Author: Uncle Jian
Blockchain games have always been a hot track in the field of blockchain. With the decline of the play to earn narrative, the narrative of the blockchain game track has shifted from GameFi chain games to fully on-chain games. Due to being in the early stages, everyone has very little understanding of fully on-chain games. Just getting acquainted with the term fully on-chain games, there are inevitably some questions in mind. Here are nine questions that most people are likely to have doubts about and their answers.
What are fully on-chain games?
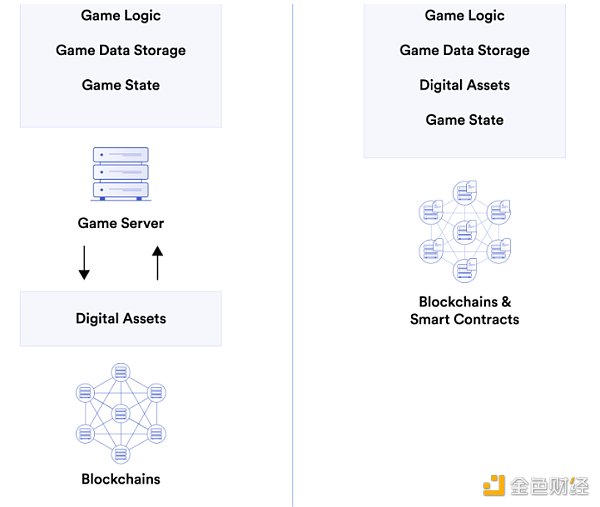
Fully on-chain games refer to games where all the actions, interactions, and target states within the game are recorded on the blockchain. This means that the core game logic and economic model are processed through the blockchain. The blockchain functions as the game’s server, and all player actions are carried out through interactions with smart contracts. Even the game’s narrative and governance are completed in a decentralized manner through DAOs.
The fundamental difference between fully on-chain games and the familiar GameFi chain games is that GameFi chain games only put some digital assets on the blockchain, while the game logic, data, and game state are all stored on centralized servers.
- Layer2 expansion solutions Why is the challenge mechanism of OP-Rollup so important?
- Behind the Balancer Attack Incident Security Team Layoffs and Concerns about Centralized Front-ends
- Australian regulatory agency sues Kraken provider over margin trading products.
What are the characteristics of fully on-chain games?
1. Decentralized game world open to everyone: Fully on-chain games eliminate the reliance on centralized servers, making the game logic completely on-chain.
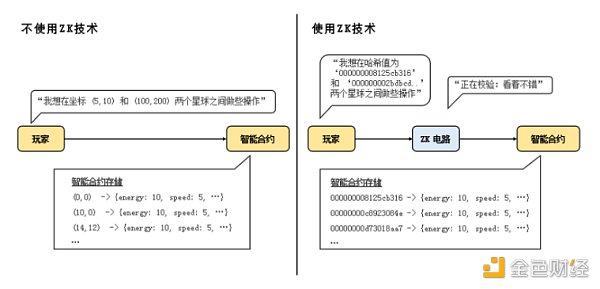
2. Trustless and verifiable: Since the game logic and data are stored on the blockchain, the game rules and state are transparent to everyone. Zero-knowledge proofs (zkSNARK) are used, and each player’s interaction generates a zero-knowledge proof (ZKP), which is submitted to the game backend and verified against the game logic through cryptographic validation. Moreover, ZKPs do not reveal the player’s interaction information, achieving privacy for player information.
3. Once on-chain, permanent operation: Due to the game state and logic being stored on the blockchain, fully on-chain games have high sustainability. Even if the original developers no longer support the game, as long as the blockchain still exists, the game can continue to operate and evolve hundreds of years later.
4. Community-driven: Fully on-chain games achieve community-driven development and governance through smart contracts and DAOs. This allows the game to better adapt to player demands and market changes, extending the game’s lifecycle and increasing its appeal.
