Project Introduction
The Ator protocol aims to reward relay node operators who make useful contributions to the anonymous network by distributing Ator tokens. Operators can register their ETH address to join the Ator system as relay nodes for supported protocols such as Tor. After registration, these relay nodes can continue to provide services to the network as usual.
Subsequently, relay node operators can assess their contribution to the network by viewing decentralized contribution metrics published on Arweave and receive corresponding rewards in $ATOR tokens. $ATOR itself is stored and distributed through the ETH blockchain, and operators who receive rewards can choose to withdraw $ATOR to their own ETH wallet.
In summary, the Ator protocol effectively incentivizes more relay nodes to join and improves the service efficiency and privacy protection capabilities of anonymous networks such as Tor through a token reward mechanism.
Table of Contents
1. Research Points
- Coinbase Officially Launches Base A New Milestone for Cryptocurrency Listed Companies
- Overview of the Development Status of NFT Lending Protocols What Innovations and Problems Need to be Solved?
- Delphi Digital Vitality spreads across the world, looking forward to the new projects coming to the Cosmos ecosystem.
1.1 Core Investment Logic
1.2 Valuation
2. Project Overview
2.1 Project Scope
2.2 Past Development and Roadmap
2.3 Team Overview
2.3.1 Overall Situation
2.3.2 Core Members
2.4 Financing Status
3. Business Analysis
3.1 Service Targets
3.2 Business Categories
3.3 Business Details
3.4 Industry Space and Potential
3.4.1 Classification
3.4.2 Market Size
3.5 Business Data
3.6 Project Competition Landscape
3.7 Token Model Analysis
3.7.1 Token Supply and Distribution
3.7.2 Token Value Capture
3.7.3 Token Core Demand
4. Preliminary Valuation
4.1 Core Issues
4.2 Major Risks
5. References
1. Research Points
1.1 Core Investment Logic
The Ator project aims to address the lack of privacy and anonymity for internet users and promote the mainstream adoption of the Tor network. As a widely used anonymous communication tool, the Tor network allows users to browse the internet and access online resources without revealing their identities. It has provided important support for the birth and development of early cryptocurrencies, protecting the anonymity of users’ transactions and communications, and becoming a crucial privacy infrastructure in the cryptocurrency community.
The Ator project creates a more resilient Tor network infrastructure through blockchain technology and the Ator currency, and rewards contributors in an anonymous and fair manner, driving the development and usage of the Tor network. In Ator, similar to the relationship between Filecoin and IPFS, an incentive layer is introduced, allowing anyone to participate in the process of node incentives by purchasing relay devices.
Ator Network has excellent actual communication bandwidth (1660.283MiB/s), which is significantly higher than the bandwidth of other mainstream public chain nodes, which ranges from 50-500MiB/s. Ator has a very good network deployment optimization capability. At the same time, the project provides tools for anonymous communication and protecting online privacy, meeting the needs of internet users for privacy and anonymity. By using blockchain technology and Ator currency, the project creates a stronger Tor network infrastructure and rewards participants in an anonymous and fair manner. These advantages enable the Ator project to provide a more private and anonymous internet environment and sustainably promote the development of the Tor network.
However, the Ator project also faces some challenges, such as network security issues, such as insufficient nodes and vulnerability to DDoS attacks, which may affect the implementation and feasibility of the Ator protocol. Although the official is improving the security of the network, investors still need to be cautious when considering investing in Ator and closely monitor the development and security of the project.
The future roadmap of the Ator project includes development plans for protocols, external relations, services, and relay hardware, which are expected to be completed in the fourth quarter of 2023 and the first quarter of 2024.
Currently, the price of Ator has increased more than 20 times since its launch, indicating its huge potential and market attractiveness. However, for investors considering value investment, caution is needed, as well as in-depth consideration and observation.
1.2 Valuation
Due to the short time since the launch of the Ator project and its characteristics that do not fully belong to the traditional privacy track, but more of an incentive layer with privacy track, there is currently no similar leading target available for benchmarking, so accurate valuation cannot be carried out. As of now, the market value of Ator is about 41.9 million US dollars, and the fully circulating market value is about 56.86 million US dollars.
2. Project Overview
2.1 Project Scope
Ator is a decentralized network incentive platform whose business is to support and reward contributors to open-source decentralized network protocols using blockchain technology. Ator’s core is its self-developed blockchain protocol, which allows node operators to register wallet addresses and receive rewards in Ator tokens based on their contributions to the open-source network protocols. This reward mechanism currently primarily serves the Tor network and encourages more Tor nodes to join.
The Ator project has also developed dedicated low-power relay hardware that can be directly configured as network nodes following the Ator protocol, such as Tor, thereby reducing the threshold for non-technical personnel to participate in node operations. On this basis, Ator has built a decentralized service market that allows various applications and services to be deployed on registered nodes and uses $ATOR tokens as a means of payment. This provides node operators with channels to generate income.
The ultimate goal of Ator is to transform into a decentralized organization governed entirely by DAO. DAO will manage various open-source network protocols and corresponding token reward pools in the Ator ecosystem. The main business focus of the Ator project is to support networks that provide strong privacy protection and anti-censorship capabilities, such as the Tor network. Through community participation and positive incentives, Ator hopes to attract more nodes to join and enhance the service efficiency of these open-source decentralized networks.
