Author: LianGuaiul Veradittakit, Managing Partner at LianGuaintera Capital; Translation: LianGuai0xxz
In the ever-evolving field of blockchain technology, the pursuit of scalability and enhanced transaction throughput has led to the emergence of so-called Layer-2 solutions or L2. These innovative enhancements are designed to strategically alleviate the inherent limitations of traditional blockchain designs. With the rise of L2 solutions that offer faster and more resource-efficient transaction processing, a new challenge arises – the need for efficient transaction ordering.
To address this efficiency challenge, centralized ordering mechanisms have been primarily employed. These coordination mechanisms manage the arrangement of transactions in distributed networks. However, the decentralized nature of the underlying blockchain philosophy clashes with the centralization pursued by these ordering mechanisms, giving birth to an extraordinary breakthrough: the advent of decentralized ordering mechanisms. This new approach aims to improve scalability, enhance security, and establish true decentralization in the field of blockchain.
- Why should Base and OP create a community of interests?
- Why do Base and OP want to create a community of shared interests?
- Stanford Blockchain Club The Moore’s Law of Zero Knowledge Proofs
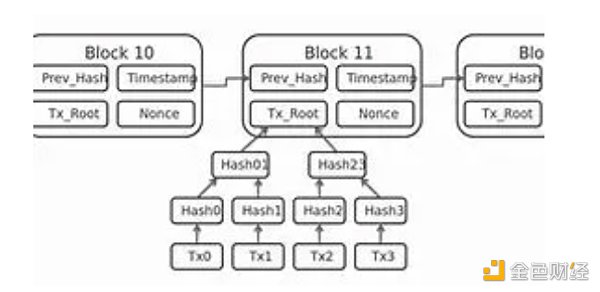
What is centralized transaction ordering?
Centralized transaction ordering mechanisms are employed by applications deployed on the blockchain to ensure the orderly and secure processing of transactions. Unlike the decentralized ordering intrinsic to the blockchain, which relies on consensus algorithms and distributed networks, these sorters operate in a centralized environment supervised by a single authoritative entity. Here is an overview of their functionalities:
-
Centralized control: In a centralized system, a single entity or authority exercises control over the database or application. This entity is responsible for overseeing transaction ordering and instructing L2 on the sequence in which these transactions should be executed.
-
Order processing: Transactions are processed in a sequential manner, occurring one after another. The determination of this order is often influenced by variables such as timestamps, submission time, MEV extraction, fees paid by users/block builders, or priority allocated by the central controlling entity.
-
Trust dependency: Users relying on this system must trust that the central entity can handle transactions fairly and accurately. However, there is a potential for manipulation or malicious behavior by this authoritative entity, which could jeopardize the integrity of the transactions themselves.
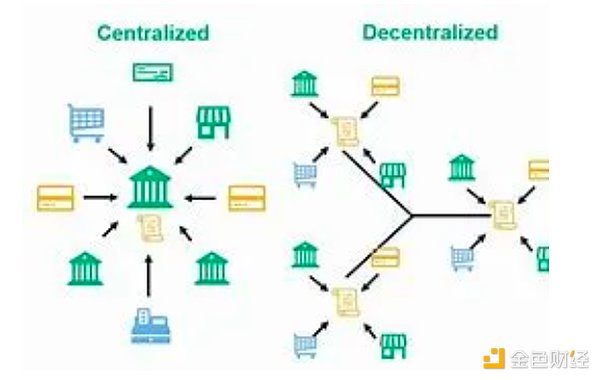
Advantages of decentralized sorters
Decentralized sorters offer several notable advantages stemming from their innovative transaction management approach. By fostering trust and transparency, these sorters establish an immutable and publicly accessible ledger, enabling the autonomous verification of transaction accuracy and order without the need for central supervision. They resist tampering, ensure data integrity, nearly eliminate the possibility of fraud, and confer authenticity to recorded information. Additionally, decentralized sorters advocate for censorship resistance and anti-monopoly principles, basing transaction execution on network consensus rather than central authority, fostering an open and inclusive ecosystem.
In addition to their security features, decentralized sorters are also able to withstand single point failures and malicious intrusions, thus strengthening their resilience. This resilience promotes participation from participants in different geographic regions, creating an environment of global accessibility and financial inclusivity. Therefore, this approach simplifies operations, automates transaction verification, reduces reliance on intermediaries, thereby improving efficiency and significantly reducing costs. The adaptability of decentralized sorters drives innovation and promotes the development of applications such as smart contracts and decentralized platforms that revolutionize traditional business models and economic paradigms. These sorters are closely integrated with decentralized principles, enhancing data ownership and solidifying their role as transformative catalysts that reshape industries and redefine trust in the digital age.
