Table of Contents
-
“Currency + Credit” dual-driven economic cycle
-
Core values and primitives of open finance
-
Core functions of DeFi protocols
3.1 Issuance and representation of digital assets
- Actively constructing a multi-polar regulatory model for legal digital currencies under the new situation.
- Logarithm Finance Will LPDFi be the next new narrative?
- Deeply analyzing why on-chain intellectual property is the future direction?
3.2 On-chain liquidity of digital assets
3.3 Creation of on-chain decentralized credit
-
Welcome to DeCredit Summer
LianGuairt 01. “Currency + Credit” dual-driven economic cycle
Ray Dalio, the founder of Bridgewater Associates, one of the world’s largest hedge funds, detailed the interrelationships between currency, credit, transactions, markets, and the economy in his article “How the Economic Machine Works”.
Ray Dalio points out that transactions involve the exchange of products, services, and financial assets between buyers and sellers using currency and credit. Different markets are formed around the trading of different commodities, such as the wheat market, stock market, etc. The economy is composed of all transactions within all markets, and all economic cycles and dynamics are caused by transactions. Transactions are the basic components of this economic machine, and understanding transactions means understanding the entire economy.
In transactions, credit is used just like currency, so currency and credit together constitute the total expenditure of the trading parties, that is, currency + credit = total expenditure. Expenditure drives the economy, making currency and credit the “dual drivers” of the economy, as shown in Figure 1-1.
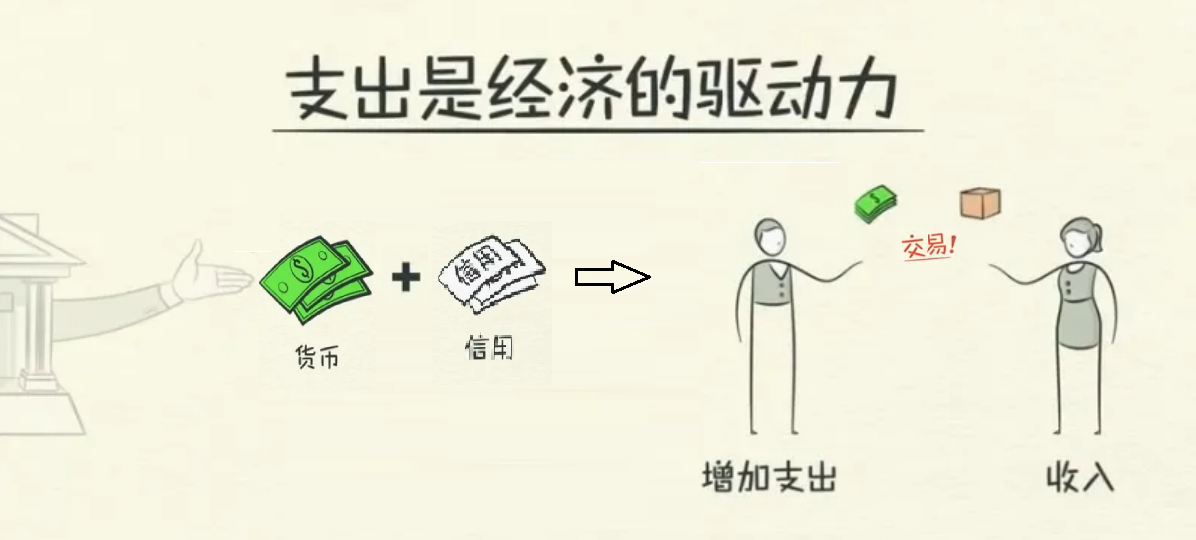
Figure 1-1 Relationship between currency, credit, transactions, and the economy (Image based on Ray Dalio's original diagram)
Under the “dual drivers”, the economy becomes volatile, exhibiting short-term and long-term economic cycles. Among them, currency, which can be simply understood as income, refers to the returns brought by the productivity and workload of traders. Since productivity and workload do not fluctuate drastically, the amount of currency held by traders is a relatively stable factor and is not a significant driving force for economic fluctuations. On the other hand, credit, which is obtained through borrowing, is referred to as “credit currency” for distinction and understanding. As long as both the borrower and the lender agree, credit currency can be created out of thin air, thereby increasing the total expenditure of traders in a short period of time. This means that we consume by borrowing, allowing consumption to exceed output brought by productivity, but consumption must be lower than output when repaying the debt, thus forming a cycle. This is where credit differs from currency in transactions, and where productivity differs from credit in economic cycles. Productivity is key in the long term, while credit is most important in the short term, as shown in Figure 1-2.