2.2 Past Development and Roadmap
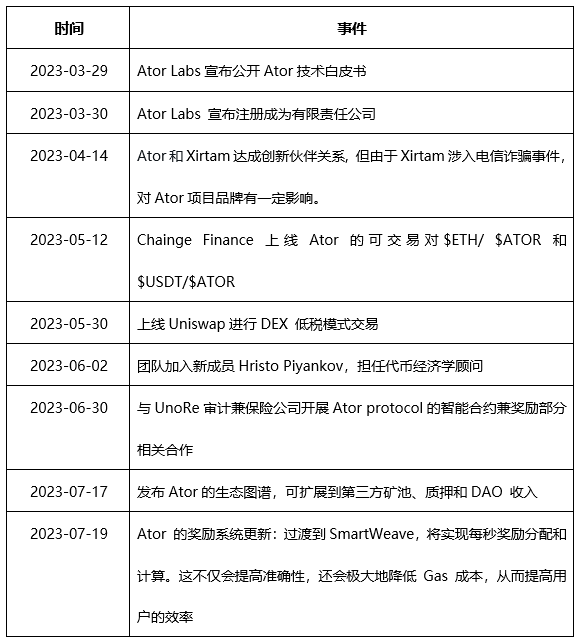
Future Roadmap
Protocol:
- Q2 2023: Registration protocol connecting ETH wallets and Tor fingerprints
- Q3 2023: Open-source guide for building Tor middleman hotspots
- Proof-of-Uptime testing and official release, allowing Tor relay node operators to passively earn $ATOR
External Relations:
- Q4 2023: Provide open-source guidance for building Tor relay nodes and distribute via external sponsorship
Services:
- Q1 2024: Use $Ator to build and verify web3 transactions on the Tor network through hidden services
Relay Hardware:
- Q4 2023/Q1 2024: Pre-configured to allow non-technical users to passively earn $Ator
2.3 Team Overview
2.3.1 Overall Situation
According to official information, the Ator team consists of 5 members responsible for the core management of the project, including full-time and part-time members. Slava serves as the CTO, and both Slava and the Memetic Block team have nearly ten years of experience in the crypto field and have been collaborating with Arweave since 2017. Jim and Andrezj serve as chief architects. On June 2, 2023, the team welcomed a new member, Hristo Piyankov, as a token economics advisor. The team covers professionals from different fields, with an education and social media team responsible for education and social media work, and a hardware team responsible for hardware-related business.
Currently, the core members work behind the scenes, and their education and work experience have not been disclosed in detail.
2.3.2 Core Members

Hristo Piyankov - Business Consultant
He is a professional with extensive experience in the cryptocurrency industry. He graduated from New Bulgarian University with a Bachelor’s degree in Economics and Statistics. He has worked on several top ten altcoin projects and has a deep understanding of the factors that contribute to the success of cryptocurrency projects. He currently works full-time at FinDaS Ltd and has been with the company for 5 years and 8 months. He has years of experience in the cryptocurrency and blockchain fields and has expertise in finance and analysis. He specializes in Tokenomics and has built Tokenomics architectures for over 220 projects, raising over $1 billion in funding.
2.4 Financing Situation
The Ator project did not rely on venture capital or other institutions for fundraising in advance, but instead raised funds purely based on performance. On March 30, 2023, Ator Labs was officially registered as a limited liability company in Norway and obtained software and hardware production licenses.
3. Business Analysis
3.1 Service Objects
1) Decentralized Network Node Operators
This is the core service object of Ator. Ator rewards individuals or organizations running open-source decentralized network nodes through a blockchain token incentive mechanism, encouraging more nodes to join, such as Tor node operators.
2) Developer Community
Ator welcomes developers to develop and deploy decentralized applications or services based on its network, using Ator tokens as a means of payment. This provides developers with new application scenarios.
3) End Users
End users can enjoy various advantages of decentralized networks, such as privacy protection and anti-censorship, by using services deployed on Ator nodes. This will increase user acceptance of decentralized networks.
4) DAO Participants
The ultimate goal of Ator is to establish a DAO organization. The community participating in DAO governance can influence the direction of network development and resource allocation.
3.2 Business Classification
Ator’s business scope mainly includes:
1) Ator Protocol: This is an autonomous system used to reward decentralized network relay node operators. Operators can register ERC20 wallets and receive $ATOR as rewards based on their contributions to supported protocols, such as the Tor network.
2) Ator Relay Hardware: This is a low-power computing device that can be configured to run according to the Ator protocol, allowing non-technical users to participate in decentralized internet protocols and passively receive $ATOR.
3) Ator Decentralized Services: This is a framework for providing specialized services on top of registered protocols, with transactions conducted through Ator tokens. The services include applications managed by the Ator team, services designed to run on Ator relays, and services provided by third parties. Service providers receive compensation from a special payment system pool.
4) Ator DAO: This transfers the protocol to decentralized management and is managed by DAO, which includes multiple protocols and their reward pools within the ecosystem. Ator tokens will be the main driving force for governance, while satisfying multiple use cases such as rewards, products, and recognition.
5) Initial focus on supporting the Tor network by providing rewards and identification for Tor relay nodes. The future expansion will include support for other open decentralized protocols.
In summary, Ator’s business scope mainly focuses on supporting and rewarding the construction of decentralized networks using blockchain technology, especially protocols or services that provide anonymous privacy.
3.3 Business Description
The Ator protocol aims to recognize the useful contributions of relay operators to decentralized networks by distributing Ator tokens. For supported protocols like Tor, operators register their relays with an ETH address and continue to operate as relays.
