Author: WJB
In this issue, WJB research will take you on a deep dive into the modular Layer 2 champion of Mantle Network. The goal of Mantle Network is to provide a high-performance, low-cost, and user-friendly platform for the Ethereum ecosystem, promoting the widespread adoption of decentralized applications.
Mantle Network is a modular Layer 2 network compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), incubated by BitDAO. It utilizes roll-up technology and a decentralized data availability layer (Mantle DA) to provide high throughput, low fees, and fast determinism while ensuring Ethereum-level security. It also uses multi-party computation and decentralized sorters to enhance network security and decentralization. The goal of Mantle Network is to provide a high-performance, low-cost, and user-friendly platform for the Ethereum ecosystem, promoting the widespread adoption of decentralized applications.
1. Research Highlights
1.1. Core Investment Logic
Mantle Network is an L2 scaling solution based on Optimistic Rollup technology, providing EVM compatibility and modular design. Its core investment logic is mainly reflected in the following aspects:
- Comprehensive interpretation of Cosmos core technology. What growth potential will there be in the future?
- Renegade Research Report Decentralized Dark Pool Protocol Adopting MPC and ZK Technology
- Mantle Deep Research Report Can BitDAO’s new Layer2, incubated with modular technology and a solid foundation, stand out?
Mantle Network is incubated by the well-known DAO organization BitDAO, giving it significant advantages in terms of technical team strength and financial support. This lays a solid foundation for Mantle to establish a strong position in the competitive Layer 2 landscape. At the same time, Mantle has formed strategic partnerships with multiple top projects, which will facilitate its rapid integration into the Ethereum ecosystem and the gathering of users and application scenarios. With the continuous growth and development of the Ethereum ecosystem, Mantle can further tap into a huge market space. It can be said that Mantle has a solid technological and financial backing, broad market prospects, and is building a win-win ecosystem. These are the key factors that give it long-term investment value. In addition, in terms of asset allocation, Mantle Treasury holds a large amount of mainstream digital assets, which provides it with stronger liquidity support and market-making capabilities, helping to consolidate the price of the MNT token. Compared to other DAOs that only hold governance tokens, Mantle’s richer asset reserves also enable it to fully finance ecosystem construction. Mantle can use its asset advantage to establish an ecological fund and attract high-quality projects. This is also a key support for Mantle as one of the important Layer 2 networks with long-term development prospects.
A sound governance mechanism benefits the long-term stability and appreciation of the token. BitDAO, the organization behind Mantle Network, has taken various measures to enhance the long-term stability and appreciation potential of its token economic model. For example, it has changed the donation model of Bybit, reducing the donation amount in fixed phases to reduce token circulation. It also addresses the inflation risk of treasury tokens through governance theory. By learning from successful cases of other L2 tokens, these governance measures reflect the strong emphasis that Mantle Network places on team efforts to maintain token value and the ability to learn from other successful cases, giving the MNT token better long-term appreciation potential compared to other crypto assets. It can be foreseen that as the ecosystem matures, Mantle Network will continue to improve its governance mechanism and develop more policies based on the collective intelligence of the DAO to enhance the intrinsic value of the token, laying the foundation for the long-term investment prospects of MNT.
The various operational mechanisms of Mantle Network provide a way to reduce the circulation of MNT tokens. Unlike other L2 networks that use ETH as the gas token, MNT tokens are used as the gas token for the Mantle chain. As the ecosystem develops steadily and on-chain interactions become active, MNT will be steadily consumed without the need for other artificial controls. It is a stable deflationary model. At the same time, through multiple token staking scenarios, the circulation of tokens will be effectively reduced and the value of the tokens will be enhanced. The economic model design of Mantle Network provides support for the long-term investment value of MNT by having mechanisms to reduce the circulation of tokens in multiple aspects, which is a core logic for investing in MNT.
Mantle Network adopts a modular technical route, which reflects the forward-looking nature of its technical system. The functions of each component of Mantle are clearly divided, and a loosely coupled design is adopted, which ensures the flexibility of the system and allows it to adjust components as needed to adapt to technological and business changes. For example, the data availability component EigenDA can be easily replaced with other storage solutions. Compared with the Monolithic architecture, the modular system of Mantle is easier to update and iterate, and it has higher security and stability. If there are problems with the system, they can be solved by upgrading individual components instead of requiring a complete reconstruction. In addition, modularity allows third parties to only access or use part of the functions of the Mantle system according to their needs, which expands the applicability and scenarios of the system. This design concept is worth learning from by other projects and is the technological foundation for the long-term investment value of Mantle.
Mantle Network achieves a level of scalability that other L2 networks find difficult to achieve. By using Optimistic Rollup and an independent data availability layer called EigenLayer, Mantle can provide lower costs and faster transactions. This architecture is different from other Ethereum Layer 2 scaling solutions such as Cartesi, Loopring, Polygon, and Arbitrum. Although Mantle is not the only L2 solution that uses an independent data availability layer, its data availability layer, MantleDA, is decentralized, while the data availability layers of other L2 networks mostly use centralized architectures. This allows Mantle to achieve true decentralization and high scalability. Through this technological architecture innovation, Mantle is expected to provide transaction performance and cost advantages surpassing other L2 networks. This scalability improvement will be beneficial for achieving widespread adoption and gaining competitive advantages. Therefore, the high scalability of Mantle is an important differentiating technological advantage and investment value proposition.
The security of Mantle Network is built on the powerful consensus mechanism and validator node set of Ethereum. The states and transactions of Mantle are validated by Ethereum’s validator nodes in the same way as on the L1 chain. In other words, the node set that verifies the security of Mantle transactions is consistent with Ethereum, which is different from other L2 networks that use their own consensus models. Mantle directly inherits the strong security of Ethereum, and its security is not weaker than the Ethereum mainnet. This design of closely integrating Ethereum’s security model gives Mantle unique advantages and higher reliability in terms of security compared to other L2 networks. This is a core competitiveness and investment value of the Mantle network.
1.2. Valuation
According to CoinGecko data, as of September 3, 2023, the price of $MNT token is $0.45, with a market capitalization of $1.459 billion. The circulating supply is 3.234 billion tokens, with a total supply of 6.219 billion tokens. The fully diluted market capitalization is $2.805 billion. After conducting in-depth analysis and valuation of the Mantle Network project, we believe that the $MNT token is somewhat overvalued at the current stage. However, in the long term, if Mantle can fulfill its technical promises, develop its ecosystem steadily, and demonstrate its technical advantages, ecosystem potential, and market space, there will be room for valuation improvement.
In the subsequent report (6.2 Project Valuation Level), we will provide a detailed explanation of the valuation analysis method and basis for Mantle Network. At the same time, we will continue to monitor its ecosystem development dynamics in order to adjust our valuation judgment in a timely manner.
1.3. Project Risks
The main risks currently faced by Mantle Network are: competition risk in the fierce Layer 2 competition environment, technical security risk, risks associated with the early stage of project development, negative impact of poor performance of the BIT token on MNT, and the risk of the OP Rollup technology direction it represents no longer receiving community support. For detailed project risk details, please refer to section 6.3 Project Risks.
2. Project Overview
2.1. Project Scope
Mantle Network is an Ethereum Layer 2 solution designed based on the Optimism OVM architecture. It adopts a modular design and attempts to utilize EigenDA as the data availability layer and Specular Network’s fraud proof system to achieve transaction validity proof.
According to official information from Mantle Network, its business scope, in addition to being an L2 scalability solution, includes providing fast and low-cost on-chain transactions, establishing a sustainable business model for public chains, and mainly involves:
1) Mantle LSD (to be launched soon)
Mantle LSD is a decentralized staking service based on Lido, which allows users to stake ETH on Ethereum 2.0 and receive mntETH as a voucher. Mantle LSD aims to become the preferred solution for ETH liquidity staking in the Mantle ecosystem by leveraging the synergies of the Mantle Network ecosystem. It can reduce Mantle’s deposit costs and allow third-party applications to use and expand without permission. Mantle LSD also has a simple and secure system architecture, which can leverage the existing capabilities of the Mantle ecosystem, such as community, governance, brand influence, etc., to promote the development of the Mantle Network ecosystem.
2) Mantle EcoFund
Mantle EcoFund is a $200 million ecological fund provided by the Mantle Treasury, jointly invested with strategic partners at a 1:1 ratio. The main goal of EcoFund is to promote the adoption of developers and DApps on the Mantle network, taking into account the sustainability and return of the fund. EcoFund will prioritize investment in teams building high-quality and innovative projects within the Mantle ecosystem and increase investment in potential outstanding projects at the appropriate time.
3) EduDAO
EduDAO is a decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) that connects different university ecosystems to enhance collaboration and data exchange, nurturing the next generation of blockchain and Web3 innovators. EduDAO is funded by the BitDAO treasury and operates as an independent governing council, allocating up to $11 million annually for project funding, research, and independent product development. EduDAO’s university partners include Berkeley RDI, Berkeley Blockchain, Penn Blockchain, Harvard Blockchain Club, MIT Sloan Blockchain Club, Michigan Blockchain, USC Blockchain, Oxford Blockchain Society, and Tsinghua University Student Blockchain Association. The goal of EduDAO is to cultivate the next generation of leaders and creators in the blockchain industry.
4) Game7
Game7 is a game accelerator that aims to drive the development of a permissionless and interoperable gaming world. Game7 provides game developers with key tools such as NFT marketplaces, cross-chain bridging, and game DAOs.
Game7 and Mantle Network are both projects incubated by BitDAO and have a close cooperative relationship. Game7 will leverage the infrastructure provided by Mantle Network to offer high-quality user experiences and ecosystem interoperability for its incubated and invested game projects.
2.2. Team Situation
2.2.1. Overall Situation
Mantle Network, as a Layer 2 network solution, is incubated and supported by the well-known DAO organization BitDAO. The initial conceptual prototype of Mantle was proposed by Ben Zhou, the CEO of Bybit, and other prominent members of the crypto community, including Sreeram from EigenLayer, Dow Jones, and Cooper Midroni. The team consists of over 50 professionals from different fields and backgrounds, working in a flat management structure.
2.2.2. Team Background
Various aspects of Mantle Network, such as its creation background, resource commitments, and future vision, are closely related to its incubating organization, BitDAO. To fully understand the historical origins and development trajectory of Mantle Network, it is necessary to explore the relevant history of its incubating organization, BitDAO. Mantle and BitDAO can be seen as two integral components, and the success of Mantle relies on the strong resource support and shared vision goals of BitDAO.