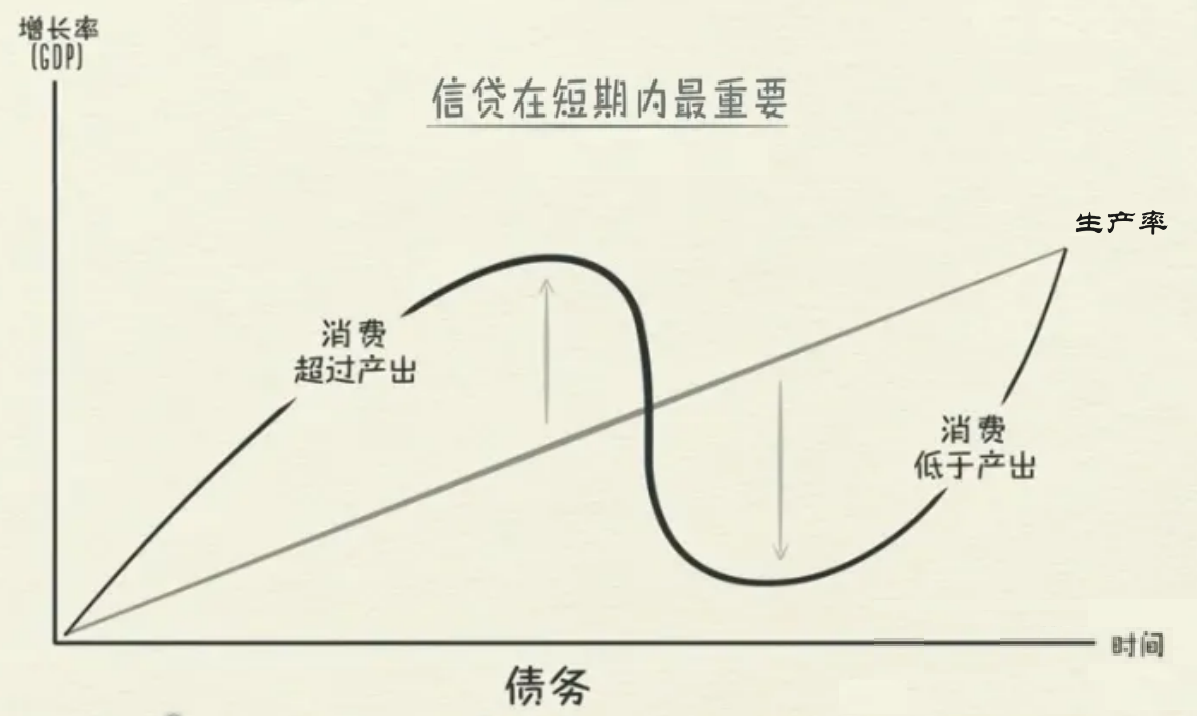
Figure 1-2 The relationship between currency and credit, productivity and credit in the economic cycle (based on the original figure edited by Ray Dalio)
It can be seen that although both currency and credit are driving forces of the economy, they play different roles and the amounts involved are vastly different. In reality, most of what we call money is essentially credit money. According to the article, in 2013, the total amount of domestic credit in the United States was about $50 trillion, while the total amount of currency was about $3 trillion. This shows that credit is the most important component in the economy, and a large amount of money in reality is credit money generated by credit. Credit money plays a more important role in the liquidity of the real economy.
