Source: Polygon Official Translation: LianGuaixiaozou
On August 30, 2023, Sandeep Nailwal, the founder of Polygon Labs, announced the launch of the Polygon Chain Development Kit (CDK). The Polygon CDK enables developers to launch their own ZK fully functional L2 (similar to OP Stack launched by OP). Sandeep Nailwal stated that Polygon CDK is the evolution of Supernet, and now with the help of Polygon ZK technology, developers can easily customize and deploy their own application chains.
Polygon officially explains what Polygon CDK is, why choose Polygon CDK, and how CDK chains adapt to the entire Polygon 2.0 ecosystem. This article is translated by LianGuaixiaozou to reward readers.
- Aave V3 vs Compound V3 Quick Comparison
- L2 Stacks War Is it about to end before it even starts?
- LianGuaintera Partner Understanding the Chainlink Cross-Chain Interoperability Protocol (CCIP) Concept, Components, Architecture, and Use Cases
What is Polygon CDK?
The Polygon Chain Development Kit (CDK) is an advanced open-source framework dedicated to quickly deploying ZK-based layer 2 blockchains on Ethereum. CDK emphasizes modularity and helps developers launch new Ethereum L2 chains or seamlessly transition existing L1 chains to L2. The chains created through CDK are interrelated, ensuring near-instant finality, infinite scalability, and a unified liquidity pool.
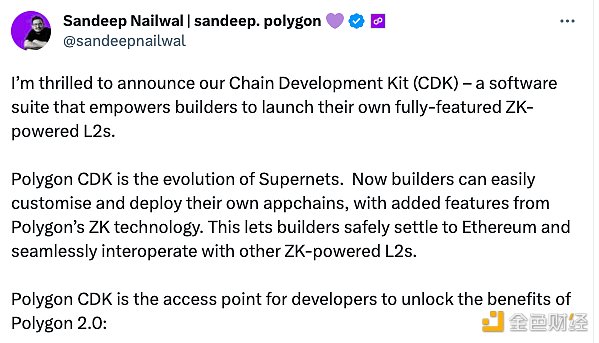
With CDK, developers can carefully design application-specific chains that meet their unique specifications. CDK’s design prioritizes core business functions and user engagement while maintaining peak performance and scalability, involving choices such as virtual machines, operation modes, data availability solutions, sorter types, and gas tokens.
For example, a chain tailored to a specific application can use the zkEVM execution environment, adopt a “verification” mode, and deploy a centralized sorter. Regardless of these personalized choices, each chain maintains perfect interoperability with all other Polygon chains, providing high-performance L2 scaling solutions.
The following diagram shows the basic components of CDK.
Note: The default for Polygon CDK in this stage is Validum. Polygon 2.0 will have content updates and extensions to reflect the new configuration.
What are Application-Specific Blockchains?
Application-specific blockchains (app-chains) are blockchain networks designed specifically for particular tasks and are more efficient compared to general-purpose blockchains. By focusing on specific applications such as supply chain management or decentralized finance, these blockchains can remove unnecessary functionalities and computational costs, thus improving speed and resource efficiency.
However, their specificity may also lead to a lack of generality, adaptability, and potential fragmentation issues in the blockchain field. Therefore, while application-specific chains have their benefits, they must also consider scalability, interoperability, and future feasibility.
What are Validiums?
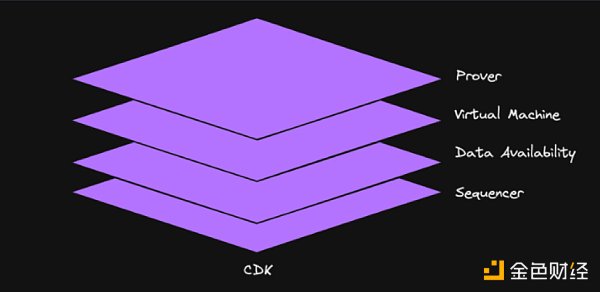
Validiums are solutions that use off-chain data availability and computation to process transactions outside of the Ethereum main network. Unlike traditional rollups, Validiums do not store transaction data on the L1 network but generate ZK proofs and publish them as validity proofs. This approach ensures data integrity while optimizing scalability and costs.
How does an L2 developed using Polygon CDK run as an application chain?
Using Polygon’s advanced zkEVM technology, chains developed using Polygon CDK can provide high-performance L2 scaling solutions. Developers have the flexibility to choose the Validium framework, which integrates a secure data availability layer managed by a Data Availability Committee (DAC). Chains developed using CDK can run like L1 chains customized for specific business logic. However, as L2 solutions, they have almost infinite scalability advantages. These chains are designed with a user-centric approach, prioritizing core business functionality and user participation strategies without compromising performance and scalability. The table below shows the high-level architecture of chains developed using Polygon CDK.