1) BitDAO
BitDAO was founded in 2021 by Daniel Yan and Ben Zhou, co-founders of Bybit, a major cryptocurrency derivatives exchange based in Singapore. The treasury assets of BitDAO come from fundraising and donations. In June 2021, it raised $230 million in a private financing round, with investors including Founders Fund, LianGuaintera Capital, Dragonfly Capital, and others. In August of the same year, BitDAO completed an auction through the BIT-ETH crowdfunding pool on SushiSwap’s MISO platform, issuing 200 million BIT tokens and raising 112,670 ETH (valued at $360 million at the time).
BitDAO is one of the largest DAO organizations to date, with its DAO treasury managing assets worth approximately $3.4 billion, mainly consisting of BIT, MNT, ETH, USDC, and USDT.
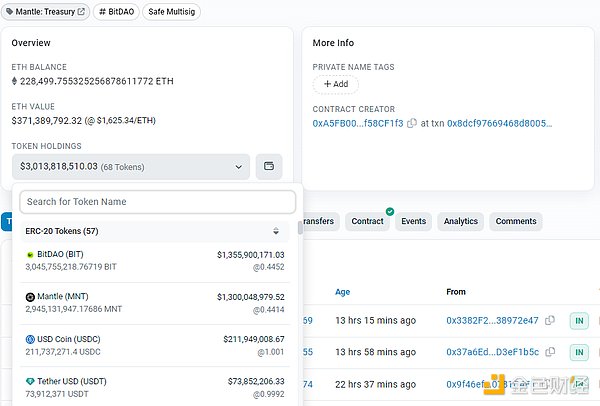
The success of BitDAO is inseparable from the contribution of its main sponsor, Bybit. As the largest supporter of BitDAO, Bybit has pledged to donate 0.025% of its futures contract trading volume to the BitDAO treasury. Some public data shows that from July 2021 to June 2022, Bybit donated over $1 billion worth of tokens to BitDAO. In June 2022, Bybit announced that it would continue to donate tokens to BitDAO regularly for the next four years, but the donation amount would gradually decrease. The specific daily donation information and disclosure may need to be obtained through BitDAO community announcements.
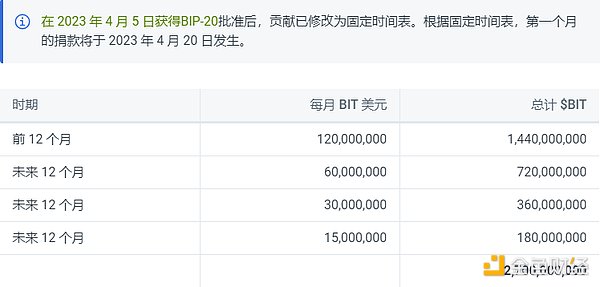
2) Ecological Merger
In May 2023, BitDAO completed a merger with Mantle Network through the BIP-21 proposal, unifying the brand and token as Mantle (MNT). This established a larger ecosystem, and the MANTLE ecosystem inherits BitDAO’s vision and receives its funding and community support for the operation and development of Mantle Network. BitDAO’s token, BIT, is also converted to MNT at a ratio of 1:1. After the merger of Mantle Network and BitDAO, the new Mantle ecosystem became the largest treasury in the cryptocurrency industry, with a value exceeding $3 billion at the time of writing this article.
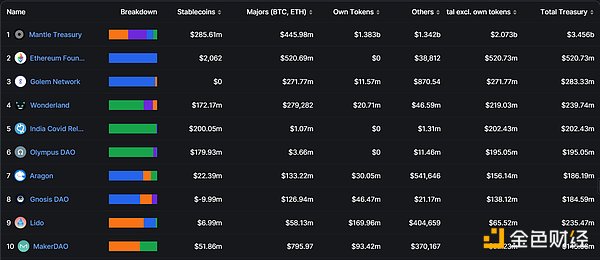
It can be seen that Mantle has obtained strong support from BitDAO, with abundant financial strength. The exploration of decentralization by the centralized exchange Bybit is beneficial to the future development of the Mantle Network. At the same time, the integration of token economics has also consolidated ecological resources, providing strong guarantees for further project development.
2.2.3. Core Members

Arjun Kalsy: Head of the Mantle Network ecosystem, responsible for project marketing and ecosystem construction. He is a successful blockchain entrepreneur and advisor, formerly the Vice President of Growth at Polygon, responsible for the platform’s business development and ecosystem expansion. He has also been involved in major corporate collaborations such as Reddit, Instagram, and Disney. Prior to this, he was a customer relations manager at Playment, where he helped clients train high-precision AI/ML computer vision models, with a focus on applications in autonomous driving and transportation.

Joshua Lapidus: Strategic advisor for Mantle Network, responsible for assisting in the development and expansion of Mantle Network, as well as collaboration and interaction with other Web3 ecosystems. He is currently the host of Unemployable, a podcast for freelancers, independent workers, and self-employed individuals. He also serves as a writer for BanklessDAO and is the founder of three successful NFT projects: Rainbow Rolls for NFTP, BufficornBUIDLBrigade for ETHDenver, and Public Nouns (a project that forked from NounsDAO and is dedicated to providing funding for public goods through creative means).

Pranjal Bhardwaj: One of the co-founders of the Mantle Network project. Pranjal has worked in the crypto field for many years, previously serving as a senior development engineer at Polygon and later joining BitDAO. At BitDAO, Pranjal is responsible for the development team and has participated in multiple projects incubated by BitDAO, including Mantle Network. In the Mantle Network project, Pranjal Bhardwaj serves as the technical lead, responsible for the design of underlying technologies such as blockchain and smart contracts. He is a key member of the Mantle Network technical team and has played an important role in the project’s technical architecture design.
Sreeram: Co-founder and Chief Technology Officer of Mantle Network, as well as co-founder and Chief Technology Officer of EigenLayer. Sreeram is an experienced software engineer and architect who has worked on projects in distributed systems, big data, machine learning, and other areas at companies such as Dow Jones and Cooper Midroni. He is the main designer and developer of Mantle DA, focusing on providing efficient and secure data availability layers.
Other members: The Mantle Network team also includes other outstanding engineers, designers, operations personnel, and marketing personnel, who are responsible for different aspects of Mantle Network, such as network development, contract writing, interface design, community management, and brand promotion. Together, they constitute the core strength of Mantle Network and have made contributions to its development and growth.
2.3. Financing Situation
As a project incubated by BitDAO, Mantle did not undergo independent public financing. Initially, Mantle was funded by Bybit, but after the approval of BIP-19, funding was provided by the Mantle budget managed by BitDAO. According to the Mantle core budget address provided by BitDAO, the current funding is over $18 million.
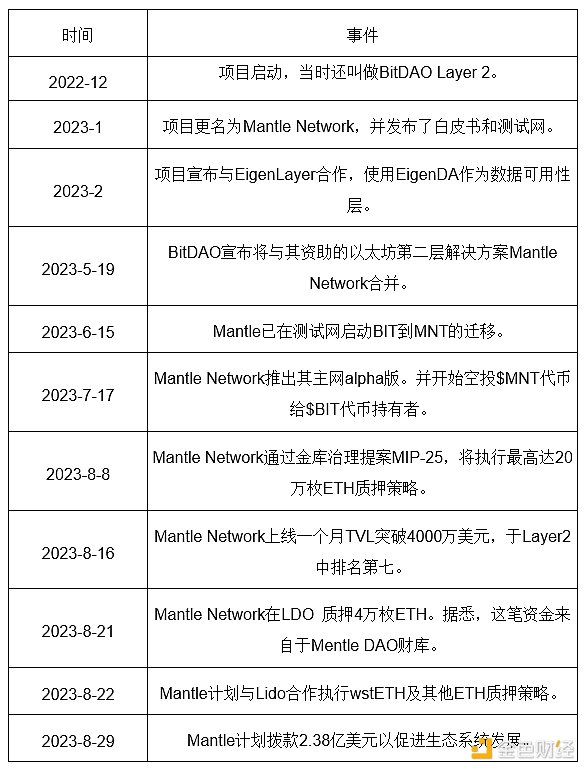
2.4. Past Development and Roadmap
2.4.1. Past Development
2.4.2. Current Progress
According to information from its official website and forum, Mantle Network is currently undergoing or planning the following major work:
▪ Improving and optimizing the technical architecture and functionality of Mantle Network, including EigenDA, MPC, and decentralized sorters.
▪ Promoting the ecosystem development and partnership of Mantle Network, including integration and support with Ethereum protocol, cross-chain bridges, DeFi applications, and GameFi applications.
▪ Launching and operating Mantle Network’s proprietary products and services, including LSD (Liquidity Staking Derivatives), EduDAO, Game7, etc.
▪ Establishing and managing the ecosystem fund and treasury of Mantle Network, including providing funding, resources, and incentives for ecosystem projects and developers.
▪ Enhancing and expanding the community and brand of Mantle Network, including organizing various activities and competitions, releasing various promotional and educational materials, and establishing various social media and communication channels.
2.4.3. Development Plan and Roadmap
According to the information on the project’s official website, the future development plan and roadmap of Mantle Network are as follows:
▪ September 2023: Mainnet beta version goes live, providing a more stable and reliable network service, and supporting more DApps and protocols.
▪ October 2023: Launch EigenLayer data availability layer and inherit Ethereum’s security and decentralization through re-collateralizing ETH.
▪ November 2023: Introduce multi-party computation functionality and use threshold signature scheme (TSS) technology to improve the correctness and privacy of off-chain transactions.
▪ December 2023: Introduce decentralized sequencer functionality and provide secure and trustless block production through a rotating permissionless sequencer set.
▪ January 2024: Introduce cross-chain bridging functionality and achieve interoperability with other L2 projects and public chains.
▪ February 2024: Introduce NFT marketplace functionality and support users to create, trade, and showcase NFTs on Mantle.
▪ March 2024: Introduce DAO functionality and allow users to participate in Mantle’s governance and decision-making through the $MNT token.
3. Project Analysis
3.1. Project Background
The emergence of Mantle Network is mainly based on the following two aspects:
1) Market Trends Background
Mantle Network was born in the context of the rapid development of Ethereum L2 and increasing global regulatory scrutiny. With the rise of DEXs, the trend of cryptocurrency trading shifting from CEXs to DEXs is evident. However, the high gas fees and low efficiency of Ethereum L1 have limited the development of DEXs and DeFi. Therefore, L2 scalability solutions have become the key to addressing this pain point. The Ethereum upgrade planned for November 2023 will significantly reduce the storage costs of L2, further promoting innovation and competition in the L2 space.