We believe that the above logic is equally applicable to the field of crypto economics, which means that credit will also play a crucial role in the crypto field. The difference is that in traditional economics, there is a complete operational system in place for qualification proof, credit assessment, credit execution, and risk control management, enabling it to function effectively in real economic activities. However, when we look at the crypto field, perhaps due to the lack or imperfection of infrastructure, or the completely different logic of on-chain operation, the current on-chain credit system is still blank, even when using the most common lending protocols, they are all over-collateralized. Although the multiplier effect can amplify the loan amount many times through cyclic over-collateralization, this is only the multiplier effect under the logic of “deposit creating loans” (note: in reality, the credit money system is “loan creating deposits”, following the binary system of “central bank + Basel agreements + commercial banks”), which is unrelated to credit and does not generate any credit.What kind of scene will be created if credit can be created in DeFi and credit can be introduced on a large scale?
However, the crypto economy and the traditional economy are still two parallel worlds. How to build credit in the crypto field? Can the credit in reality be transmitted to the crypto world? What are the considerations? How is it different from the traditional economy…
We have already realized the importance of creating credit and implementing credit in the crypto economy. Next, we will focus on the topic of “building decentralized credit” within the crypto field. Here, we attempt to sort out some thoughts on crypto digital assets, the core values of open finance, DeFi protocol primitives, and core functions. These thoughts help clarify the underlying logic of open finance and its fundamental differences from traditional finance, and explore possible implementation paths based on this.
Section 02. Core values and primitives of open finance
With the emergence of blockchain, the concept of “decentralization” has been continuously mentioned and emphasized. When people talk about “decentralization”, it is often related to “self-sovereign identity, ownership, currency issuance, distributed nodes, distributed ledgers, decentralized governance, and organizations,” and so on.
However, the success of open finance, led by Uniswap and other decentralized finance (DeFi) protocols, has brought us closer to the core value proposition of “decentralization” in open finance, as shown in Figure 2-1.
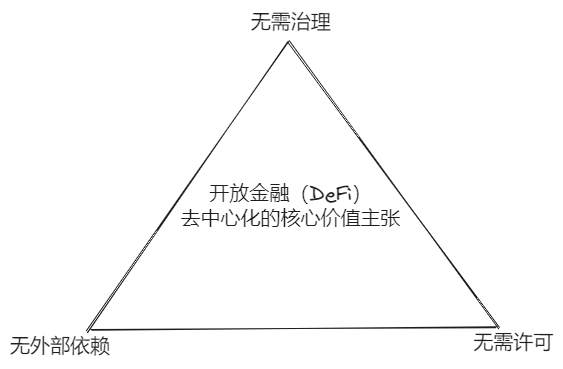
Figure 2-1 Core value proposition of open finance (DeFi)
●Permissionless: Permission implies control, rights, opacity, and inequality, which means centralization. On the other hand, permissionless expresses freedom, equality, transparency, and decentralization. For example, you can provide ETH-DAI to add liquidity to Uniswap and receive LP rewards without any authorization from individuals or protocols. It solely depends on your willingness and ability, and the amount of rewards you receive depends entirely on the value you provide with ETH-DAI. Everyone follows these rules without any privileges.
●No external dependencies: Blockchain is a closed system designed to protect state consistency and system security, which is the basis for forming global consensus. If external data is introduced into contracts through oracles, the contracts inherit risks associated with external dependencies, such as data accuracy, timeliness, and consistency. External oracles can bring centralization, single point of failure, and consensus disruption to contracts. Decentralization also means no oracles and no external dependencies, fully on-chain, and OR Native. Therefore, applications that rely on oracles to provide prices and data in the blockchain world are difficult to achieve “trustless,” undoubtedly increasing friction costs.
●No governance required: Governance implies human intervention, which may bring uncontrollable and uncertain factors and centralization risks, introducing external risks to contracts. At the same time, implementing governance also implies upgradability of contract functions, which may lead to compatibility issues before and after state changes, affecting on-chain consensus security. It may also cause unfairness and losses to capital invested, posing significant trust risks to smart contracts built around value. Therefore, once contracts are deployed, they are not upgradable. The feasible method for upgrades is to redeploy independent versions, such as Uniswap V1, V2, V3, etc., which are independent of each other and have no relationship.
