the cryptocurrency field. However, Singapore has an indefinite exemption period for DPT operations, allowing operations to proceed without a license. In 2022, institutions such as Circle, LianGuaixos, Blockchain.com, Coinbase, Luno, Digital Treasures Center, Crypto.com, and Genesis have successively obtained DPT licenses.
(Source: From Crypto Center to Crypto Node: Singapore's Web3 Regulatory Framework)
V. Future Vision of Web3 Payments
From a market perspective, this is still an appealing blue ocean market. According to statistics, there are currently 1.7 billion people worldwide without bank accounts but in urgent need of financial services. Countries with high inflation, a majority of the population without banking services or insufficient banking services, or countries where the traditional financial system is considered unreliable, have witnessed a surge in crypto payments due to these innovations. The number of over 420 million cryptocurrency owners worldwide alone is enough to show that the cryptocurrency industry is not a speculative industry but a flourishing and rapidly developing one.
From the perspective of innovative development, in order to meet the growing demand for cryptocurrencies, Layer 2 solutions that continuously innovate and optimize scalability, stablecoins that solve the problem of cryptocurrency volatility, compliance asset management solutions provided by wallet service providers and custodians to address asset security issues, and Web3 payment companies offering deposit and payment solutions to solve merchant collection and mobile payment problems, these flourishing technological innovations have laid a solid foundation for Web3 to achieve Mass Adoption.
Looking back at the implementation path of Web3 payments by giants such as LianGuaiyLianGuail, Coinbase, MetaMask, and their respective strong traffic and scene entry, and imagining the exclusive advantages of players like X (Twitter), Telegram, and other players who are currently making a strong push, it is not difficult to see that after the giants have connected the basic functions of wallets, custody, stablecoins, and payments, they will form their own massive Web3 encrypted ecosystems. In such a context, the current cryptocurrency market, which is mainly dominated by exchanges, will inevitably undergo changes.
In addition to the massive Web3 encrypted ecosystems of the giants, the compatibility of Web3 products with the outside world is also one of the points of change. Taking Web3 wallets as an example, Web3 wallets are tools closely integrated with the DApp ecosystem, providing direct access and use of DApps. Currently, users of the OKX Web3 wallet can access over 5,500 DApps, and the wallet has already integrated over 500 DApps. Not to mention MetaMask, which has nearly 30 million monthly active users, and MetaMask Portfolio DApp, which has aggregated functions such as Sell, Buy, Stake, Dashboard, Bridge, and Swap.
(Source: Tech giants are making bets, can Web3 wallets become the lever to move the industry?)
From the perspective of the monetary system, the BIS states in its “Blueprint for the Future of the Monetary System” that the current monetary system is on the brink of another major leap. After digitization, the key to the development of the monetary system is tokenization, the process of representing rights and claims in a digital manner on a programmable platform, which can be seen as the next logic of digital record keeping and asset transfer.
The future currency system will use tokenization to improve the old currency system and support the new currency system. By utilizing new intermediaries (such as a unified ledger) to serve end users, artificial intervention and reconciliation resulting from the separation of traditional message transmission, clearing, and settlement can be eliminated, thereby eliminating delays and uncertainties. Tokenization can significantly enhance the capabilities of the currency and financial system. The future currency system is expected to unleash new economic growth potential through tokenization, which is unrealistic in the inherent friction of the current currency system.
This tokenization is not only the recent hot topic of Real World Asset Tokenization (RWA), but also the tokenization of the currency itself. Tokens define assets and, through the programmability of tokens, define what assets can be used for by encapsulating the payment logic of the token.
(Source: Blueprint for the future monetary system: improving the old, enabling the new)
Six. Conclusion
Undoubtedly, Web3 payments will become commonplace in the near future and may completely replace existing payment methods, both within enterprises and between individuals. At the same time, traditional finance will be interconnected through Web3 payment finance and trade, making the expression, circulation, transaction, programming, and regulation of assets the main value proposition, highlighting efficiency advantages.
The biggest opportunity for cryptocurrencies may not be seen as cryptocurrencies, but as a new set of payment methods. Some believe that the killer application of Web3 has not yet arrived, but it may have quietly arrived: it is payment!
Digitization and tokenization will give traditional currency systems new value, overcome previously insurmountable boundaries, and may permanently change the world economy.
-END-
REFERENCE:
[1] ZONFF Research, Comprehensive Interpretation and Trend Analysis of Web3 Payment Track
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/nty-98HtnBIVaXljOrZdrA
[2] Blueprint for the future monetary system: improving the old, enabling the new
https://www.bis.org/publ/arpdf/ar2023e3.htm
[3] Bing Ventures, Crypto LianGuaiyments Market Size To Reach Hundreds Of Billion Dollars In Three Years
https://www.bing-ventures.com/insights/52-Crypto-LianGuaiyments-Market-Size-to-Reach-Hundreds-of-Billion-Dollars-in-Three-Years-Report-by-Bing-Ventures
[4] TokenInsight, 2021 Digital Assets LianGuaiyment Industry Research Report
https://alchemyLianGuaiy.org/2021_Digital_Assets_LianGuaiyment_Industry_Research_Report_2_compressed.pdf
[5] Ripple & FPC, Blockchain & Crypto in LianGuaiyments: Transforming the Way Money Moves
https://fasterLianGuaiymentscouncil.org/blog/11590/Blockchain-Crypto-in-LianGuaiyments-Transforming-the-Way-Money-Moves
[6] B2BinLianGuaiY, How Crypto LianGuaiyment Solutions Have Changed the Market
https://b2binLianGuaiy.com/en/how-crypto-LianGuaiyment-solutions-have-changed-the-market/
[7] Sygnum Bank, Crypto as a means of LianGuaiyment: An evolving megatrend
https://www.sygnum.com/future-finance/crypto/crypto-as-a-means-of-LianGuaiyment-an-evolving-megatrend/
[8] Celine Wee, On/off Ramps in Web3: an Introductory Guide
https://celinewee.medium.com/introduction-95d8558ebbe0
[9] LianGuaiYLianGuaiL CRYPTOCURRENCY TERMS AND CONDITIONS
https://www.payLianGuail.com/us/legalhub/cryptocurrencies-tnc?locale.x=en_US#fees-pricing
[10] LD Capital: Analysis of Coinbase investment logic and growth potential
https://news.marsbit.cc/20230912135649053295.html
[11] Okeyun Chain, Can Web3 wallets become the fulcrum of the industry with the support of technology giants?
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/BjRxQygMyfWiagNs2K_NTQ
[12] Visa, Crypto stablecoin settlement
https://usa.visa.com/solutions/crypto.html
[13] Application of FinCEN’s Regulations to Certain Business Models Involving Convertible Virtual Currencies
https://www.fincen.gov/resources/statutes-regulations/guidance/application-fincens-regulations-certain-business-models
[14] Meng Yan’s blockchain thinking, “Reflection on the Chain Circle” for ten years
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Advoy5E86nPhE20Dqm6LianGuaiw
[15] CSDN, [Payment Architecture] Cross-border payment
https://blog.csdn.net/u010482601/article/details/122052403
[16] Head Leopard Research Institute, Cross-border payment
https://pdf.dfcfw.com/pdf/H3_AP202308111594152732_1.pdf?1691784953000.pdf
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!