In addition, the wave of compliance has ushered in an efficient era of Layer 2. As regulatory authorities tighten control over the use of cryptocurrencies, compliance has become an important issue in the blockchain industry. This has led many Layer 2 projects to adopt a model without token issuance, profiting through gas fees and MEV revenue. The mainstream Arbitrum and Optimism currently adopt a centralized sequencer architecture. This efficient setup allows them to enjoy the benefits brought by Layer 2 while better addressing regulatory requirements. It can be foreseen that under the trend of compliance, lightweight Layer 2 networks will unfold more rapidly, forming scalable applications, which is almost a certain future for the development of Layer 2. As a new generation Layer 2 network, Mantle is also affected by changes in the regulatory environment. Adapting to compliance will be the external situation that Mantle needs to pay attention to, and together with other Layer 2 projects, it will promote the arrival of the Layer 2 era.
2) Technical Background
In the L2 rollup technology camp, Optimistic Proof (OP) and ZK zero-knowledge proof each have their advantages and challenges in terms of storage and computational costs. In addition, existing solutions mostly use a centralized sequencer, which can easily lead to single point of failure. As an Optimistic Rollup solution, Mantle’s key innovation lies in its modular network architecture design. Mantle can decouple and optimize different components such as transaction execution, data storage, and confirmation processes. This modular approach can improve network throughput and scalability without compromising security. It also enables Mantle to achieve more economically efficient contract development and deployment. Furthermore, to address the centralization issue of sequencers, Mantle Network plans to decentralize sequencers in the future, allowing community participation in the operation and governance of sequencers to enhance the network’s decentralization and resistance to attacks.
In addition, the current challenge period for OP Fraud Proof is 7 days, which means users need to wait for 7 days to extract assets from L2 to L1. This has a certain impact on user experience and liquidity. In order to solve this problem, Mantle Network plans to shorten the challenge period to 1 to 2 days by implementing Multi-Party Computation (MPC).
3.2. Project Principles
The core principle of Mantle Network is to use Optimistic Rollup to achieve L2 scaling solutions. Optimistic Rollup is a technology that uses fraud proofs to ensure the security and synchronization between L2 and L1 networks. The basic principle of Optimistic Rollup technology is as follows:
1) Deploy a fraud proof contract on the L1 network to receive block hashes from the L2 network and provide a mechanism for challenge and proof.
2) Run an execution layer on the L2 network to execute transaction requests initiated by users on the L2 network and update the state of the L2 network according to state transition rules.
3) Select a sequencer on the L2 network responsible for collecting user transaction requests, packing them into blocks in a certain order, and submitting the block hashes to the fraud proof contract.
4) Run multiple validators on the L2 network responsible for monitoring the block hashes on the fraud proof contract, replaying transactions in the blocks according to state transition rules, and verifying their correctness.
5) If validators discover errors or fraudulent transactions in the blocks submitted by the sequencer, they can initiate a challenge to the fraud proof contract and provide corresponding evidence. If the challenge is successful, the sequencer will be punished and the erroneous or fraudulent transactions will be rolled back. If no one challenges the blocks submitted by the sequencer within a certain period of time, or if the challenge fails, the blocks will be considered valid and the transactions in them will be finalized.
Next, let’s compare the network architecture of Mantle Network:
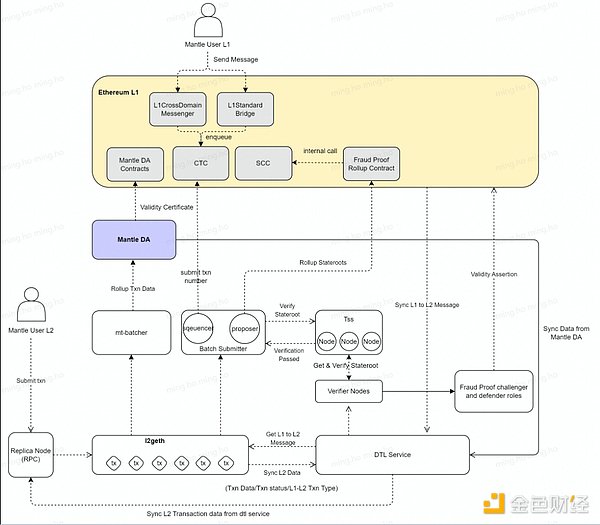
Image Source: Mantle Network Official Website DOC
According to the network architecture of Mantle Network, let’s briefly explain how its system works:
1) When a user initiates a transaction or executes a contract on the L2 network, the transaction request is sent to the sequencer, which sorts the transaction requests according to certain rules and packs them into blocks.
2) Each block has a unique identifier called a state root, which represents the L2 network state after the block is executed. The latest state root is submitted to Multi-Party Computation (MPC) nodes for verification. The MPC nodes use Threshold Signature (TTS) algorithm to sign the state root to confirm its correctness. After the state root receives the MPC signature, it is submitted to the Fraud Proof Contract (SCC) on Ethereum L1 for storage, which is used for future state verification and withdrawal operations.
3) When a user wants to extract assets from the L2 network to the L1 network, they need to wait for a certain period of time called the fraud proof window period. This is to prevent the sequencer or others from cheating or submitting incorrect transactions on the L2 network. If someone discovers an incorrect transaction, they can initiate a challenge to the SCC contract during the window period and provide evidence. If the challenge is successful, the cheater will be punished and the incorrect transaction will be revoked.
4) In addition to the state root, each block also contains the specific data of transactions, called CallData. While the state root is being verified, CallData is compressed and submitted to a data layer on the L1 network called Mantle DA, which is used to store transaction data on the L2 network. The data availability nodes of Mantle DA will sign the transaction data and put the signature certificate on the chain.
5) Other nodes can obtain transaction data from Mantle DA through the DTL service and perform verification and confirmation, which can enhance the security and reliability of the L2 network.
6) If a user wants to transfer assets from the L1 network to the L2 network, they need to use the enqueue method of the CTC (deposit contract) to complete this process. This method places the user’s assets in a queue and then the sorter transfers them to the L2 network.
7) When a user wants to transfer from L2 to L1, it needs to be verified and executed by L1 through a message mechanism.
The Mantle system also has other contracts and roles for different functions, such as verifying states, managing permissions, and upgrading the system. Moreover, its key operational roles are controlled by multi-signature wallets to prevent single-point failures or malicious operations.
By comparing the operation principles of OP Rollup and Mantle, we can see that Mantle has made a series of innovations and optimizations based on OP Rollup technology, including:
1) Modular design significantly reduces transaction costs
Mantle adopts a modular network design, combining Optimistic Rollup with an independent data availability layer, which avoids the high cost of submitting all transaction data to Ethereum’s Calldata. (As transaction volume increases, this cost can account for 80-95% of the total cost, severely limiting the cost efficiency of Rollups.)
Mantle’s modular design separates the four key functions of blockchain and processes them at different levels, instead of completing them on a single network layer like most single-blockchain networks. These four functions are:
▪ Transaction execution: conducted on Mantle’s compatible EVM execution and settlement layer. The sorter of Mantle generates blocks on the L2 execution layer and submits the state root data to the main blockchain.
▪ Consensus and settlement: handled by the Ethereum L1 network.
▪ Data availability: assisted by EigenDA technology. EigenDA is a data availability layer built on EigenLayer, used to store callback data that is usually broadcasted to L1.
▪ Data retrieval: other nodes obtain transaction data from Mantle DA through the DTL service and perform verification and confirmation.
The following diagram shows an example of the modular chain design.
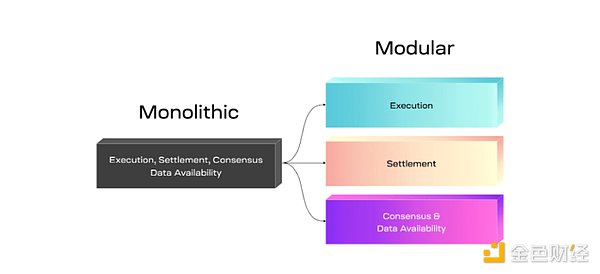
Image source: Modular Chain Design: Celestia Docs
The modular design also makes it easier for Mantle Network to adopt new technologies, such as replacing the consensus mechanism with zk-Rollup or zkEVM. At the same time, compared to the base layer, the modular architecture of Mantle significantly reduces transaction costs and improves network efficiency due to its layered advantages. Additionally, through Optimistic Rollup, it also reduces the overall load on nodes.
2) EigenLayer achieves high-performance data availability
Mantle uses EigenLayer as a decentralized data availability layer solution. EigenLayer allows Ethereum validation nodes to participate in data availability guarantee by re-collateralizing ETH. The Mantle data availability layer is a data layer supported by EigenDA, which can store and transfer transaction data on the Mantle execution layer. This allows Mantle to inherit the security of Ethereum without needing to publish all data to L1. At the same time, EigenLayer provides high throughput of 1TB per second. Compared to other L2 networks that rely solely on centralized storage, this technical design significantly enhances Mantle’s data availability and censorship resistance.
EigenLayer provides Mantle with highly secure and high-performance data availability support, which is one of the key technological innovations of the Mantle network. This also gives Mantle a clear competitive advantage in scalability and decentralization.
3) Multi-party computation shortens fraud proof time
Mantle network uses multi-party computation (MPC) protocol, which is a key technological innovation to accelerate fraud proof and improve transaction speed. The validation node network of Mantle adopts threshold signature scheme (TSS) based multi-party computation mechanism, which allows a group of validation nodes to quickly reach consensus on transactions on Layer 2, generate state root information with multi-signatures, and then submit them to Ethereum. Compared to directly submitting transaction batches to Ethereum, this multi-party pre-validation method can greatly reduce the need for fraud proofs and shorten the proof time to 1-2 days. Although multi-party computation is not as reliable as zero-knowledge proofs, with the setting of node staking and punishment mechanism, it can ensure a certain level of security while balancing costs. Overall, Mantle’s multi-party computation protocol mechanism helps achieve a better balance between transaction speed and security, and is one of the key innovations for achieving high throughput and low latency.
4) Decentralized sorter eliminates centralization risks
Decentralizing the sorter provides secure and trustless block production. The sorter is a role in the L2 solution that is responsible for collecting transactions, computing states, and generating blocks, and is crucial for the security of the network. In traditional Rollup solutions, the sorter is usually a single centralized node, which is susceptible to failures, manipulations, or censorship. Mantle replaces the centralized sorter with a permissionless sorter cluster, bringing the following benefits:
▪ Improves the network’s availability by eliminating the risk of single point failures and ensuring continuous operation of the network.
▪ Enhances the consensus reliability of the network, preventing manipulation or censorship of the sorter, and ensuring fair and transparent transactions.
▪ Improves the incentive compatibility of the network by driving compliant behavior of the sorter through reward mechanisms, ensuring the long-term sustainability of the network. In contrast, centralized sorters face the tragedy of the commons.
▪ The decentralized sorter itself improves resistance against attacks, and its trustless consensus enhances security. This is also an important step towards full decentralization.