Subsequently, relay operators will be able to view their contributions to the network through decentralized metrics published on Arweave and receive corresponding Ator recognition rewards. Ator is distributed on Arweave and supported by sealed tokens on the Ethereum blockchain, which users can choose to withdraw to their ETH wallets.
1) Tor Network
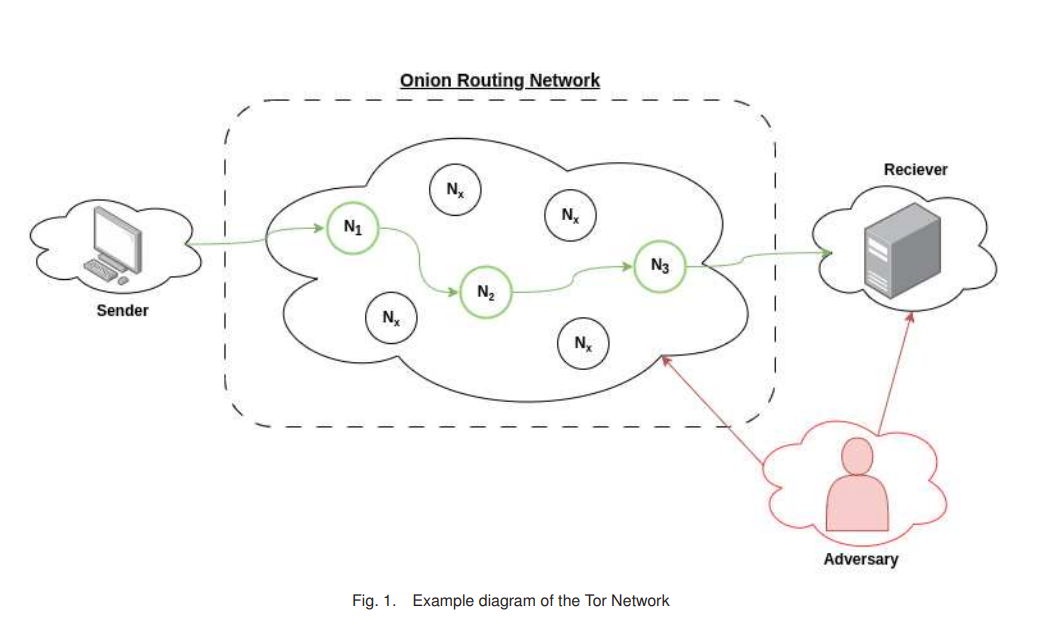
In order to understand the Ator protocol, it is necessary to first understand the Tor network. Tor, short for “The Onion Router,” is software used for anonymous communication on the internet. It achieves this by routing internet traffic in an untraceable manner between a series of servers (nodes) located worldwide. When users connect to Tor, their data is encrypted and then passed through a chosen series of Tor nodes, with each node decrypting a layer of the data to expose the address of the next node. This process continues until the data reaches its final destination.
Each node in the chain only knows the addresses of the previous and next nodes, making it extremely difficult for any intermediary to trace the data back to its source. Additionally, the way services are provided on the Tor network further enhances user anonymity, as certain websites and services can only be accessed through the Tor network. This essentially allows both users and services to benefit from Tor on both ends. These services utilize different routing mechanisms, where the address of a website is encrypted and passed through several nodes before reaching its destination, making it very difficult to locate the servers hosting the websites. The following diagram shows a network view of the Tor network.
However, the Tor network also has some drawbacks, which the Ator protocol aims to address. For example, internet service providers can still infer user identities by capturing data request times and frequencies. Additionally, the Tor network currently only has around 6,000 nodes, which means the number of nodes is limited and may result in performance and scalability issues, especially when facing demands from millions of users, causing the network to become less stable and efficient.
The Ator protocol addresses these scalability issues through relay mechanisms and device optimization. The relay mechanism allows more nodes to participate in the network, thus improving network capacity and performance. Device optimization helps reduce resource consumption for running nodes, enabling more nodes to support the access demands of more users.
In summary, the Ator protocol aims to address some of the drawbacks of the Tor network and provide a more reliable and scalable solution for anonymous communication to meet the growing demand for user privacy.
2) Relay Nodes: Earning Rewards through Ator
Ator enhances the Tor network through an on-chain rewarding mechanism. As a participant in Tor relay nodes, you can contribute to internet anonymity and earn Ator tokens as rewards through the proof of online time protocol.
- Enhancing Network Ambiguity
The goal of Ator is to increase the number of active Tor relay nodes, strengthen network capacity, and accommodate larger user traffic.
- Proof-of-Uptime
Tor relay nodes, including Ator’s own hardware, can earn Ator token rewards by contributing to the encryption and transmission of data packets.
- End-to-End Privacy Protection
The registration of relay nodes is specially optimized for anonymity. Through proxy registration, registration without gas fees can be achieved without revealing the user’s IP.
- Relay Node Registration
Relay node owners can register to join the Ator protocol. Devices register with both Ethereum key pairs and Tor key pairs to prove ownership.
Using the main offline key can establish a secure communication system between users and the network.
- Relay Contribution Assessment
Using the Proof-of-Uptime system, the network rewards relay nodes in the form of Ator tokens based on their stable online time. The rewards are calculated and distributed based on the actual online time of the relay nodes, avoiding the situation of only rewarding large relays.
The project team has also developed additional incentive mechanisms, setting up independent reward pools to provide extra rewards for bridge relays, exit relays, and relays in specific regions.
- Hardware
Ator relays are pre-configured hardware that can provide relay services for Tor and gain Ator recognition without the need for user configuration.
