
Source/elliptic
Compilation/Nick
The Lazarus hacking group from North Korea seems to have intensified its operations, with four confirmed attacks on the cryptocurrency industry since June 3. Recently, they are suspected to have carried out a fifth attack. 23pds, the Chief Information Security Officer of SlowMist, tweeted that the $55 million hacker attack on the cryptocurrency exchange CoinEx was the work of state-sponsored hackers from North Korea.
- Ethereum Validators Surge, What Problem Does the New Proposal EIP-7514 by Dencun Seek to Solve?
- A panoramic analysis of South Korea’s latest cryptocurrency regulatory landscape
- Binance Research Interprets OP Stack The Weapon for Optimism to Compete for the King of Layer2 in the Superchain Era
It is worth noting that, according to the National Intelligence Service (NIS) of South Korea cited by the Associated Press, state-sponsored hackers from North Korea have stolen approximately $1.2 billion in cryptocurrencies from around the world since 2017. NIS believes that North Korea is one of the most motivated countries in the world when it comes to stealing cryptocurrencies. After the United Nations strengthened economic sanctions against North Korea in 2017 in response to its nuclear and missile tests, the country shifted its focus to cybercrime.
In addition, in the past 104 days, the Lazarus hacking group from North Korea has been confirmed to have stolen nearly $240 million in cryptocurrency assets from Atomic Wallet ($100 million), CoinsLianGuaiid ($37.3 million), Alphapo ($60 million), and Stake.com ($41 million).
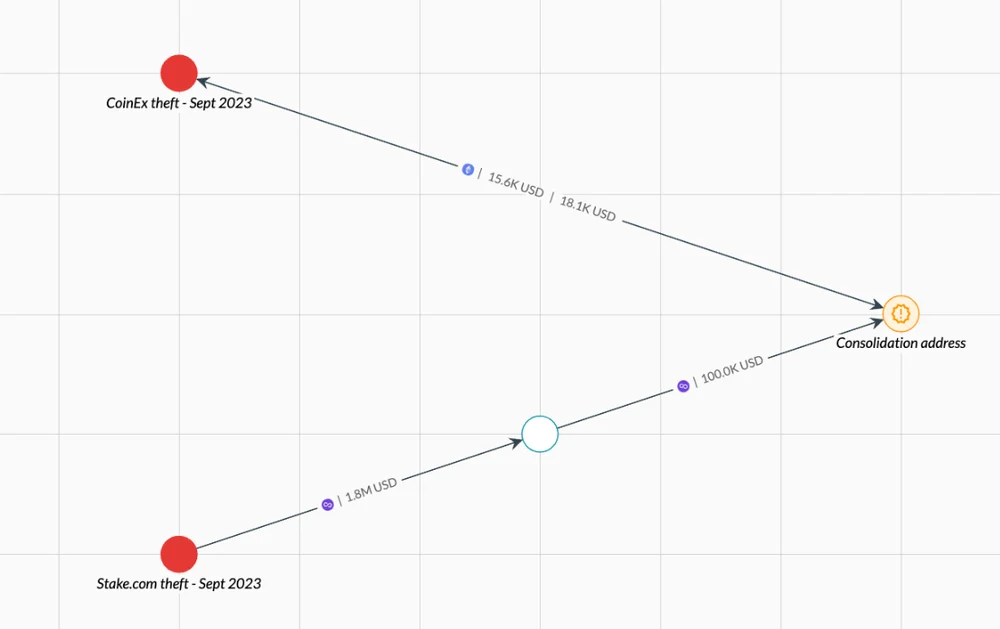
As shown in the above figure, Elliptic’s analysis indicates that some of the funds stolen from CoinEx were sent to addresses used by the Lazarus group to store funds stolen from Stake.com, despite being on different blockchains. Subsequently, the funds were cross-chained to Ethereum through a cross-chain bridge previously used by Lazarus, and then sent back to addresses controlled by the CoinEx hackers.
Elliptic has observed this mixing of funds from different hackers in the Lazarus incidents before, with the most recent example being the mixing of cryptocurrency stolen from Stake.com with funds stolen from the Atomic Wallet. The merging of funds from different hackers is represented in the following figure in orange.