In summary, the decentralized sequencer is one of the obvious advantages of Mantle over traditional Rollup. It eliminates centralized risks and provides a more efficient, reliable, and secure block generation. This makes the Mantle network more robust and better protects user rights.

3.3. Project Network Nodes
Mantle Network currently defines four types of node roles: sequencer nodes, threshold signature scheme (TSS) nodes, Rollup verification/replica nodes, and data availability (DA) nodes. They each have different responsibilities:
1) Sequencer Nodes:
The sequencer is responsible for receiving and recording transactions sent by users on the L2 network, and packaging the transactions into blocks. The sequencer is also responsible for performing Rollup on the transactions in the block, generating batches containing execution state roots, and submitting the batches to the L1 network. The sequencer also needs to broadcast block data to the entire network (L1 and L2). In the initial stage of the Mantle Network, the sequencer is operated by the Mantle core team and is a centralized node. However, in the development roadmap of the Mantle Network, the sequencer will gradually become decentralized, providing opportunities for other nodes to participate.
2) Threshold Signature Scheme (TSS) Nodes:
TSS nodes are responsible for “signing” the batches generated by the sequencer in order to send them to the L1 network. TSS nodes need to verify the state root generated by the sequencer to ensure its correctness. The state root must be signed by TSS nodes before it can be recorded on Ethereum. In the initial stage of the Mantle Network, TSS nodes are operated by a group of reputable institutions, but eventually, they will be elected through the governance mechanism of the Mantle Network without permission.
3) Rollup Verifier/Replica Nodes:
Rollup verifier/replica nodes are responsible for synchronizing Rollup data from the trusted sequencer on the Mantle Network and verifying the state roots submitted on the L2 network. If the verifier/replica nodes discover invalid state data, they can initiate fraud proofs to revoke incorrect transactions. The verifier/replica nodes are also responsible for providing Rollup data to users.
4) Data Availability (DA) Nodes:
DA nodes are responsible for storing and transmitting transaction data on the Mantle Network and providing data availability services. DA nodes use EigenLayer as the data availability layer, which is a protocol based on ETH re-collateralization that ensures the security and efficiency of the Mantle data availability layer. DA nodes do not need to publish data to the L1 network, but instead publish it to EigenDA secured by re-collateralized ETH. This greatly improves throughput and scalability, and allows for the development of new types of DApps.
3.4. Project Ecosystem
The Mantle Network ecosystem is mainly reflected in ecosystem incentives, ecosystem applications, and its planning in the LSD field.
1) Ecosystem Incentives
Mantle has a strong ecosystem, including over $2 billion in funds, including the BitDAO Treasury, and a large user base, which lays a solid foundation for the development of the Mantle ecosystem. At the same time, according to the latest news on August 28th, the Mantle Network governance page shows that the Mantle community has recently initiated a proposal to use the Mantle Treasury to promote ecosystem development, planning to allocate $238 million to promote ecosystem development, including providing up to $160 million in liquidity support for applications, providing up to $60 million in seed liquidity for RWA-backed stablecoins, and providing up to approximately $18 million in liquidity support for third-party cross-chain bridges.
At the same time, the special relationship between Mantle Network and Bybit will effectively promote high-quality projects within the Mantle ecosystem to gain a wider user base and liquidity. Bybit, as one of the world’s entry-level cryptocurrency trading platforms, has a large user base. Excellent projects in the Mantle ecosystem have the opportunity to be discovered by more investors through Bybit’s recommendations and listed for trading on the platform. Obtaining higher liquidity and wider investor recognition will benefit their long-term development, and a prosperous ecosystem will further enhance the value of the Mantle network. It can be foreseen that projects and assets in the Mantle ecosystem will greatly benefit from Bybit’s traffic and resource advantages. This win-win situation will continue to attract more high-quality projects to join Mantle.
These measures indicate that Mantle Network will rely on its strong treasury resources to strongly support the prosperity and development of the ecosystem. Through liquidity incentives and ecological funds, Mantle will attract more high-quality applications to join its network and promote a virtuous cycle.
2) Ecological Applications
Mantle Network has built a rich ecosystem, currently quoting 119 projects on its ecosystem page, a few of which are still in the testnet stage. In terms of subdivision of tracks, project parties and developers mainly focus on three categories: 38 DeFi projects, 27 infrastructure projects, and 25 GameFi projects, with the rest being other categories such as social, entertainment, and tools. Here are some representative projects in the Mantle Network ecosystem:

A. DEFI Track
iZUMi Finance
iZUMi Finance is a multi-chain DeFi protocol that provides one-stop liquidity services (LaaS). Its concept is that every token should obtain better on-chain liquidity in an efficient and sustainable manner.
UMi currently offers three on-chain liquidity products: LiquidBox, iZiSwap, and iUSD.
iUSD is a USD-denominated convertible bond launched by iZUMi, which uses transparent on-chain funds managed by smart contracts and multi-signature wallets as excess collateral to support the value of iUSD.
FusionX
FusionX is a decentralized trading protocol that aims to provide secure and reliable trading services for the Mantle Network. The project was launched by a senior blockchain team in 2022 and is one of the early projects to join the Mantle ecosystem. FusionX adopts the AMM model, allowing users to participate in liquidity mining, trading, borrowing, and other operations. It supports multiple trading pairs, including ETH/WETH, MATIC, and other ERC20 tokens, providing liquidity for users. The project’s feature is an efficient on-chain order book system that ensures the immediacy of transactions.
Symbiosis
Symbiosis is a cross-chain AMM DEX that aggregates liquidity from different networks, including L1 and L2, EVM and non-EVM. With Symbiosis, users can easily exchange any tokens between different networks. Symbiosis issues the algorithmic stablecoin mUSD, collateralized by Mantle ecosystem assets, which can be exchanged for other assets in the Mantle ecosystem. The dynamic interest rate mechanism is used between mUSD and Mantle ecosystem assets to stabilize the price of mUSD.
B. Infrastructure
EigenLayer
EigenLayer is an Ethereum-based protocol that introduces a new cryptographic economic security primitive called restaking. Restaking allows ETH stakers in the consensus layer to choose and validate new software modules built on top of the Ethereum ecosystem, thereby extending cryptographic economic security. WJB has an in-depth research report on EigenLayer, interested readers can refer to it. The link is as follows:
https://www.panewslab.com/zh/articledetails/5402965u1dvj.html
Pyth Network
Pyth Network is an oracle on the blockchain that publishes financial market data to multiple blockchains in a high-precision and low-latency manner. Pyth Network’s data comes from over 80 primary data providers, including some of the world’s largest exchanges and market makers such as Jane Street, CBOE, Binance, OKX, and Bybit. It provides price data for various asset classes such as US stocks, commodities, and cryptocurrencies. Each price data is aggregated from multiple data providers and can be updated multiple times per second.
Biconomy
Biconomy is an open decentralized blockchain bridging platform, with the following main functions:
Cross-chain asset transfer: Supports secure and efficient transfer of digital assets between different public chains, such as ETH, BTC, etc.
DApp interoperability: Allows DApps to access resources on other multi-chains, such as contracts, data, accounts, etc., to achieve true cross-chain interoperability.
Contract development: Provides a contract library for cross-chain interactions, allowing developers to easily add cross-chain capabilities to their DApps.
C. Gamefi

Roboworld
Roboworld is a free card game where players can collect unique robots and trade them as NFTs, using them to battle opponents. Players must strategically choose and use robot-themed cards to outsmart their opponents and achieve victory.
Chesslers
Chesslers is a Web3-based gaming platform that allows users to play chess and earn rewards. Based on their staking protocol, Chesslers enables Web3 economic models on existing Web2 games. Users can bet and play high-quality skill-based games with real currency or Chesslers tokens.
Age of Zalmoxis
Age of Zalmoxis is a game that combines historical authenticity, captivating stories, and mythological elements inspired by the legendary Dacia Kingdom (modern-day Romania). It is a third-person massive multiplayer online role-playing game (MMORPG) with NFT and GameFi mechanisms. It is based on the historical background of the ancient Dacia Kingdom, which successfully resisted the invasion of the Roman Empire until it was eventually conquered by Emperor Trajan in two bloody wars.
Regarding the Mantle Network blockchain gaming ecosystem, it is worth mentioning that Mantle, as a high-performance Layer 2 network, can provide necessary high throughput and low gas fees for blockchain games, which is crucial for achieving the vision of interconnected blockchain games. Mantle inherits rich gaming ecosystem resources from BitDAO, including projects like Game7 and HyperPlay, which lay the foundation for attracting game users and developers to Mantle. Game7 provides valuable tools and resources for blockchain game developers, such as the web3.unreal plugin, which helps developers build blockchain games more conveniently. HyperPlay, as a blockchain game store and asset interoperability platform, also helps facilitate seamless in-game asset circulation. The Mantle ecosystem has already gathered a large number of gaming projects and is rapidly growing, demonstrating its immense potential in the gaming field.
We can see that Mantle provides strong support for blockchain games in both technology and ecosystem aspects, and is expected to drive the scalability of blockchain games.
Overall, the Mantle Network ecosystem has obvious advantages and disadvantages.
Specifically, the advantages are:
▪ The total number of Mantle ecosystem projects has reached 100+, comparable to other leading L2 networks.
▪ The projects cover multiple domains, such as gaming, DeFi, and infrastructure, and the ecosystem continues to grow with new additions.
▪ There are some unique application scenarios, such as direct computation.
▪ The ecosystem has strong asset support and a series of incentive programs.
▪ It offers a good user experience, especially suitable for the development of blockchain gaming ecosystems.
The main disadvantages are:
▪ Compared to other L2 networks, Mantle has a shorter development time and the ecosystem construction is still relatively early-stage.
▪ Mainstream protocols like DApps on Ethereum have not officially integrated with the Mantle ecosystem yet.
▪ The team background and funding scale are not as prominent as some L2 pioneers.
▪ Except for DeFi applications, the number of applications in other domains is relatively limited.
▪ The user base and TVL scale need to be improved.
In general, the number of projects in the Mantle ecosystem has reached a certain scale, but it is still in the early stages, and the concentration of mainstream resources needs further observation.
3) Mantle Network’s Plans in the LSD Field
From the official website planning and network architecture of Mantle Network, it can be understood that the LSD ecosystem of Mantle Network is about to go live and occupies an important position in its network architecture.