Ator routers are hotspots that allow consumer devices to connect to Tor.
Ator tokens will be widely used throughout the protocol as a prerequisite for relay registration and the main payment method for purchasing hardware. Tor can be exchanged for Ator hidden services, including decentralized website hosting provided through the Tor-Arweave integration, as well as blockchain transaction routing.
Ator tokens can be used for governance and protocol-related voting, as well as to pay for relevant proposal fees.
3) Proof-of-Uptime
Uptime refers to the length of time a relay node is continuously running and accessible. The longer the uptime, the more stable and reliable the relay node is, indicating less frequent downtime.
Uptime is an important metric for the Tor network. Clients prioritize connecting to relay nodes with longer uptime because it implies greater stability. Directory authorities also assign “stable” labels based on the relay nodes’ uptime, which affects client selection.
It is recommended to use the consensus weight of the relay as a standard for proof-of-uptime. The ATOR system uses directory authorities to collect information about nodes, such as their IP addresses, public keys, and bandwidth capacities. The directory authorities use this information to create a “network consensus” document that includes a list of all known nodes and their consensus weights. Consensus weights are influenced by various factors, including bandwidth capacity, uptime, and exit policies. The higher the consensus weight of a node, the higher its status in the network and the greater the probability of being selected. Specifically, these factors include:
1. Bandwidth Capacity: The larger the bandwidth, the higher the weight, because it can handle more traffic.
2. Online Time: The longer the online time, the higher the weight.
3. Export Policy: The looser the export policy, the more allowed traffic, the higher the weight.
The directory server will publish all the relay information and weights in the consensus document. The online time contribution of the relay can be judged based on the weight of the relay, which serves as the basis for distributing rewards.
4. Performance Measurement: The directory authority may consider the relay’s latency, reliability, and other indicators when allocating consistency weights.
Using this information, a minimum threshold can be set for the current normal operating time mechanism. It should be noted that the directory authority protocol is centralized. ATOR, on the other hand, has adopted this approach to create an alternative decentralized solution.
4) Registration (Operation Aspect)
- Support multiple signature methods for authentication
In order to establish a connection between the relay node and the ETH wallet, so that the wallet can obtain Ator rewards based on the contribution of the relay node, a dual signature system is required.
- ETH wallet signs to declare relay ownership
The official registration page allows the ETH wallet to sign and declare ownership of a specific relay fingerprint to join the protocol. Subsequently, this declaration will be verified by Ator or an authorized validation entity (oracle). It is important to note that the registration page will be hosted on a decentralized storage network to prevent Ator or any single hosting provider from obtaining the IP addresses of registered users. In addition, registration is completely free.
- Relay broadcasts ETH wallet address
As part of the registration protocol, the relay node needs to include the Ator protocol header and the ETH wallet address that registers the relay in the data packet in order to continue receiving Ator rewards. Ator will analyze the original metric data to verify the declaration.
5) Verification
Registered relay nodes can obtain Ator rewards based on their contributions to the network. The server will collect data from the relay nodes and record it on the blockchain as a basis for judgment. The smart contract will then distribute Ator rewards based on this data.
- Consensus Weight
For the Tor network, existing consensus weights are used to measure the contribution of relay nodes. Consensus weights take into account factors such as node bandwidth.
- Arweave Data
The collected relay node data will be published on Arweave’s blockchain storage in real time. This data can be read by smart contracts to determine reward distribution.
- Smartweave Oracle
The Ator rewards to be allocated within a certain period of time (such as one day) will be divided based on the time interval between the last reading data and the current data. For example, if the interval is 70 minutes, the planned daily reward amount will be distributed according to the proportion of 70/(24*60). Then, a $ATOR will be allocated on Smartweave, and the ETH contract can be read by the redstone oracle.
In general, the data of relay nodes will be recorded on the chain, and smart contracts will verify the data and distribute Ator rewards to the nodes.
3.4 Industry Space and Potential
3.4.1 Classification
The privacy track is mainly divided into four sectors: privacy computing networks, privacy transaction networks, privacy applications, and privacy coins.
- Privacy transaction protocols
The privacy transaction network mainly focuses on the privacy protection of on-chain transaction data (types and quantities of held or traded coins). It supports users to conduct private transactions natively through technologies like zero-knowledge proofs, without the need for tools like Tornado Cash, ensuring that their privacy data will not be viewed by external parties. It also supports the development of more types of privacy applications on this protocol.
- Privacy computing protocols
The privacy computing protocol mainly protects privacy in the process of data generation, collection, storage, analysis, utilization, and destruction. In addition to common scenarios like DeFi and NFT, it also plans to integrate deeply with the big data and AI industries.
Compared with other forms of privacy projects, privacy computing protocols are more fundamental infrastructures. Specific transaction information (such as coin types and quantities) can often be publicly viewed through block explorers, but more emphasis is placed on the privacy of user data usage. The main privacy technologies currently include zero-knowledge proofs, secure multi-party computation, learning based on modern cryptography, and trusted execution environments (TEE).
- Privacy applications
Privacy applications refer to applications built on Layer1 or Layer2 protocols that provide privacy protection features for users or DApps in different application scenarios, such as transactions, payments, emails, etc.
- Privacy coins
Privacy coins are encrypted currencies that natively support privacy. The specific transaction types and amounts of the two parties cannot be viewed by external parties. They usually do not support smart contracts and related applications. The earliest related projects emerged in 2014.