DeFi protocols that achieve permissionless, no external dependencies, and no governance must not require external oracles. They are fully implemented on-chain, non-custodial, and settle automatically. They are self-endorsing and credit-enhancing, and truly OR Native. All these features combined, it brings pure “Code is Law” to the DeFi world, demonstrating the greatest value of blockchain – trustlessness. Looking back at various economic crises and incidents of fraud, it is easy to understand how valuable the quality of “trustlessness” is. It carries the original intention and mission of blockchain technological innovation.
DeFi protocols with the above characteristics can be called “primitives”, which means they are basic, open, and shareable, with scalability and composability.
DeFi protocols that become “primitives” have the self-attribute of “driving consensus”. They are a “consensus engine” that can gather, expand, and strengthen consensus. They are trusted and used by users, spontaneously spread by the crypto community, and adopted by developers to build dApps or composable protocols. A well-known example is Uniswap, which has achieved tremendous success since its deployment. It has the largest trading pool depth and occupies over 60% of the entire Dex market, becoming the most basic financial infrastructure on-chain.
LianGuairt 03. The Core Functions Triangle of DeFi Protocols
Ethereum has innovated smart contracts and decentralized application platforms, bringing about two waves of trends so far: ICO and DeFi Summer. Today, DeFi has become the most significant and successful application in the Ethereum ecosystem and the entire crypto world.
Looking back at the development of DeFi, DeFi protocols have already played two core functions: issuing and expressing digital assets, and creating on-chain liquidity for digital assets. However, according to the principle of “dual-wheel drive” in economics, DeFi urgently needs to build “decentralized credit”, namely DeCredit.
3.1 Issuing and Expressing Digital Assets
Although the Bitcoin protocol pioneered and issued the BTC cryptocurrency, due to the limitations of its protocol, it can only issue and operate BTC.
However, with the introduction of general-purpose smart contracts on Ethereum, issuing encrypted digital assets has become simple and efficient, leading to the “ICO craze” and the emergence of tens of thousands of cryptocurrencies, realizing the “free issuance of currency”.
Although ICO has been controversial, the “spiritual core” of “permissionless and free issuance” is widely recognized in the native crypto world and has become an inevitable choice for building open finance. From the neutrality of the protocol, we should give ICO a reasonable evaluation. If we rank the most successful blockchain applications based on their launch time, the top 3 should be BTC, ICO, and then DeFi.
ICO (Initial Coin Offering) is essentially a smart contract that defines a certain token and its issuance method. The simplest implementation is when a user sends ETH to a smart contract, the smart contract will send the corresponding amount of “tokens” to the user’s associated wallet address.
In order to make it more versatile and scalable, Ethereum developers standardized the ICO technology and proposed token standards, starting with the homogeneous token (FT) standard ERC20. Subsequently, the token standards continued to evolve, resulting in non-fungible (NFT) ERC721, ERC1155, as well as semi-fungible (SFT) ERC3525, etc.
In summary, the implementation of smart contracts enables the expression and free issuance of encrypted digital assets, which provides the most basic core element – encrypted digital assets for the development of DeFi protocols, and based on its innovation, various DeFi protocols and application scenarios have been created on the chain, creating financial liquidity.
3.2 On-chain liquidity of digital assets
The so-called finance refers to the circulation of funds. According to the explanation on Wikipedia: “金” refers to gold, and “融” originally referred to the liquefaction of gold for the purpose of circulation. In other words, the original meaning of finance is to liquefy gold for the purpose of trading and circulation.
It can be seen that the two core elements of finance are: first, funds such as gold, US dollars, RMB, and encrypted digital currencies; second, the liquidity of funds, which refers to the exchange of value across time and space. Liquidity is the core demand of finance. Only when funds are in circulation can their value be demonstrated and they can play a role in economic activities. It can be imagined that even if a person is wealthy, their wealth is of no value if it does not enter circulation. This is the importance and significance of fund liquidity.