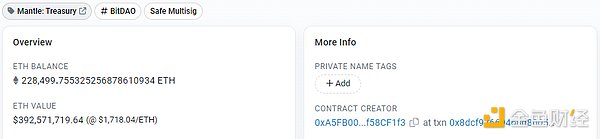
From the Mantle Treasury, it can be known that Mantle has a reserve of over 220,000 ETH, which serves as its financial strength in the LSD field. The network is expected to carry out strategic cooperation with major top LSD protocols to jointly promote the research and application of LSD solutions based on the Mantle network. Specifically:
A. Release Mantle LSD
Mantle plans to release a decentralized protocol called Mantle LSD for liquidity ETH deposits, which will be based on the Ethereum mainnet. Users can deposit ETH into the protocol to obtain equivalent mntETH tokens and earn staking rewards. This model can leverage the advantages of the Mantle ecosystem, including its large-scale initial deposit scale and liquidity, as well as the diversified use cases of mntETH in the Mantle network.
B. Innovative use of mntETH
mntETH can be directly used within the Mantle network, which will greatly enhance the use cases of mntETH and strengthen its stickiness in the Mantle ecosystem. The operational mode of Mantle LSD can maximize the utilization of resources such as the established community, governance structure, and brand influence of Mantle, thereby reducing operating costs and risks.
C. Efficient overall governance
Mantle LSD will operate under the overall governance framework of Mantle, ensuring its long-term competitiveness and sustainability. At the same time, the simple system architecture of Mantle LSD will reduce complexity risks and make it easy to be accessed and compatible with other applications and ecosystems.
D. Strategic cooperation and DAO construction
In addition to the issuance of mntETH, Mantle will also establish strategic partnerships with multiple top DeFi protocols to form a strong ecological force and jointly promote the research and application of LSD solutions based on the Mantle network. For example, Mantle has reached a cooperation with Lido Finance to establish the stETH ecosystem on the Mantle network. Mantle is also considering partnerships with Pendle, StakeWise, and other protocols, which can not only generate synergistic network effects but also optimize capital utilization efficiency. In addition, Mantle is also exploring revenue schemes such as direct staking and proposing to establish an Economic Committee as a sub-DAO to improve asset management efficiency.
From these aspects, we can see that Mantle’s planning in the LSD field is systematic, innovative, and efficient. It not only enriches Mantle’s DeFi ecosystem but also brings more unique user stickiness and value capture capability to the Mantle network. Compared to other L2 solutions, Mantle has significant advantages in this regard, which will strongly promote the rapid growth and cross-chain interoperability of the Mantle network.
3.5. Project Data
3.6.1. Project-related Data
-
Token-related Data
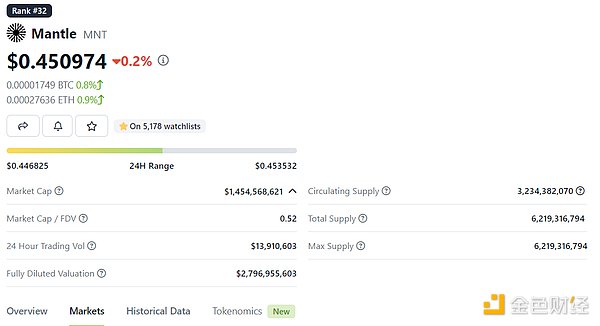
According to Coingecko data, the native token of Mantle Network is MNT. As of September 2, 2023, the price of MNT is $0.45, with a market capitalization of $1.454 billion, ranking 32nd among all cryptocurrencies. In terms of trading volume, MNT’s liquidity mainly comes from Bybit, a centralized exchange with strong financial strength, while its trading volume on other mainstream exchanges is not high. Currently, MNT has not been listed on major exchanges, which may affect its liquidity and exposure. In addition, according to on-chain data, there are currently approximately 163,406 MNT holding addresses.
Overall, the liquidity of the MNT token still heavily relies on Bybit exchange, while the value transmission channels in mainstream exchanges and the blockchain community need further expansion. The number of holding addresses also has room for growth. With the gradual enrichment of the ecosystem, the external liquidity and distribution of MNT are expected to become more balanced.
-
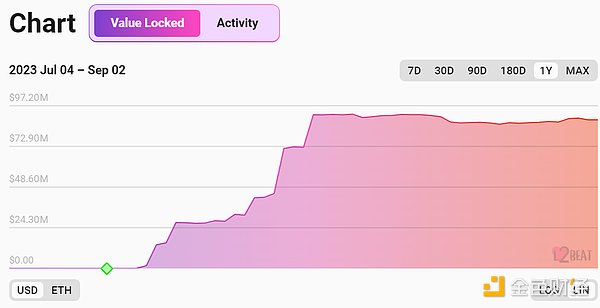
L2 Lock-up Data
According to L2Beat’s statistics, as of September 2, 2023, the total lock-up value of Mantle Network is approximately $88.79 million, ranking ninth among all Layer 2 networks, accounting for 0.94% of the total market share.
In terms of TVL scale, Mantle Network lags behind top projects in the current L2 field, such as Optimism and Arbitrum. This is mainly because Mantle Network is still in the early stage of its mainnet operation as an emerging L2 solution.
With the gradual enrichment of the Mantle ecosystem and the expansion of its user base, its TVL scale is expected to continue to grow. Proper incentive mechanism design and user cultivation will also help Mantle Network further enhance its influence and competitiveness in the L2 field.
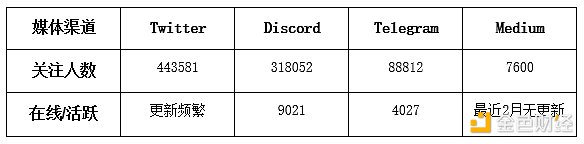
3.6.2. Social Media Data
As of September 2, 2023, Mantle Network has performed well on social media platforms, indicating high project popularity. The main channels currently operated by the project include Twitter, Discord, Telegram, and Medium. Currently, Mantle’s Discord account has attracted nearly 320,000 followers, with over 9,000 people online daily, making it one of the most popular channels. At the same time, there are frequent updates and interactions on Twitter. The specific data for each platform is as follows:
4. Token Economic Model Analysis
4.1.1. Token Model
The Mantle ecosystem and $MNT token are currently undergoing a governance approval process to determine key aspects, including token addresses, token design, and initial token allocation. This process involves key proposals and discussions, such as the BIP-21 merge proposal and the MIP-22 token design proposal.
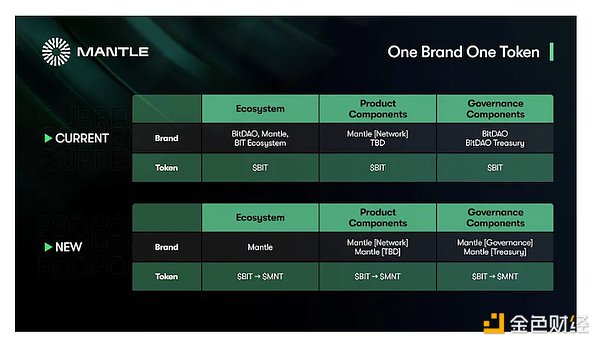
1) Key Points of BIP-21 Merger Proposal
▪ Proposed the principle of “one brand, one token” to merge the brands and tokens of BitDAO and Mantle into Mantle, in order to simplify the structure and dissemination of the ecosystem.
▪ Authorized a token conversion plan to convert all holders’ $BIT tokens into the new Mantle token at a fixed ratio, which will have more advanced design and functionality to support Mantle’s products and governance.
▪ Simplified the tokenomics model and accelerated the contribution of all BIP-20 and the lock-up plan of BitDAO issuance, making the circulation supply of Mantle tokens more transparent and predictable.
▪ Retained the existing governance and resource management processes, Mantle token holders can still vote to determine the direction, budget, treasury, and other matters of the ecosystem.
▪ Does not affect the existing initiatives such as sub-DAO types, communities, and product categories, they can still autonomously decide their own brand, governance, mission, and strategy.
2) Key Points of MIP-22 Token Design Proposal
▪ Designed a new Mantle token, $MNT, which should have similar upgradability and minting functions as $ARB and $OP tokens to support Mantle’s products and governance.
▪ Established a token conversion plan to convert all holders’ $BIT tokens into $MNT tokens at a 1:1 ratio, providing multiple conversion channels and flexible conversion periods.
▪ Created a temporary conversion vault to support the token creation and conversion process, received $BIT tokens will be burned, and sent $MNT tokens will maintain a 1:1 ratio.
▪ Does not change the existing governance and resource management processes, $MNT token holders can still vote to determine the direction, budget, treasury, and other matters of the ecosystem.
▪ The Mantle core contributor team will be authorized to determine the best timing and order for delisting $BIT tokens, listing $MNT tokens, opening conversion channels, and launching the Mantle network mainnet.
4.1.2. Token Supply and Distribution
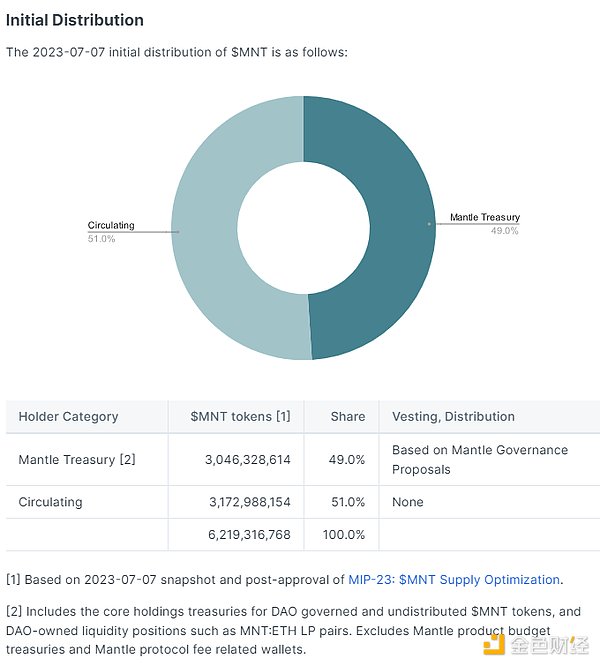
1) MNT Token Supply
MNT is the utility and governance token of the Mantle ecosystem. MNT holders can participate in important ecosystem decisions through voting, such as treasury management, protocol parameters, product direction, etc. To simplify the tokenomics model, MNT holders have passed the MIP-23 proposal to halve the number of MNT tokens in the treasury from 6.05 billion to 3.05 billion. At the same time, this proposal maintains the unchanged circulating supply of MNT at 3.17 billion and reduces the fully diluted supply from 9.2 billion to 6.2 billion. As a result, the proportion of tokens in the treasury decreases from the original 65.6% to 49%, and the proportion of circulating supply increases from the original 34.4% to 51%. This change aims to increase the demand and scarcity of MNT and enhance its value.
2) Token Economics of BIT
On July 15, 2021, the $BIT token was launched with a maximum supply of 10 billion tokens (no inflation), later changed to 6.2 billion.