Currently, the development of privacy coins is generally average, with significantly smaller user and transaction volumes compared to smart contract platforms, DeFi, and other track projects.

3.4.2 Market Size
Regulators are actively supervising the centralized cryptocurrency market; analysis companies have unauthorized ownership and use of user data; the regulation of privacy coins and sanctions on Tornado Cash are examples that advocate Web3 privacy.
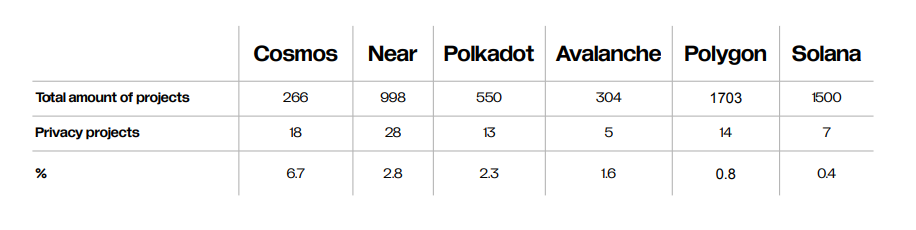
According to the Web3privacy annual report on GitHub, over 300 projects are building privacy solutions, committing to provide over $1 billion in funding to projects and ecosystems in 2022. Privacy applications have been downloaded over 110 million times on Google Play, and there are currently over 300 job vacancies in the market. The total number of Zcash addresses is 727,681, and 4,300 contributions from 177 countries participated in the trusted setup of Manta Network. The following figure shows the situation of different public chains betting on privacy in their ecosystems.
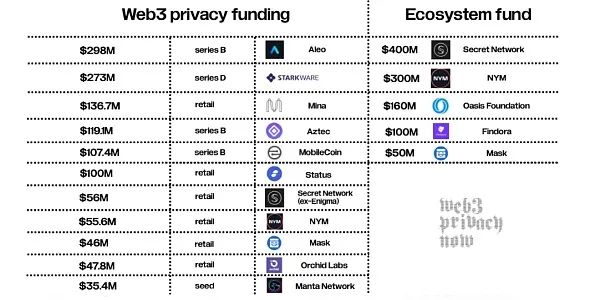
Venture capitalists have shown strong interest in the privacy sector. Aleo raised a total of $270 million in 2022, and projects like Aztec or Espresso Systems successfully completed new rounds of financing even in a sluggish market. Last year, NYM and Secret Network announced the commitment of partners to support developers in the privacy sector. Savvy investors know that a strong ecosystem will attract more retail investors and utility token users. The report states that a total of $1.3 billion in venture capital and retail investors have supported the development of privacy technology.
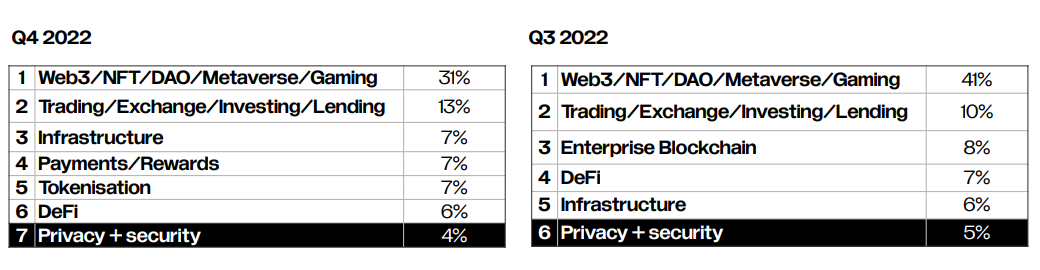
However, in the past year, privacy-centered investments still play a relatively small role in the overall Web3 investment sector, accounting for only about 4-5%.
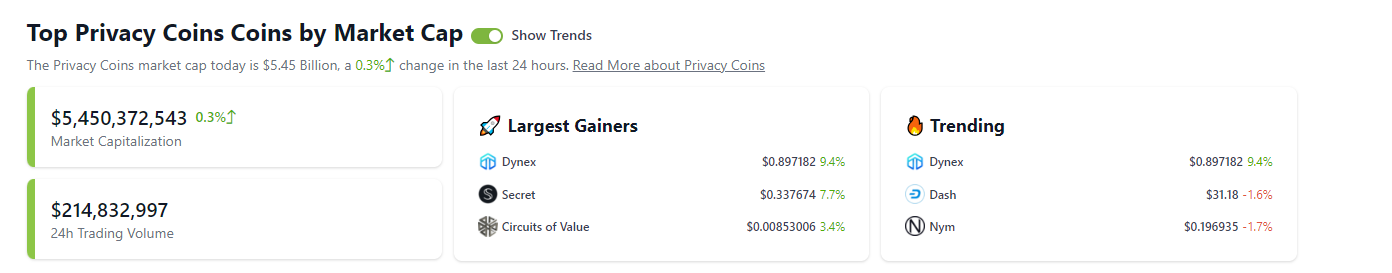
In addition to last year’s annual report data, looking at the latest data, the total market value of privacy track tokens is about $5.45 billion, with a daily trading volume of about $210 million. However, although the market value of the entire privacy track is large, the three tokens with the highest increase, Dynex, Secret, and Circuits of Value, have a maximum increase of only 9.3%. This shows that the current market for the privacy track is relatively stable, and investors need to recognize that the market may be in a relatively sluggish period and carefully evaluate investment risks and project potential.