In the world of blockchain, creating liquidity for encrypted digital assets and realizing the cross-time and cross-space value exchange of tokens in a decentralized manner is decentralized finance (DeFi). It is achieved through different protocols, demonstrating different functional application models, such as:
● Decentralized Exchange (DEX)
DEX provides liquidity for tokens through swapping, allowing one token to be exchanged for another token, provided that the token already exists in the DEX, which is what we commonly refer to as “listing on the exchange”.
Unlike centralized exchanges (CEX), listing on DEX does not require permission. It embodies freedom and fairness, avoids the “will of authority”, but may also bring fraud and worthless tokens. Whether good or bad, these are left to the market to achieve balance and equilibrium through free play.
In terms of liquidity implementation, taking Uniswap as an example, DEX abandons the order book model of CEX and adopts the automated market maker (AMM) mechanism based on the constant product formula X * Y = K. In CEX, trades are matched based on the prices provided by market makers, and liquidity is reflected in the depth of buy/sell orders at different prices. In DEX, users interact with a liquidity pool defined by a constant product curve, which enables token price discovery and exchange. Liquidity is reflected in the sizes of X and Y and the total value locked (TVL) of the pool. The larger the TVL, the better the liquidity, the smaller the impact of price fluctuations, and the lower the trading slippage.
● Lending
DeFi lending protocols have characteristics such as decentralization, trustlessness, transparency, open-source, automatic execution, and automatic settlement. Without the need for a third party and relying only on smart contracts, users can deposit and borrow funds to provide or obtain liquidity, similar to decentralized banks.
However, the difference is that DeFi is permissionless and open to everyone. Users are anonymous, there is no qualification review, and no qualification proof is required. At the same time, DeFi does not have an operating center, it is decentralized, without external dependencies, and does not rely on the credit of borrowers. It generally adopts over-collateralization.
Lending protocols have become the cornerstone of the DeFi industry, with Total Value Locked (TVL) reaching a peak of $46 billion and now around $14 billion. However, due to the lack of credit mechanisms and corresponding infrastructure support, lending protocols do not generate credit, therefore their application scale and driving force for the DeFi industry are limited.
● LP Liquidity Pool
DEX creates liquidity pools (LP Pools) based on price curve functions, realizing Automated Market Making (AMM). LP Pools are permissionless, and any user can provide liquidity to DEX protocols by offering trading pairs and receive LP tokens in return.
LP tokens are usually ERC20 or ERC721 standard digital assets, with composability, which can be used as liquidity inputs for other DeFi protocols, such as collateralized lending, yield farming, etc., providing flexibility for DeFi applications.
In addition, the AMM mechanism based on curve functions also provides a price discovery mechanism and liquidity governance. For example, in Friend.tech, Key=16000, as X changes, the price of Key is rediscovered. If X represents liquidity, then this curve function provides an on-chain native liquidity governance mechanism (rather than off-chain governance), enabling price discovery for certain types of tokens, which can be widely applied in various scenarios such as financial instruments, game items, membership tickets, etc.
● Liquidity Staking (LS&LSD&LSDFi)
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchains require staking tokens for block production, transaction validation, and security, but staked tokens lose liquidity, which may incur high opportunity costs.
Liquidity Staking (LS) protocols provide liquidity staking derivatives (LSD) to unlock liquidity from staked tokens, and based on the combination of LSD and DeFi, various LSDFi scenarios are innovated, such as stablecoins, re-staking, collateralized lending, interest rate swaps, etc., providing users with diversified income and risk hedging strategies, promoting ecosystem prosperity.
Since the upgrade in Shanghai on April 13th this year, TVL contributed by LSDs has grown rapidly, from $60 million to nearly $700 million in 3 months, with a maximum growth of 12 times. Although it has fallen back, it remains between $300 million and $400 million.
From this, it can be seen that the industry is eager for sufficient and high-quality liquidity, and it also reflects that LSD, backed by strong consensus blockchain tokens, stable interest rates, and low risk, is such a high-quality liquidity asset. It will become an important and foundational narrative for the future development of DeFi.
Above, we have selected several liquidity use case scenarios that have gained initial scale in the DeFi field, analyzed how liquidity is created in different scenarios, and the characteristics and value contribution of such liquidity.