After the approval of MIP-22, it will be converted to $MNT at a 1:1 ratio.

3) Token Distribution
The distribution of $MNT tokens in the Mantle Treasury needs to follow the governance process of Mantle. The budget, fundraising, and allocation processes all adhere to strict procedures, such as BIP-19 Mantle Network Budget. As of August 2023, there has been no formal discussion on macro goals or restrictions for the distribution of $MNT tokens. However, it is expected to have the following major categories:
▪ User incentives: Priority is given to promoting user adoption of Mantle products through various strategies such as implementing multi-season achievements, tasks, and other incentive programs. The target metrics for user adoption include daily active users, total transactions and protocol fees, total value locked (TVL), and other relevant product adoption metrics. These incentives are designed to attract and retain users of the Mantle ecosystem.
▪ Technical partner incentives: This category focuses on incentivizing decentralized applications, infrastructure service providers, and core protocol technology partners who contribute to the growth and development of the Mantle ecosystem. By providing incentives to these partners, Mantle aims to promote collaboration and partnerships within the ecosystem, enhancing overall ecosystem efficiency and scalability.
▪ Core contributors team and advisors: This category also needs to follow the same budget proposal process to ensure transparency and accountability in allocating resources to teams and advisors who have made positive contributions to the project’s success.
▪ Other opportunities: This category includes potential opportunities such as acquisitions, token swaps, treasury sales, and other transactions. Each opportunity will be evaluated based on specific circumstances, considering their potential benefits to the Mantle ecosystem and alignment with project goals.
▪ Burning: The MNT token includes a burning function, which allows the removal of MNT tokens from circulation and total supply analysis. The burning of MNT tokens from the treasury is determined through the Mantle governance process.
4.1.3. Token Value Capture
The value of MNT token comes from its utility and governance within the Mantle ecosystem.
1) As a utility token, MNT can be used to pay for gas fees in the Mantle network and as collateral for node operators, increasing the demand and scarcity of MNT, thereby enhancing its value. In the long run, when the Mantle ecosystem expands into the LSD track and even Restaking business, $MNT can also be used individually or paired with LP as collateral.
2) As a governance token, MNT gives holders the right to vote on decisions within the Mantle ecosystem. These decisions include treasury management, protocol parameters, product direction, etc. These features increase the influence and participation of MNT, thereby increasing its value.
4.1.4. Core Token Demand
1) Mantle users: They need to use MNT to pay GAS fees in the network and participate in network governance.
2) Mantle network node operators: Individuals or organizations that provide infrastructure support for the Mantle network, such as validators, storers, computators, etc. They need to use MNT to stake as nodes and receive network rewards and fee income.
3) Mantle ecosystem developers: Personnel who develop the ecosystem on Mantle, they need to use MNT to obtain ecosystem incentives and support, develop on-chain DApps, and as developer incentives, the demand for MNT will increase with developers.
4) Of course, the planned LSD platform will also use MNT as the main LP staking token.
5. Industry Space and Potential
5.1. Industry Overview
5.1.1. Project Categories
Mantle Network belongs to the category of Layer 2 scaling solutions, aiming to solve the congestion, high gas fees, and low transaction speeds of the Ethereum network. In detail, L2 scaling solutions typically involve technologies such as Optimistic Rollup, zk-Rollup, Plasma, State Channels, etc. Currently, the mainstream L2 scaling solutions are mainly Optimistic Rollup and zk-Rollup.
Mantle Network is an L2 solution based on Optimistic Rollup.
5.1.2. Market Size
The market size of L2 scaling solutions can be measured from the following dimensions:
1) Scale of the Ethereum network
The Ethereum network is currently the largest public chain platform, with over 1.6 million active addresses, over 62 million smart contracts, over 4,200 DApps, and a market value of nearly $200 billion. The Ethereum network is the foundation and target of L2 scaling solutions, and its scale and activity determine the demand and potential of L2 scaling solutions, providing a huge potential user demand for L2 scalability.
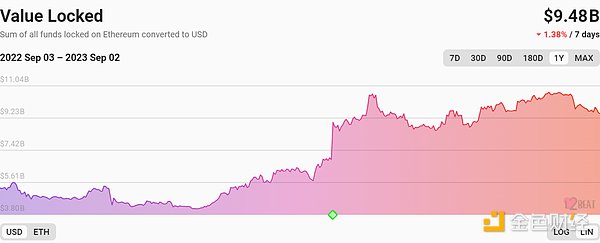
2) Scale of L2 scaling solutions
Currently, there are multiple L2 scaling solutions in operation or under development in the market, each adopting different technical approaches. According to data from L2Beat, as of September 2, 2023, the total value locked (TVL) of L2 scaling solutions has reached $9.48 billion, showing strong development momentum and user demand. Among them, Arbitrum is currently the most popular L2 scaling solution, accounting for 54.99% of the TVL, followed by Optimism with 25.21%, and zkSync with 4.3%. It is worth noting that in the past six months, despite the overall market downturn, the total TVL of L2 scaling solutions has almost doubled, indicating the advantages and potential of L2 scaling solutions in improving user experience and reducing transaction costs. This provides a market opportunity for projects like Mantle Network to develop.
5.1.3. Industry Development Background
L2 is a scaling solution built on top of the Ethereum L1, aiming to improve transaction speed and efficiency, reduce user costs and friction. The emergence of L2 is to solve existing problems and create value, rather than to compete with or replace L1. However, from a business perspective, L2 seems to be more profitable and has better development prospects.
1) From a business model perspective
L2 can provide equivalent functionality to the Ethereum mainnet, but with lower gas fees and faster transactions, which can attract dApps and users to join and increase on-chain transactions, generating revenue. L2 only needs to pay gas fees to periodically package transactions to L1, and can earn the difference between income and expenses. Its business model has significant advantages.
At the same time, the R&D and operational costs of L2 are also lower. It can reuse existing solutions such as Optimistic Rollup, eliminating the need for independent research and development of consensus mechanisms, and lowering the barrier to launching an L2 network.
In contrast, building a competitive L1 requires a huge investment of time and resources.
① First, it is necessary to develop a consensus mechanism that the market can accept, which requires a lot of research and development resources, time, and accumulation;
② Second, it is necessary to attract enough nodes to participate in the network to ensure security and decentralization;
③ Finally, it is necessary to build differentiated narratives, such as emphasizing privacy or security.
Meanwhile, in a bear market environment, it is more difficult to raise funds from VC and gain acceptance from retail investors. Launching a new L1 from the primary market to the secondary market will inevitably encounter difficulties. Instead of starting from scratch to build a distinctive public chain, which requires large investments and has slow effects, it is better to parasitize on Ethereum’s L2, which requires smaller investments and has relatively fast effects.
2) From a traffic perspective
More importantly, there is the “traffic business”, which refers to where users come from. L2 can start from its own product ecosystem or the existing user base in the Ethereum ecosystem, and expand to more fields through product integration, user migration, and cooperation scenarios. The participation of centralized exchanges or large wallets in L2 can bring natural user traffic. However, regardless of the project and capital, most choose to start with their own product ecosystem or the existing user base in the Ethereum ecosystem, and then expand to more cooperation scenarios (such as Polygon’s actions in the Web2 field). In comparison, L1 needs to build a user base from scratch and face competition from hundreds of other public chains.
3) From an external competitive landscape perspective
The L1 track is already very crowded and fierce. According to data from DeFiLlama, there are currently nearly 200 public chains on the market, of which about 190 are L1, which means that the L1 market is experiencing excessive competition. Among these public chains, only a few can occupy user mindshare and market share. With recent black swan events and the withdrawal of capital, many once popular public chains have lost their shine in various indicators such as user activity, revenue composition, and transaction volume. Most L1 chains still exist as concepts, but they are not thriving. Choosing to enter such a dead sea is not a wise choice from a business perspective.
By comparison, the L2 track is relatively loose and favorable, with less competition pressure, lower market concentration, and diverse technical routes. Specifically, there are currently 26 L2s that L2Beat can count, with a competition intensity of about one-seventh of L1. The top two projects in terms of market share in the L2 market are Arbitrum and Optimism, with market shares of 55% and 25% respectively. The market shares of other L2 projects are relatively scattered, still providing opportunities to become leading projects. At the same time, L2 adopts various technical routes, including Optimistic Rollup, ZK-Rollup, etc., which provide users with more choices and also provide greater space for the development of L2.
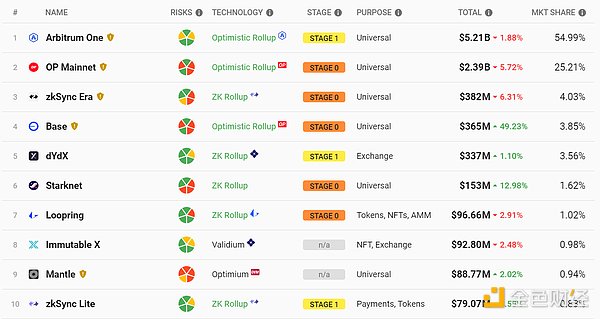
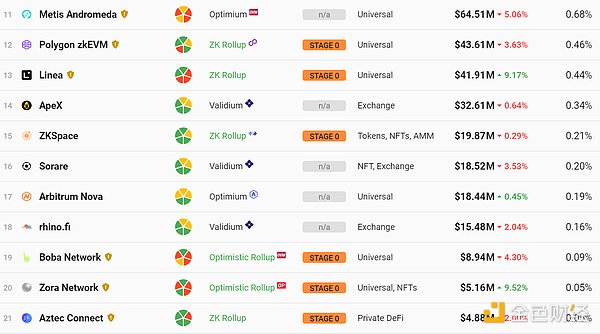
With the completion of Ethereum’s technical upgrades this year and subsequent upgrades, the narrative around performance will continue to exist for a long time, and L2s still have a considerable development window. At the same time, there are not many narratives and tracks that can sustain heat in a bear market. In the environment of attention and scarce capital, L2 also has the advantage of continuous attention. Therefore, from the perspective of competition pattern and external environment, it seems that doing L2 is also a profitable business.
5.2. Track Pattern
5.2.1. Competition Pattern
The current L2 market is in a fiercely competitive stage. With the approaching of the London upgrade, L2 networks have become the hottest narrative track in the second half of 2023. Since July, the TVL of L2 layer has often remained above $10 billion, and many well-known public chains have announced their shift to L2 or launched their own L2 projects and obtained financing support. At the same time, native L2 networks are also promoting technological innovation. According to the crypto data platform Rootdata, there are already 77 L2-related network infrastructures included. Currently, the L2 market is mainly dominated by the two mainstream expansion solutions, Optimistic Rollup and zkRollup.