3.5 Business Data
Operational Data

According to official website data, the current total number of users of the Ator project is 284, with 449 validated relay nodes and 161 active relay nodes. At the same time, the actual communication bandwidth between Ator nodes on the blockchain network reaches 1660.283MiB/s. This data shows that Ator is highly configured among blockchain nodes, and its network deployment optimization capabilities perform outstandingly compared to other mainstream public chain nodes such as Cosmos and Polkadot. Such high bandwidth configuration provides Ator project with stronger network performance and provides users with more efficient and stable anonymous communication experience.
Social Media Data
- Twitter followers: 15K Discord followers: 3205 Telegram followers: 2367
As an Alpha project, Ator has shown a certain level of influence on social media. Its Twitter followers have reached 15K, indicating community interest in the project. On Discord, the number of active followers has reached 3205, indicating active communication and interaction among community members. Although the number of Telegram followers is relatively small, at 2367, this does not necessarily reflect the project’s potential.
Price Trend
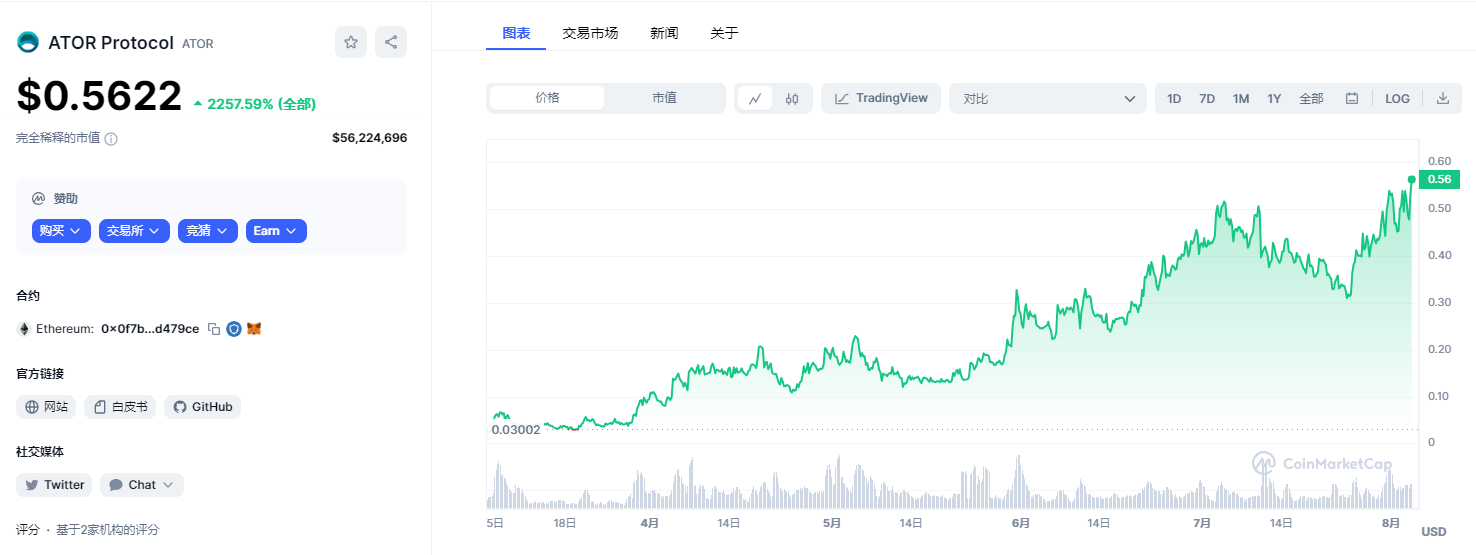
Ator is a remarkable project. Its opening price was $0.03, and the current price has soared to $0.56. Since mid-May, it has been rising all the way with a staggering increase of 2184.27%. Such strong performance has attracted the attention of many investors. The trading volume in the past 24 hours is also considerable, reaching $735,000, indicating the market’s activity and enthusiasm for trading $Ator.
Technical Data
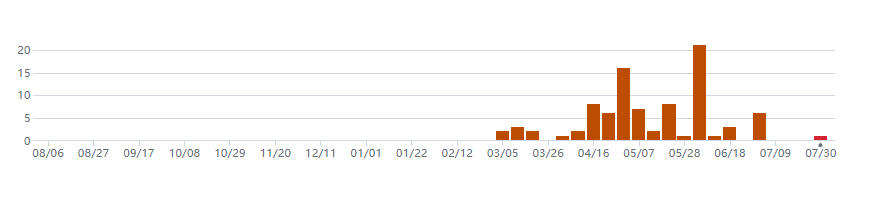
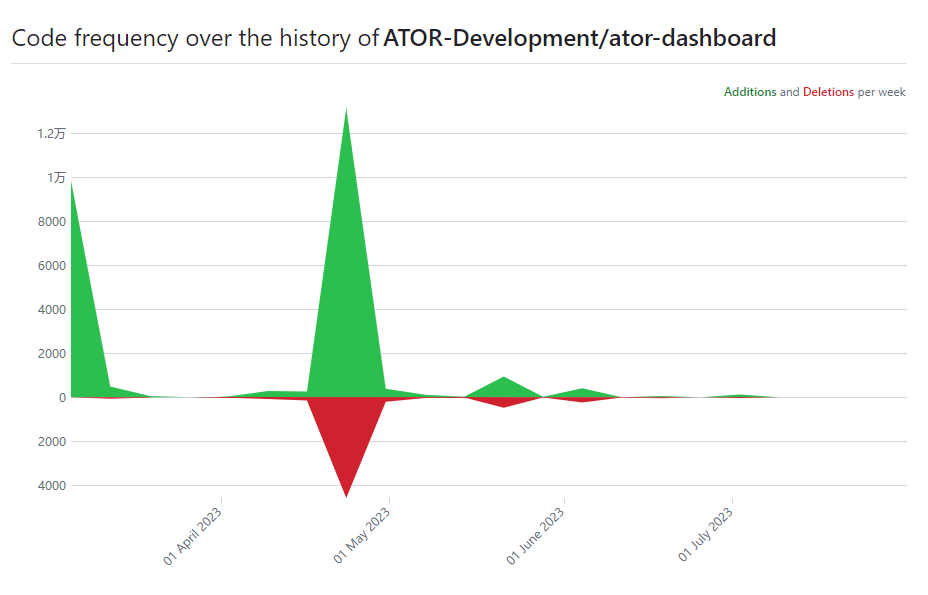
According to data from Github, the current number of followers for the $Ator project is 12, with 4 main contributors. However, it should be noted that code commits are not very frequent, with the main active period being between the 4th and 5th months after the project went live. During this period, the number of code commits reached its peak, with a maximum of 21 commits in a single day. This indicates that the project team had active development activities in the early stages, but the frequency of commits has since decreased.