What needs to be emphasized here is that since the emergence of thousands of encrypted digital assets in the encryption field, regardless of how these “Tokens” are classified, what application scenarios they are in, how they create liquidity, and how they improve liquidity efficiency, these have become the core propositions and indispensable core functions of DeFi, and will continue to exist throughout the entire lifecycle.
3.3 Creating On-Chain Decentralized Credit
Although the above use cases have brought on-chain liquidity to DeFi and actually generated TVL, contributing value to the industry. However, due to the lack of credit creation, the liquidity scale is limited, and DeFi lacks strong expansion.
As mentioned earlier, currency and credit are the “dual wheels” driving the economy, and in the absence of credit, the development of the entire encrypted economy relies more on the “currency” for “single-wheel” driving. Some people say that encrypted digital assets are showing a trend towards dollarization, and the expansion and contraction of the dollar largely drive the cyclical fluctuations of the encrypted economy, which is the current situation.
However, “single-wheel driving” is very limited, especially in a bear market, where it manifests as a stock game between cryptocurrencies; even as the market warms up and external funds continue to enter, the lack of a credit support system prevents credit expansion, resulting in only half the driving effect on the encrypted economy.
Based on the above analysis, after smart contracts realize the issuance and expression of encrypted digital assets, and various DeFi protocols bring on-chain liquidity of digital assets, DeFi, as the financial layer of Web3, still has a missing link in its functional chain. Only by building a “decentralized credit (DeCredit)” module can we form a complete “DeFi core function triangle,” as shown in Figure 3-1.
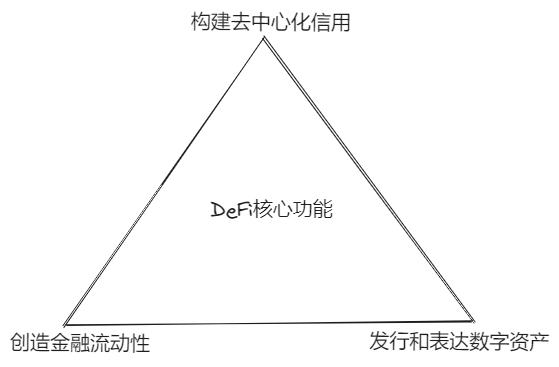
Figure 3-1 DeFi Core Function Triangle
LianGuairt 04. Embracing the Arrival of DeCredit Summer
We hope to see that on the basis of building a complete DeFi core function triangle, DeFi and even the encrypted economy gradually show a development trend of “Crypto+DeCredit” dual-wheel driving:
● Crypto: Cryptocurrencies or assets will be associated with real-world currencies or transactions, carrying external liquidity injections, and realizing value exchange between the encrypted economy and the real economy. This is the driving force from “currency,” and it has externality.
● DeCredit: DeCredit is native to the chain based on Crypto. It is the native driving force of DeFi and the encrypted economy. It obtains decentralized consensus and decentralized endorsement through on-chain liquidity governance, realizes dynamic expansion of decentralized credit, improves the scale and efficiency of DeFi liquidity, and accelerates the scaled development of the encrypted economy.
In this way, “DeCredit” will play a crucial role in encrypted economic activities, just as in traditional economic activities.
What needs to be emphasized is that because DeCredit is “Trustless”, it is a decentralized, high-dimensional trust that can flow into low-dimensional trust domains. For example, it can provide open, transparent, and verifiable trust endorsements for real-world application scenarios, thereby achieving the integration and value expansion of the encrypted economy into the real economy.
We are very interested in devoting our energy to paying attention to the innovations and changes happening in the encryption industry, and we are also pleased to see the emergence of “decentralized credit modular protocols and primitives” and OR Native applications. We will analyze them in subsequent research reports, so please stay tuned. Perhaps, with its development, in the next industry cycle, we will have the opportunity to usher in a “DeCredit Summer” driven by two wheels. Once it happens, it will be different from the past.
So, are you ready?
References:
1. Ray Dalio “How the Economic Machine Works”
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!