1) Optimistic Rollup Series
Optimistic Rollup is the most mature technical route in the current L2 network, and its representative networks include Arbitrum, Optimism, Metis, Boba, and Mantle Network.
2) zkRollup Series
zkRollup is another potential technical route in the Layer 2 network, and its representative networks include zkSync, StarkNet, Polygon zkEVM, Linea, Scroll, and Taiko.
3) Simple Comparison
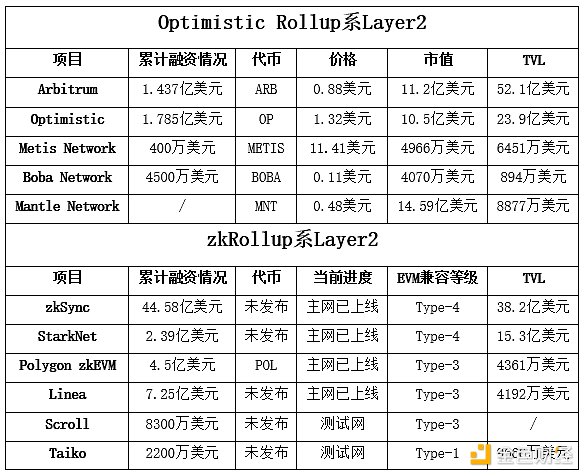
5.2.2. Competitive Projects
The Mantle Network project faces fierce competition from other L2 scaling solution projects, and the core competitive factors mainly include technical solution advantages, ecological prosperity, and user experience. Here are some of the main competing projects:
1) Arbitrum:
Arbitrum is a Layer 2 scaling solution built on Arbitrum Rollup (an improved version of Optimistic Rollup) technology, which went live on the mainnet in August 2021. Arbitrum has the highest total locked value among all L2 solutions, and it also has the most abundant ecosystem with 559 projects already integrated. The Arbitrum ecosystem currently consists of three subchains: Arbitrum One is the mainnet, Arbitrum Nova is for high-frequency applications, and Arbitrum Orbit is a toolkit for building L3 solutions.
Advantages of Arbitrum: Arbitrum has the largest ecosystem among major Layer 2 solutions, with over 550 projects. Arbitrum Rollup adopts a multi-round block production mechanism, which provides higher block production efficiency and lower gas fees compared to the single-round mechanism of Optimistic Rollup. Additionally, Arbitrum has its own Arbitrum virtual machine, which supports a wider range of programming languages.
Disadvantages of Arbitrum: Compared to Optimistic Rollup, Arbitrum has higher transaction confirmation latency. Furthermore, Arbitrum Nova uses the AnyTrust framework, which is less secure than Arbitrum One that directly leverages the security of Ethereum.
2) Optimism:
Optimism is an Ethereum Layer 2 scaling solution built on Optimistic Rollup technology, which went live on the mainnet in August 2021. The goal of Optimism is to provide a user experience identical to Ethereum while reducing transaction costs to a small fraction of Layer 1. Optimism currently ranks second in TVL among L2 scaling solutions.
Advantages of Optimism: Optimism introduced an open-source modular toolkit called OP Stack, which allows developers to assemble a custom Layer 2 network according to their specific needs. Many well-known blockchain projects have launched their own Layer 2 networks based on OP Stack, forming the Optimism super-chain kingdom, injecting richer application scenarios and network effects into the Optimism ecosystem. Additionally, Optimism has significantly reduced transaction costs and improved performance through optimizations such as the Bedrock upgrade. It now has one of the lowest gas fees among Ethereum Layer 2 solutions.
Disadvantages of Optimism: Compared to Arbitrum, Optimism’s on-chain ecosystem is slightly less prosperous. Its transaction speed is around 1000 TPS, which still has room for improvement compared to Rollup networks using zkRollup technology.
3) zkSync:
zkSync is a well-known zkRollup-based Layer 2 scaling solution, and its core network, zkSync Era, adopts zkEVM design. zkSync has a total locked value of $500 million, ranking third among all L2 solutions. zkSync is currently transitioning from zkSNARKs to zkSTARKs for proofs, which will improve the efficiency of the network. It has also launched a community airdrop program to incentivize users.
Advantages of zkSync: Recently, zkSync introduced the zkStack toolkit, which allows developers to build custom zkRollup-based L2 and L3 (also known as HyperChains). This helps expand the technical application scenarios of zkSync. Additionally, zkSync can utilize the compression feature of zero-knowledge proofs to pack more transactions into a single proof without waiting for a challenge period. This improves transaction throughput and speed while ensuring security and correctness.
Disadvantages of zkSync: The zkSync ecosystem is still relatively small and needs further expansion. Additionally, the recent airdrop incident reflects the need for strengthening community building efforts. Moreover, zkSync has a high level of technical complexity, requiring developers to have a certain level of technical foundation to build applications on the ZkSync network.
4) Starknet
StarkNet is a zkRollup-based scaling network developed by StarkWare and launched its mainnet in November 2021. StarkNet is currently the second-ranked zkRollup network in terms of TVL.
Advantages of StarkNet: StarkNet is gradually achieving compatibility with Ethereum’s EVM through projects like kakarot and Warp. This is currently the main focus of StarkNet’s development. Additionally, StarkNet will also support developers in building application chains, expanding its use cases.
Disadvantages of StarkNet: Due to its current lack of EVM compatibility, the ecosystem prosperity of StarkNet is relatively weak. Furthermore, StarkNet has a high level of technical complexity, requiring developers to have a certain level of technical foundation to build applications on the StarkNet network, resulting in a less developer-friendly environment.
5) Polygon EVM
Polygon is a blockchain dedicated to enhancing Ethereum scalability, achieving this goal through various solutions. Their flagship product is the Polygon PoS sidechain, which currently processes 300,000-400,000 addresses and 2-3 million transactions per day.
Advantages of Polygon EVM: Polygon not only provides its own Layer 2 networks, Polygon PoS and Polygon zkEVM, but also offers modular open-source components called Supernets for building custom Layer 2 and Layer 3 networks, enriching Polygon’s technical roadmap. Additionally, the recent release of Polygon 2.0 further unifies different networks, updates the native token code to POL, and introduces a new governance framework, forming a multi-chain interoperable ecosystem, enhancing Polygon’s network effects. Furthermore, Polygon has partnered with multiple Web2 companies, resulting in a large user base, and its ecosystem projects are steadily growing.
Disadvantages of Polygon EVM: The Polygon ecosystem is primarily focused on its own sidechains and subchains, limiting its interoperability with the Ethereum mainnet. There is also room for improvement in its governance mechanism.
Overall, compared to other L2 networks, Mantle Network’s advantages mainly lie in its modular design, strong support from BitDAO, focus on data availability, and efforts to enhance user experience, making it promising in the gaming sector. Its disadvantages mainly stem from being a newcomer in the L2 field, with core technologies like modular architecture requiring practical validation, an early stage of ecosystem development, and a lack of established DApps, resulting in uncertainty regarding long-term competitiveness.
6. Preliminary Valuation
6.1. Core Question
Which stage of the business cycle is the project in? Is it in the mature stage or the early to mid-stage of development?
Mantle Network is currently in the early to mid-stage of development. It is a newly established project founded in 2021 and has yet to form a complete and mature ecosystem. The mainnet is scheduled to launch in July 2023 and will require more testing and optimization to improve its stability and reliability. Although it has some high-quality partners and applications, such as EigenLayer and Biconomy, its user base and market share are still relatively low. It needs to attract more developers and users to join its platform in order to increase its influence and competitiveness.
Does the project have a reliable competitive advantage? Where does this competitive advantage come from?
Mantle has some potential differentiating advantages, such as modular architecture, and with community support, it is expected to stand out in the competition. However, overall, these advantages still need to go through product iterations and application validations, and face strong competitors. They have not formed very obvious competitive barriers yet, and the operational effectiveness after the mainnet launch still needs to be observed.
What are the main variable factors in the project’s operations? Are these factors easy to quantify and measure?
Technological progress: The Mantle Network project needs to continuously develop and improve its technical solutions to enhance network performance and security, and fix any potential vulnerabilities or defects. Technological progress can be quantified and measured through update logs, code commits, test results, etc. released by the project team.
Ecosystem development: The Mantle Network project needs to constantly expand its ecosystem partners and application scenarios to attract more users and funds to enter the L2 network, and provide more diverse and high-yield on-chain activities. Ecosystem development can be quantified and measured through metrics such as the number of DApps, TVL, trading volume, and number of users.
Community engagement: The Mantle Network project needs to continuously incentivize and reward its community members and partners to enhance community cohesion and influence, and provide support and feedback for project governance and decision-making. Community engagement can be quantified and measured through metrics such as social media followers, community members, voting participation rate, and number of proposals.
What is the project’s management and governance approach?
Mantle adopts a relatively flexible off-chain governance mechanism. Specifically, governance issues and proposals are first raised and discussed by the Mantle core team or community members in the forum. If a proposal receives enough attention and support, it forms a formal MIP (Mantle Improvement Proposal), which is voted on-chain by MNT token holders. Once a MIP proposal is approved, the core development team and contributors of Mantle are responsible for executing and monitoring the project progress based on the proposal. Compared to fully automated on-chain voting execution, this governance mechanism offers higher flexibility. It allows Mantle to adjust the execution progress based on actual circumstances, rather than being strictly guided by a simple majority vote. However, this also means that Mantle’s governance has a certain degree of centralization dependency, with a larger role for the core team in governance. This off-chain governance approach is still exploratory in the decentralized autonomous field, and its effectiveness needs to be observed in its actual application in the Mantle project.
6.2. Project Valuation Level
We conduct a horizontal comparison of L2 valuations in the same track to evaluate Mantle Network’s valuation.
The valuation of smart contract public chains is a complex and challenging issue. DeFi protocols can be valued by factors such as yield multiples, while smart contract public chains are more similar to a country, and evaluating the current situation and potential of a public chain from the perspective of “comprehensive national strength” may be more appropriate.
For the “comprehensive national strength index” of public chains, data such as the number of active DAPPs, number of active users, TVL, total on-chain asset value, number of active developers, number of on-chain transfers, total value of on-chain transfers, etc. should be considered and calculated through weighted processing. However, there is currently no similar index.
Therefore, we focus on selecting indicators in four dimensions: assets, user base, network activity, and developers to compare Mantle Network with other L2 competitors.
1) Asset indicator: TVL. Users’ willingness to place valuable assets on a particular chain indicates their comprehensive recognition of the security, usability, and investment value of the chain. We use market capitalization/TVL as the asset indicator for horizontal comparison (MTV). The smaller the value of this indicator, the more on-chain assets correspond to each unit of market capitalization, indicating a lower valuation.