For investors, the activity level and frequency of code commits on Github are also important reference indicators. An active project code repository usually means that the team is constantly making improvements and updates, while fewer commits may indicate relatively slower development progress.
3.6 Project Competition Landscape
The privacy track is mainly divided into four categories: privacy computing networks, privacy transaction networks, privacy applications, and privacy coins. Ator belongs to the category of privacy computing networks.
Ator belongs to the node incentive layer of privacy computing networks, which is equivalent to a scalable blockchain solution. Next, we will introduce two extended solutions for node incentives.
Project Introduction
- Web MIXes
Web MIXes is an anonymous communication system based on MIX technology, proposed by Berthold et al. MIX is a privacy protection technology that hides users’ identities and communication content by obfuscating and delaying the transmission path of messages. In Web MIXes, users need to purchase tokens to use the network. This token-based incentive mechanism helps maintain the sustainability and stability of the network. Tokens can be transferred between different MIX servers and have expiration dates. In addition to basic anonymous communication functions, Web MIXes also provides some additional features such as content filtering and caching. However, due to its implementation and deployment not being clear enough, and the lack of publicly available evaluation results, the actual effectiveness and security of Web MIXes are still unclear.
- BitTorrent
BitTorrent is a famous peer-to-peer file sharing network proposed by Bram Cohen. It uses a Bitcoin-based incentive mechanism that allows users to pay or receive fees for file transfers using Bitcoin. The incentive mechanism of BitTorrent aims to improve the efficiency and fairness of file sharing and prevent selfish or cheating behavior. However, BitTorrent is not an anonymous communication network, and users’ IP addresses and transmission content may be exposed or monitored. It primarily focuses on the efficiency of file sharing and transmission, without providing specific measures for user identity and privacy protection.
3.7 Token Model Analysis
3.7.1 Token Supply and Distribution
Tokenomics
- Distribution
Total supply of $ATOR: 100,000,000
45% added to liquidity (Uniswap Ator/WETH trading pair)
10% allocated for basic relay rewards (2-year lock-up period)
10% allocated for the team (2-year lock-up period)
10% allocated for development, marketing, and centralized exchange (CEX) listing (locked-up)
25% reserved in the contract for fundraising purposes*
- Lock-up Information
Locked tokens will be released linearly on a weekly basis for 2 years.
*The Ator contract initially reserved 25% of the token supply and during the fundraising period, users did not pay any taxes. However, the contract will sell tokens proportionally based on the trading volume to simulate a similar effect to taxation. The funds raised are used for protocol and hardware development. The fundraising period ended in May 2023.
3.7.2 Token Value Capture
The $ATOR ERC20 token will play several key roles in the development of the Ator project:
Firstly, the $ATOR token will facilitate the implementation of the Ator Proof-of-Uptime protocol; registered relays will be incentivized with it. Thus, the $ATOR token will provide a recognized tokenized way for contributors to participate in relaying.
The $ATOR token circulating on Uniswap automated market maker (AMM) enables investors to allocate market value to the entire protocol and hold a stake in its development and influence.
$ATOR holders will have the right to enter the whitelist and receive early access to the project’s custom hardware. Tokens can be used to redeem this hardware (refer to the roadmap).
The $ATOR ERC20 contract is specifically designed to facilitate limited-time fundraising; the contract exchanges tokens strictly in proportion to the trading volume, without charging transaction fees to buyers and sellers. This allows the Ator protocol to raise funds for development without the concentration of risk capital (refer to the distribution).
As a token on the highly dispersed Ethereum blockchain rather than a standalone blockchain, it enables quick adoption and registration.
3.7.3 Core Token Demand
1. Relay Node Operators: The $ATOR token will facilitate the implementation of the Ator Proof-of-Uptime protocol and provide incentives for registered relay nodes. Relay node operators contribute to the stability and security of the network by receiving $ATOR token rewards.
2. Investors: The $ATOR token circulates on Uniswap automated market maker (AMM), allowing investors to capture the market value of the entire protocol and hold a stake in its development and influence. Investors can participate in the development of the Ator project by holding $ATOR tokens.
3. Hardware (Relay) Buyers: $ATOR holders will have the right to enter the whitelist and obtain the first batch of custom hardware. Tokens can be used to exchange for this hardware, which is an additional incentive for token holders.