Main Advantages
-
Trustless Environment: Decentralized sorters eliminate the need for participants to individually trust a central authority. Transactions are validated and agreed upon in a distributed node network, promoting transparency and reducing the risk of manipulation.
-
Immutability: In decentralized sorting, transactions are recorded in an immutable and inviolable manner. Once integrated into the blockchain, they become unalterable or deletable unless the network reaches consensus, enhancing data integrity.
-
Censorship Resistance: Traditional sorters may be susceptible to censorship or interference from central authorities. Decentralized sorters counteract this vulnerability by attaching transactions to the blockchain, provided they comply with the consensus rules set by the network.
-
Resilience: Traditional sorters are vulnerable to threats from single points of failure. In contrast, decentralized systems with widely distributed network architectures enhance resilience, preventing attacks or failures of individual nodes.
-
Reduced Intermediaries: Traditional sorters often require intermediaries to verify and authorize transactions. In contrast, decentralized sorters have the potential to reduce or eliminate the need for intermediaries, achieving cost-effectiveness and improving operational efficiency.
Types of Decentralized Sorting
Let’s break down some exciting solutions that are classified based on the builder-proposer aspect of the sorting mechanism design.
Builder
Schnorr Sorter: Schnorr Sorter introduces a novel approach to transaction confirmation, moving away from traditional transaction grouping methods. In this innovative system, unique indices are assigned to individual transactions, initiating a collaborative process between sorters (or validators) and senders. They jointly create Schnorr signatures associated with the transaction index, which serve as proof of the sender’s intention to include that particular index in the blockchain ledger. This technology may bring various benefits, including improved efficiency, enhanced privacy, and smoother transaction sequencing. Additionally, it has the potential to offer new solutions for arranging and sorting transactions within blockchain networks.
Suave: Suave is an innovative initiative introduced by Flashbots in response to the centralized challenges brought by Miner-Extractable Value (MEV). At its core, Suave proposes a novel concept: the Single Unifying Auction for Value Expression. This innovative solution aims to reshape the pattern of block construction, with a focus on maintaining decentralization principles. The framework of Suave consists of three key components: the Universal Preference Environment, which empowers users to express their preferences to guide execution; the Optimal Execution Market, a complex network of executors competing to provide optimal execution, including MEV capture; and Decentralized Block Building, a network that aggregates preferences into blocks across multiple domains. In the Suave architecture, these components are integrated into a decentralized ecosystem where users, validators, builders, and searchers collaborate seamlessly across multiple chains. By doing so, Suave not only addresses centralized risks but also promotes a more fair and decentralized trajectory for the cryptocurrency field, reshaping the future of blockchain technology.
Proposer
Espresso Ordering: Espresso Ordering is a decentralized network tailored for Rollups, with the primary goal of providing secure, fast throughput and minimal latency in arranging and ensuring transaction availability. This ordering is envisioned as a valuable asset accessible to both optimistic and zk-Rollups, allowing Rollups to achieve decentralization while leveraging the benefits of interconnectivity, which are achieved through a common ordering layer.
Based Ordering: Based Ordering mechanisms based on Rollups utilize the sorting capabilities of the underlying Layer 1 (L1) blockchain. These Rollups synchronize their block ordering with L1, enabling seamless collaboration between L1 proposers and the Rollup ecosystem. This brings a set of advantages: strong liveness guarantees, efficient settlement processes, resistance to MEV-driven front-running, network effect protection, and compatibility with existing L1 infrastructure. The simplicity of their architecture, combined with recent innovations such as Proposer-Builder Separation (PBS), results in gas efficiency and simplified development. Although sacrificing some MEV revenue, these Rollups enhance security and economic scarcity through alignment with the economic incentives of the L1 ecosystem. These Rollups retain sovereignty through governance tokens and base fees. The term “Base Rollup” interestingly responds to their reliance on L1 infrastructure. This innovation embodies the core principles of blockchain while enhancing decentralized consensus.
Conclusion
From scalability limitations to the emergence of Layer-2 solutions, this process has undergone profound transformations. The core role of ordering mechanisms in managing transaction sequencing is crucial for the efficiency and effectiveness of these solutions. As the blockchain community continues to embrace decentralization principles, the rise of decentralized ordering mechanisms provides a promising path forward. By striking a balance between improving scalability and achieving true decentralization, decentralized ordering mechanisms symbolize the maturity of blockchain technology, leading us into an era of a more inclusive, secure, and resilient digital future.
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!