5. Open collaboration, faster game iteration and evolution by player creations: Open-source code and an open ecosystem promote open collaboration between individuals, unleashing players’ creative vitality. User-generated content (UGC) brings more diverse, richer, and more sophisticated gaming experiences.
What is the comparison between traditional games, GameFi chain games, and fully on-chain games?
For now, let’s categorize games into three types: traditional games that do not involve blockchain at all, GameFi chain games that only put some assets on the chain, and fully on-chain games that are completely on the blockchain.
Here we compare two aspects separately.

-
Depth of game content: First of all, let’s start with the conclusion. The depth of content in the current stage of full-chain games is far inferior to that of Gamefi blockchain games, not to mention traditional games. Traditional games have undergone thirty years of development and are incomparable to the few years of development in game content in blockchain games. Since Axie Infinity became popular in 2018 and after several years of development, Gamefi blockchain games have evolved from casual games similar to traditional games to AAA-level blockchain games, with increasingly rich game content. With the participation of professional teams from traditional games, the depth of content is gradually approaching that of traditional games. On the other hand, full-chain games generally only have a worldview and mostly feature strategy gameplay based on games of chance. In terms of content depth, they are far behind the previous two. Moreover, they are still in the pixel stage in terms of art and are not expected to change for a long time.
-
Economic model: In traditional games, since in-game assets are published on centralized servers, the main attraction for users lies in the rich game experience. There are complex internal economic systems in the game, but basically, users can only recharge and cannot withdraw unless they trade on off-chain platforms. Gamefi blockchain games introduce NFT and token economic models, incentivizing all participants to jointly maintain a complex economic incentive system, reducing the difficulty of investment and financing, and shortening the cost recovery cycle. On the other hand, full-chain games depend on the project’s own choices. Blockchain games basically issue tokens, but not many full-chain games have a token system in their rule settings. The teams prefer to focus on exploring gameplay. Therefore, it is relatively difficult for participants to create an economic model and gain recognition. The result is that speculative purposes like Fi are filtered out, making the participation of players more pure.
What is the current state of the full-chain game ecosystem?
Currently, there are relatively few active users in the full-chain game ecosystem. Since full-chain games are on different blockchains and in their early stages, specific ecosystem data cannot be found for now. Taking the most famous project, Dark Forest, as an example, the official blog shows that each round of the game has about 600 participants, generating 250,000 transactions. Of course, the small number of participants is also due to the need for an invitation code from the official to participate in the game.
Currently, most popular projects in the full-chain game ecosystem are built on Ethereum’s Layer2 and Starknet. Mud and Dojo, game engines that facilitate game development, have been built on Ethereum and Starknet. Examples include LootRealms, a game built on Dojo, Influence, a space strategy MMO blockchain game, and Topology, a game based on the Three-Body Problem story.
What projects should players interested in full-chain games focus on?
Dark Forest:
Game Introduction:
Dark Forest is an MMO space conquest game launched in July 2020. The earliest proposer and founder of the idea was Gubsheep. He was convinced by Liu Cixin’s Dark Forest theory and came up with the idea of creating a cryptographic world called Dark Forest. It attracted the attention of many geeks as soon as it was launched, and even Vitalik Buterin tweeted about it.
Players can obtain invitation codes to participate in the game on the official website or Discord. The game operates on a mechanism of several months per round, and it is currently in the fifth round. The official has set a limit on the number of participants in each round, with around 500 participants per round. The project primarily focuses on the gaming experience and does not issue its own cryptocurrency.
Gameplay:
In Dark Forest, players will be born on randomly generated planets and conquer other planets to obtain more energy and vision. The universe where players are located will continue to generate and expand, requiring computational power to uncover the fog of war. Until all fog of war is lifted, players do not know the cards their opponents hold. Players may be attacked by other players, but if they have not explored the territory of the attacking party, they will not know who the attack is coming from or the true strength of the enemy.