What is a data availability layer?
In the blockchain field, data availability ensures that all nodes can access and verify the complete transaction history, which is crucial for maintaining network transparency, security, and integrity.
However, storing all transaction data on the main chain (L1) can be costly and may compromise privacy. The data availability layer addresses these issues by separating transaction execution from data storage. This allows transaction data to be stored off-chain, reducing costs and enhancing privacy while still being accessible and verifiable.
This separation creates new challenges, such as ensuring secure and reliable management of off-chain data. Features like DAC in the Polygon CDK framework address these issues by providing trusted oversight of off-chain data.
The diagram below provides an overview of the blockchain infrastructure approach for Polygon CDK Validium.

What is DAC?
Data Availability Committees (DACs) are key elements in many blockchain protocols, tasked with ensuring the reliability and accessibility of off-chain data. Essentially, they verify the availability of data related to specific blockchain blocks.
For L2 solutions, DACs play a crucial role in enhancing scalability. They help offload important computational work and data storage from the main L1 chain.
Why choose Polygon CDK?
Polygon CDK is an important component of Polygon 2.0, reshaping blockchain infrastructure. It ensures unparalleled liquidity, optimizes performance, facilitates seamless asset transfers, and prioritizes user experience and data security.
(1) Design Principles
— Highly modular: Polygon CDK provides a modular environment for designing ZK-based L2 chains. Developers can customize chains according to their needs, whether it is choosing the execution environment or determining gas tokens.
— Super Scalability: The L2 chain developed by CDK improves transaction speed and can be exponentially accelerated to achieve the vision of a highly scalable ecosystem for Polygon 2.0.
— Unified Liquidity: The chain developed using CDK supports unified liquidity, ensuring the transfer of liquid assets across multiple chains in the L2 ecosystem of Polygon 2.0, promoting the development of a vibrant and efficient digital economy.
— Independent Data Availability: The chain developed using CDK provides powerful off-chain data accessibility and reliability through dedicated data availability layers and DAC. The independent structure from Ethereum ensures high data resilience and integrity.
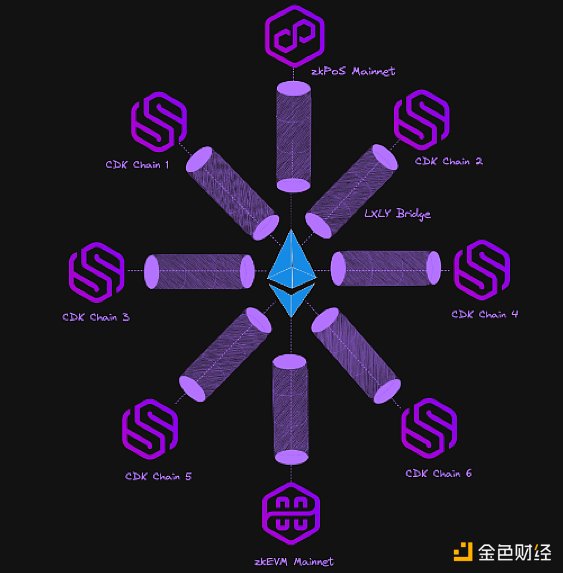
— Composable Interoperability: With the LXLY bridge, the chain developed using CDK enhances seamless interaction and asset transactions across different blockchains. This interoperable infrastructure fosters an interconnected and universal ecosystem, facilitating cross-chain collaboration and interaction.
— Near-Instant Finality: Chains deployed using Polygon CDK rely on cryptographic security to ensure transaction integrity without relying on full nodes. This approach guarantees near-instant finality and reliable security.
The following diagram shows how the chain developed using CDK adapts to the entire Polygon 2.0 ecosystem.
(2) Key Factors of Adopting Polygon CDK
— Ethereum Scalability: Chains developed using CDK significantly expand Ethereum. They allow projects and enterprises to build applications to meet their own block space requirements while maintaining the security and integrity of the Ethereum mainnet.
— Customizable Business Logic: Chains developed using CDK fully support the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and enable custom gas limits, opcode compatibility, and technical integration. The flexibility and scalability of business logic design are enhanced through Polygon zkEVM.
— Privacy Options: Chains developed using CDK support the creation of private application chains, providing an option for those who prioritize privacy in their applications. This feature allows clients to maintain the confidentiality of their application data while still enjoying the benefits brought by blockchain technology.
— Compliance-Oriented: Chains developed using CDK achieve network sovereignty and compliance. They allow network maintainers to choose administrators who comply with local regulations, ensuring compliance with regional regulatory requirements.
— Extensive Web3 Support: Chains developed using CDK (direct branches of the zkEVM stack) facilitate service portability. They also leverage a comprehensive ecosystem with advanced service providers offering necessary tools for application integration, development, and deployment.
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!