4. Preliminary Valuation
4.1 Core Issues
Does the project have a reliable competitive advantage? Where does this competitive advantage come from?
1) Emphasizing privacy protection and anonymous communication: The Ator project aims to address the challenges faced by the Tor network and promote mainstream adoption by internet users. It emphasizes the threats to privacy and anonymity posed by internet surveillance, cloud computing, and big data processing. By providing tools for anonymous communication and protecting online privacy, the Ator project has a competitive advantage in privacy protection and anonymity.
2) Based on blockchain technology: The Ator project utilizes blockchain technology to create a more resilient Tor infrastructure and uses the Ator currency to reward contributors. This blockchain-based distributed system provides reliability to the Tor network while rewarding participants in an anonymous and fair manner.
3) Continuous development and sustainability: The document discusses the implementation and mechanisms of the Ator project to ensure the protocol’s sustainability. This involves designing incentive mechanisms for the stability of the circulation and supply of $ATOR tokens. The project also focuses on expanding adoption and adaptability with Tor relays.
What are the key variable factors in the operation of the project? Are these factors easy to quantify and measure?
The key variable factors in the operation of this project are “reliability” and “defensibility”.
Reliability refers to the continuous uptime of relay nodes and their contribution to the Tor network.
Defensibility refers to the ability of relay nodes to resist threats such as DDoS attacks.
These factors can be quantified and measured through indicators such as uptime, which represents the continuous online time of relay nodes. By monitoring and recording the online time of relay nodes, their reliability can be evaluated, and weights and rewards can be allocated based on the duration of online time. Additionally, the document also mentions other factors for measuring relay nodes, such as traffic capacity and performance indicators.
Therefore, these factors can be quantified and measured, and can serve as key indicators for project operations.
4.2 Main Risks
This project has several risks. First, from a technical perspective, the Tor network itself faces challenges such as insufficient nodes, vulnerability to DDoS attacks, and a lack of incentives for individuals to run nodes. These issues may pose certain difficulties and risks to the implementation and feasibility of the Ator protocol.
Second, although the Ator protocol uses blockchain technology and the Ator currency to provide a more robust Tor infrastructure and reward contributors, it also brings some risks. For example, due to the performance limitations of blockchain technology, there may be performance bottlenecks and scalability issues. Additionally, blockchain technology itself may face challenges in terms of security and privacy.
In addition, the project also needs to address the security risks caused by centralized storage institutions. The rewards in the Ator protocol will be distributed and stored by centralized institutions rather than being directly owned and controlled by users. This may make centralized institutions a target for attacks and may lead to trust and security issues.
Lastly, due to the ongoing development and evolution of the project, the final code and implementation may differ from the description in the current whitepaper. Therefore, the actual feasibility and risks of the project may depend on its final implementation and deployment.
In summary, the Ator project faces challenges from the Tor network itself, limitations and security issues of blockchain technology, and risks from centralized storage institutions.
5. References
1. https://Ator.io/ Official website
2. https://docs.Ator.io/ Official Gitbook
3. https://github.com/Ator-Development/resources/blob/main/Ator_Technical.pdf Whitepaper
4. https://relayseries.Ator.io/welcome/welcome-to-Ator-relay-education Relay deployment tutorial
5. https://twitter.com/Atorprotocol Official Twitter
6. https://Ator-dashboard.ar-io.dev/ Official Dashboard
7. https://ETHerscan.io/token/0x0F7B3F5a8FeD821c5eb60049538a548dB2D479ce Ether browser
8. https://www.techshidai.com/article-102589.html Comprehensive interpretation of the current situation of Web3 privacy track
9. https://www.coinonpro.com/news/toutiao/247185.html Web3 privacy track research report
10. https://github.com/web3privacy/web3privacy/blob/main/Market%20overview/Privacy%20market%20outlook%20in%20Web3%20by%20Mykola%20Siusko%20(Jan%202023).pdf WEB3 privacy track
11. https://unore.io/ Partner’s official website
12. https://www.bitTorrent.com/ BitTorrent official website
– Investment Risk and Disclaimer –
The content analysis provided in this report is for reference only and does not constitute any form of investment advice or decision-making basis. We strongly recommend that you do not engage in any investment activities based on this report to avoid potential risks. WJB and the report authors are not responsible for the investment results made by users based on this report.
The preparation time of this report is the date shown, and subsequent changes in the market or economic conditions may cause the content to change. The graphics, charts, and other visual aids in the report are for reference only and should not be used as a basis for making investment decisions. Any graphics, charts, or other visual aids in the report cannot cover all the factors and variables required to make such decisions. Please note that WJB does not assist anyone in making specific investment decisions.
Some of the discussions in this report may be WJB’s assumptions and other forward-looking views. However, these assumptions and views are subject to known and unknown risks and uncertainties that may cause actual results, performance, or events to differ significantly from the stated views and assumptions.
All speculations, predictions, and estimates contained in this report are based on certain assumptions and are speculative in nature. These forward-looking statements may prove to be incorrect and may be affected by incorrect assumptions or known or unknown risks, uncertainties, and other factors, most of which are beyond our control. It is expected that some or all of such forward-looking assumptions will not be realized, or there may be significant differences between them and actual results.
— Copyright Information —
This report is copyrighted by WJB only. Without written permission, no institution or individual may infringe WJB’s copyright by means of reproduction, copying, quotation, or redistribution to others.
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!