Social media:
The official Twitter account currently has 26,000 followers. The number of participants in interactions is not high, mainly consisting of internal projects within the ecosystem retweeting each other.
Related links:
Dark Forest blog: https://blog.zkga.me/v4-recap
Dark Forest official website: https://zkga.me/
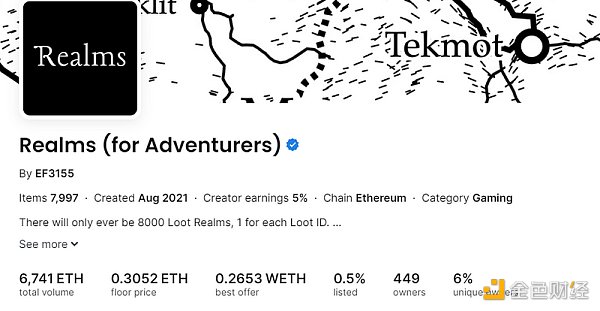
Loot Realms:
Game introduction:
On August 27, 2021, Loot sparked a wave of text-based NFT frenzy in the crypto community. 8,000 NFTs were sold out within 4 hours, consisting of just 8 lines of text that left a lot of room for community imagination. Developers have subsequently built projects based on Loot NFT, and Loot Realms is one of them.
Initially, Realms was built on the Rinkeby testnet of Arbitrum, and later successfully migrated to Starknet in December 2021.
Gameplay:
The initial release of assets in Realms consists of 8,000 Realm NFTs, which represent a series of kingdom states. Each Realm NFT has its own unique geographical location: they can be cities or regions, adjacent to rivers or near ports. Each Realm produces different mineral resources, with a total of 22 different combinations of resources, each with varying quantities (scarcity).
Tribes can gather armies and attack each other to plunder resources. The victorious side receives 50% of the defeated side’s treasury. In order to defend and expand their own territory, lords can lead armies to launch attacks on other territories. Each army consists of 25 warriors, and different skill values (agility, aggressiveness, defense value, vitality, intelligence) determine the outcome of battles between two teams.
Asset market situation:
The current market price for Realms NFT is 0.3052 ETH. Due to recent trends in the NFT market, the price is relatively low.
The native Token $LORDS serves as a transaction medium for various in-game assets, props, and equipment, in addition to its governance function;
The current price of $LORDS is 0.09618, with a market value of $4,892,785;
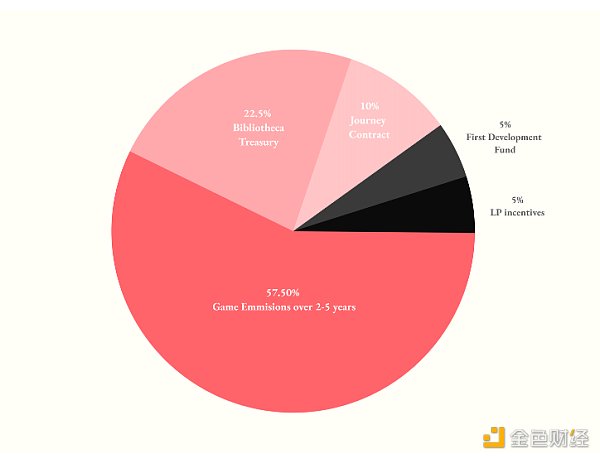
The LORDS token is also released through Reamls NFT staking and later in-game mechanisms. Among them, Reamls NFT staking will release 10% of the total supply, which is also the main source of circulating tokens in the early stage. In the first 10 epochs, 625x $LORDS will be released every week for each Realm, gradually decreasing over time.
The release ratio of the later in-game mechanisms is 57.5%, which will be completed within 2-5 years. The specific details will be adjusted based on the game supply and demand situation in the later stage. Other parts include Bibliotheca Treasury (22.5%), LP incentive (5%), and developer fund (5%) releases.