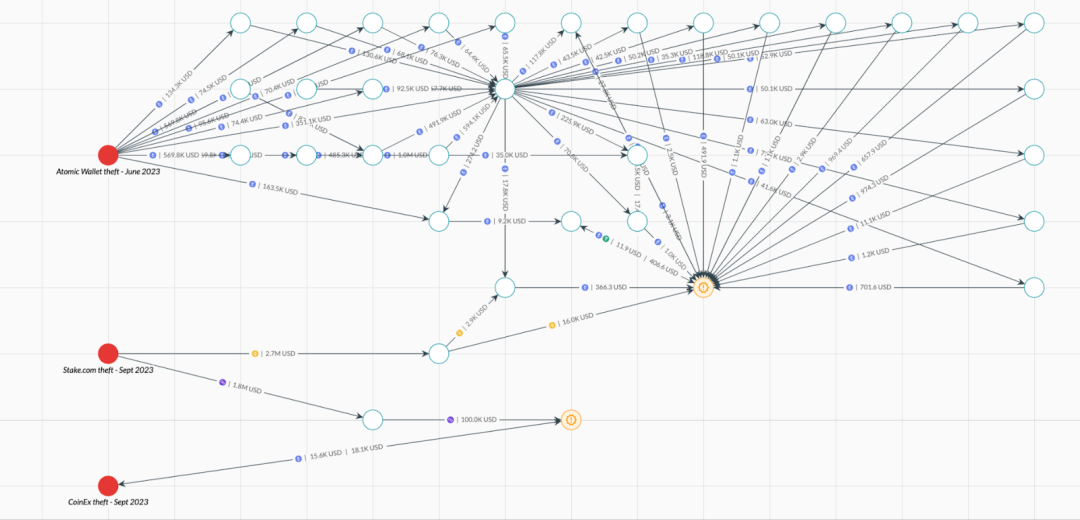
01. Lazarus conducted five attacks in 104 days
In 2022, several high-profile hacker attacks were attributed to Lazarus, including attacks on Harmony’s Horizon Bridge and Axie Infinity’s Ronin Bridge, both of which occurred in the first half of last year. From then until June of this year, no major cryptocurrency theft cases were publicly attributed to Lazarus. Therefore, the various hacker attacks in the past 104 days indicate an increase in the activities of this North Korean hacking group.
On June 3, 2023, users of the non-custodial decentralized cryptocurrency wallet Atomic Wallet lost over $100 million. After Elliptic identified multiple factors indicating the responsibility of the Lazarus hacking group for this, the attack was officially attributed to Lazarus on June 6, 2023, and later confirmed by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI).
On July 22, 2023, Lazarus gained access to the hot wallet of the encrypted payment platform CoinsLianGuaiid through a social engineering attack. This access allowed the attacker to create authorization requests and extract approximately $37.3 million worth of encrypted assets from the platform’s hot wallet. On July 26, CoinsLianGuaiid released a report stating that Lazarus was responsible for the attack, which was later confirmed by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI).
On the same day, July 22, Lazarus carried out another high-profile attack, this time targeting the centralized encrypted payment provider Alphapo and stealing $60 million worth of encrypted assets. The attacker may have gained access through previously leaked private keys. The FBI later confirmed that Lazarus was behind this attack as well.
On September 4, 2023, the online cryptocurrency gambling platform Stake.com was attacked and approximately $41 million worth of virtual currency was stolen, possibly due to stolen private keys. On September 6, the FBI announced that the Lazarus group was behind this attack.
Finally, on September 12, 2023, the centralized cryptocurrency exchange CoinEx was hacked and $54 million was stolen. As mentioned above, multiple pieces of evidence indicate that Lazarus was the hacker behind this attack.
02. Has Lazarus changed tactics?
Analysis of Lazarus’ latest activities indicates that since last year, they have shifted their focus from decentralized services to centralized services. Four out of the five recent hacker attacks discussed above targeted centralized encrypted asset service providers. Before 2020, when the decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystem rapidly emerged, centralized exchanges were the main targets chosen by Lazarus.
There are several possible explanations for Lazarus’ renewed focus on centralized services.
Increased difficulty in attacking DeFi protocols
Previous research by Elliptic on DeFi hacker attacks in 2022 found that an attack occurred on average every four days during that year, with an average theft of $32.6 million per attack. Cross-chain bridges became one of the most frequently attacked types of DeFi protocols in 2022. These trends may have prompted improvements in smart contract auditing and development standards, narrowing the scope for hackers to identify and exploit vulnerabilities.
Complexity of social relationships in centralized institutions
In many previous hacker attacks, Lazarus Group used social engineering as their attack method. For example, the $540 million hack of Ronin Bridge was the result of a former employee being deceived by a false job posting on LinkedIn. However, decentralized services often have fewer employees, and projects are to some extent decentralized. Therefore, gaining malicious access to developers may not necessarily mean gaining management access to smart contracts.
At the same time, centralized exchanges may hire relatively more employees, thereby expanding the potential target range. They may also use centralized internal information technology systems to operate, which gives Lazarus malware a greater chance to infiltrate the business.
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!