2) User indicators: Indicators such as the number of active users and active addresses can reflect the user base and activity level of a public chain. We choose the average daily active address number over 30 days to measure the user scale. The ratio of market capitalization to daily active addresses, i.e., market capitalization/daily active addresses, is used as the comparative indicator. A lower value of this indicator represents a larger user scale under the same market capitalization.
3) Transaction activity indicators: The activity of on-chain transactions is an important indicator to measure the activity level of users on a public chain. Traditionally, the daily dollar value of gas consumption is used to measure activity, but this indicator has certain limitations:
① High gas prices can reduce user activity, but this indicator does not reflect this.
② This indicator cannot distinguish between different types of transactions, such as transfer transactions and contract invocations.
To overcome these limitations, we use two indicators, the daily dollar value of gas consumption and the daily transaction volume, to measure activity. Specifically, we convert the dollar value of gas consumption in the past 30 days and the transaction volume in the past 30 days into annualized data, obtaining two indicators that can be compared horizontally:
③ Market capitalization/annualized gas consumption: The smaller this indicator, the more business activity the unit market capitalization of the chain can support, indicating a lower valuation.
④ Market capitalization/annualized transaction volume: The smaller this indicator, the more transaction volume the unit market capitalization of the chain can support, indicating a lower valuation.
These two indicators can more comprehensively reflect the activity of on-chain transactions and overcome the limitations of traditional indicators.
4) Developer indicators: Indicators such as the number of active developers and the number of on-chain verification contracts can reflect the developer ecosystem of a public chain. The number of active DApps is an important indicator for evaluating the prosperity of Layer 2 networks, but reliable statistics on the number of active DApps are currently lacking. We can use the following methods to measure the developer activity of Layer 2 networks:
① The average daily number of newly deployed contracts on the official browser can be chosen as the evaluation criterion.
② Calculate the indicator “market capitalization divided by the average daily number of newly deployed contracts” to reflect the developer activity that can be supported by each unit of market capitalization.
③ The smaller this indicator is, the more developers can be accommodated at the same market value, and the relative valuation is also lower.
By comparing this indicator with different Layer 2 networks, the ecological prosperity and valuation level of the network can be intuitively judged, so as to better evaluate the development potential of Layer 2. This calculation method can provide a concise comparison of ecological activity under current conditions, compensating for the incomplete statistics of direct DApp data and more comprehensively reflecting the developer’s profit space of the network.
In addition, before making the comparison, we also need to note that: unlike other L2 networks that use ETH as the Gas token, MNT token is used as the Gas token for the Mantle chain. When comparing with other L2 networks, this needs to be taken into consideration. Therefore, based on this comparison method, the valuation of Mantle will be slightly lower.
The results of the horizontal data comparison are as follows:
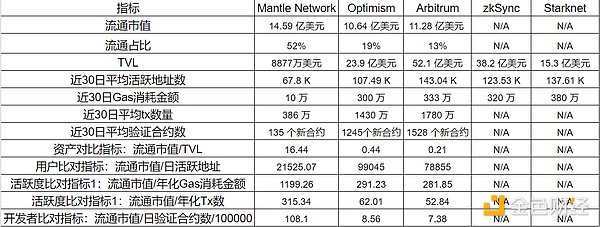
We can clearly see that after the completion of the ecological merger between Mantle and BitDAO, the current valuation is significantly overestimated. Compared with other Layer 2 networks in the OP Rollup track, the ecosystem of Mantle is still in the early stage, and there are certain lagging indicators. However, the native token MNT of Mantle has already had a 50% circulation, which supports its high valuation.
Looking ahead, with the continuous improvement and prosperity of the Mantle ecosystem, its business foundation will gradually strengthen. At this time, if Mantle can maintain a moderate valuation level, it is expected to achieve greater growth in the OP Rollup track and break the current situation.
6.3. Project Risks
Early-stage project development: Mantle Network launched the mainnet alpha version in July 2023, so as an emerging public chain, its technology and commercialization are still in the early stage of development. From the perspective of mainnet operation time, the network effect and technological stability still need to be tested for such a long time. Some key governance topics, such as staking mechanism design and zkEVM technology roadmap, are also under discussion. As a new project, Mantle also needs to continue technical iteration and role expansion to attract users and ecology, which requires the team to maintain efficient governance and development. In summary, the development of the Mantle network is still in the early stage, and key governance and technological aspects need to be improved. The uncertainties in this development process will become potential risks for the further development of Mantle.
Competition risk: Facing fierce competition in the Layer 2 environment. As an emerging Layer 2 solution, Mantle Network faces an important risk of increasingly fierce public chain competition in its future development. Currently, there are already several more mature projects in the Layer 2 market in a leading position, such as Arbitrum, Optimism, etc. These pioneers have strong technical strength and a large user base. At the same time, various new Layer 2 projects continue to emerge, and these new projects are competing for users and market resources. Moreover, the future upgrade of Ethereum will also enhance its own scalability. Facing such a competitive environment, Mantle needs to continuously enhance its product strength through technological innovation in order to break through the competition, otherwise it may face the risk of user loss. In summary, the increasingly intense competition in public chains is one of the risks that Mantle Network needs to prioritize and respond to. How to stand out in the competition is a key consideration for the Mantle project team.
Poor performance of BIT token has a negative impact on MNT. Mantle Network’s native token MNT is generated through the conversion of BitDAO’s token BIT. However, the market performance of BIT token has been poor, dropping from the ICO price of $1.4 to around $0.5 currently. This continuous downward price trend may have a negative impact on MNT. On one hand, BIT holders may lack confidence in the expected value and prospects of MNT, and may be unwilling to actively participate in the ecosystem construction of MNT. On the other hand, external investors and users may have doubts about the value and appreciation potential of MNT due to the price history of BIT token. This is not conducive to the widespread recognition and liquidity of MNT. If MNT is unable to effectively change this linked expectation on the performance of BIT in the future, its own token demand and price may face downward pressure. This is a risk factor that Mantle Network needs to focus on in token design and operation.
Technical security risks: The current technical risks of Mantle mainly include: 1) The development of fraud-proofing for the current Mainnet Alpha version is still ongoing; 2) The data availability layer is not yet online. Mantle plans to use fraud-proofing to ensure the correctness of the state, but this functionality is still under development and the system allows for invalid state roots. Moreover, because the data is not stored on-chain but maintained externally by the team, fraudulent behavior may not be detected, and if a malicious user submits an invalid state root, the user’s funds may be stolen even off-chain. At the same time, Mantle’s data availability layer, MantleDA, is a forked version based on EigenDA, but it has not yet been integrated into the EigenDA mainnet, and the slashing mechanism in MantleDA is currently disabled, and the fraud-proofing mechanism for data availability has not yet been activated. As a result, users will be unable to access their funds. In addition, if external data is tampered with, users’ funds may be lost.
6.4. Reflection
From our overall analysis of Mantle Network, Mantle is an L2 solution with both advantages and disadvantages. Whether it can become a mainstream L2 solution depends on whether it can fulfill its technical promises and build a secure and efficient Rollup network. We need to continue monitoring Mantle’s technical evolution path and the progress of its ecosystem construction in order to make a comprehensive judgment on its future prospects. Mantle is working hard to explore new paths for L2 networks, and we also look forward to its positive contribution to the entire Ethereum ecosystem. From its development plan, there are some short-term development opportunities that we can pay attention to:
1) Launch of Mantle Journey incentive program.
Mantle Network provides users with various ways to earn Mantle Journey (MJ) miles and exchange exclusive rights in the Mantle ecosystem. Users can accumulate MJ miles by trading, providing liquidity, participating in governance, and completing specific tasks on the Mantle network. These miles can be used to forge unique Mantle Citizen NFTs, acquire rare attributes of NFTs, and redeem ecosystem rewards, etc. The operation of Mantle Journey provides users with more incentives to participate in the ecosystem construction of Mantle. It effectively aggregates users, enhances user stickiness, and also provides users with a channel for monetization, which will attract more users to join Mantle. From a project opportunity perspective, Mantle Journey provides users with a new mechanism to obtain rewards. It opens up a new model for Web3 community construction and is worth learning from for other public chains, which also reflects Mantle’s community operation capabilities.
2) Mantle Network is in a period of rapid growth, and there are multiple profit opportunities in its ecosystem.
Mantle is actively building the LSD ecosystem and collaborating with other innovative DeFi protocols. This provides users with various ways to earn profits through participation in staking, trading, and portfolio management. As the number of protocols in the ecosystem increases, users can focus on potential high-quality applications, choose to participate in their IDOs or provide liquidity at the right time to achieve higher returns. After the Mantle ecosystem reaches a more mature stage, network effects will further amplify, allowing users to follow the development trends of the ecosystem and seize opportunities in emerging hot directions for additional profits.
7. References
https://www.mantle.xyz/zh Mantle Network official website
https://docs.bitdao.io/liteLianGuaiper-1/tokenomics BitDAO economic model
https://twitter.com/0xMantle Mantle Network official Twitter
https://discord.com/invite/0xMantle Mantle Network official Discord
https://medium.com/0xmantle Mantle Network official Medium
https://snapshot.org/#/bitdao.eth Mantle Network official proposal center
https://docs.mantle.xyz/governance/introduction/overview Mantle Network official D O C
https://www.coingecko.com/en/coins/mantle Mantle Network token information
https://tokenterminal.com/terminal Tokenterminal
https://l2beat.com/ L2beat
Share to WeChat

Author: WJB. This article represents the views of the columnist for LianGuaiNews and does not represent the position of LianGuaiNews. The article and views do not constitute investment advice. Image source: WJB. If there is any infringement, please contact the author to delete.
Deep zero-knowledge proof zkEVMUSDTBitDAOArbitrum mainnetETHEigenLayer investorDAO financing security
Recommended reading
-
 Manqu Blockchain
Manqu Blockchain2023-09-07
Do foreign trade companies need to use USDT cryptocurrency for receiving payments and exchange?
-
 LianGuai First Line
LianGuai First Line2023-09-07
An address transferred 6012 ETH to Binance half an hour ago, which would generate a profit of $970,000 if sold
-
 Odaily Planet Daily
Odaily Planet Daily2023-09-07
Polygon launches CDK to attract more developers
-
 LianGuai First Line
LianGuai First Line2023-09-07
Alert: Official X account of Ordinals Wallet was SIM swapped and phishing links were posted
-
 LianGuai First Line
LianGuai First Line2023-09-07
A certain whale loses $24.23 million worth of stETH and rETH due to phishing attacks
-
 EMC Labs
EMC Labs2023-09-07
EMC Labs August Brief: The rising channel is broken, on-chain and off-chain are two different worlds
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!