Social media:
The official Twitter currently has 13,000 followers. Similar to Dark Forest, there are not many participants in the interaction, mainly updates on the project’s progress and retweets of ecological content.
Related links:
LootRealms official Twitter: https://twitter.com/LootRealms
Is full-chain gaming an inevitable development or another pseudo-demand?
Full-chain gaming is an inevitable development. Why do I say that? After the narrative of Gamefi reached its climax on STEPN, the narrative of some on-chain gaming assets has raised a big question mark about its future development in this cycle of practice. The blockchain gaming field urgently needs a new narrative. Full-chain gaming did not receive widespread user acceptance after Dark Forest emerged in 2020, mainly because the infrastructure was not well-developed enough. Therefore, the narrative of some on-chain gaming assets had a moment, but in the next cycle, as the infrastructure becomes more and more complete, the future of full-chain gaming is worth looking forward to. The full-chain gaming in 2023 is very similar to DeFi in 2019, and early layout has ushered in the outbreak of the DeFi summer in 2020. With the development of infrastructure, more and more complex on-chain applications like full-chain gaming will appear, and the narrative of full-chain gaming is enough to support the narrative of the grand autonomous world (Autonomous World). In summary, this is a very good concept that encompasses many things, including games, NFTs, DeFi, and DAOs, because the Autonomous World also requires governance and a financial system, which also aligns with Ethereum’s vision of creating a Network state, making it a grand narrative.
The dilemma of full-chain gaming?
Although full-chain gaming has great potential, it still faces a series of challenges. The underlying infrastructure mainly includes the chain and corresponding development tools, and its impact on games is reflected in latency, cost, and iteration issues.
-
Latency: As mentioned earlier, multiplayer online games are often very sensitive to network latency and stability. A large number of high-frequency transaction processing requires high performance from the blockchain;
-
Cost: The cost includes the development cost of the game and the on-chain interaction cost for players. Since the industry is still in its early stages, mature web3 game engines like UE and Unity have not yet appeared, which makes the initial work of developing full-chain games more demanding. And since all on-chain transactions require payment of miner fees, when entering high-interaction scenarios such as games, this cost often becomes a burden for players, especially against the background of current simplified concepts of deposit and withdrawal;
-
Iteration: The tamper-proof feature of the blockchain undoubtedly brings fairness and decentralization, but it also poses certain challenges to code iteration. Developers need to carefully audit their code to ensure that there are no vulnerabilities and that the game logic is correct. For any game with a relatively large volume, this is still a relatively labor-intensive task.
Everything has two sides, just like centralization means efficiency while also meaning monopoly, and complete decentralization brings freedom but may also bring chaos.
First of all, from a narrative perspective, the free narrative framework and the low threshold for user-generated content do give content a broader scope. However, when anyone can participate in the act of storytelling, the quality of the content will inevitably vary. On the one hand, the overall progress of the narrative will be slowed down due to the community’s selection and review of content. On the other hand, when a large number of narrative branches appear, it will blur and disperse the attention to high-quality content, causing community members’ focus to become chaotic and requiring more time to establish consensus.
In addition to the challenges mentioned above regarding user experience and mechanism design, the economic model also needs to be reconsidered from a new perspective. When the game as a whole is placed on the chain, it does gain maximum openness and composability in the economic system, but at the same time, it also means losing almost all control over the game’s economic system. This will bring significant uncertainties for the development of the game.
How will the future develop?
In the future, full-chain games will give birth to numerous innovative core gameplay mechanics and may provide design inspiration for DeFi and even traditional games. Due to the separation of development, operation entities, and governance, the assets of full-chain games can achieve true ownership. Full-chain games that have the opportunity to dissociate from development and operation entities may integrate more closely with DAO governance in their lifecycle. And one day, when the development engine and toolkits of full-chain games are mature enough, ordinary players may also have the opportunity to use them to realize their unique ideas.
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!