According to SlowMist Intelligence, on October 7, 2022, the BNB Chian cross-chain bridge BSC Token Hub was attacked. Hackers took advantage of the cross-chain bridge vulnerability to obtain a total of 2 million BNB in two times, exceeding 570 million US dollars. After the analysis by the SlowMist security team, it will be shared with you in the form of a brief analysis. (Note: BSC Token Hub is a cross-chain bridge between BNB Beacon Chain (BEP2) and BNB Chain (BEP20 or BSC))
Briefly analyze
1. During the cross-chain process between BNB Chain and BSC, the pre-compiled 0x65 contract will be called by the cross-chain contract deployed on BSC to perform IVAL tree verification on the submitted appHash, key, vale, and proof. IAVL tree is a variant of AVL tree, which is an implementation of AVL tree that provides a verifiable root for key values.
2. The verification is mainly performed by two ops, IAVLValueOp and MultiStoreProofOp. IAVLValueOp will first calculate and verify the roothash through ComputeRootHash. After the verification is passed, the output roothash will be given to MultiStoreProofOp, and MultiStoreProofOp will check whether the obtained roothash is consistent with that obtained by lightClient.
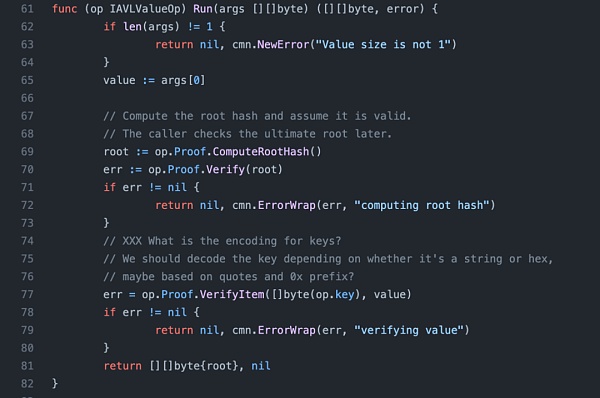
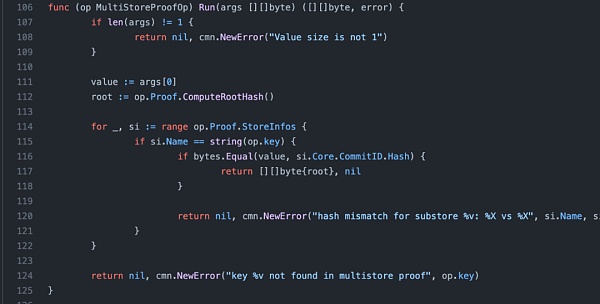
3. ComputeRootHash will recursively hash the leaf hash with the rest path (innernode) and check whether it is consistent with the right of the last path node.
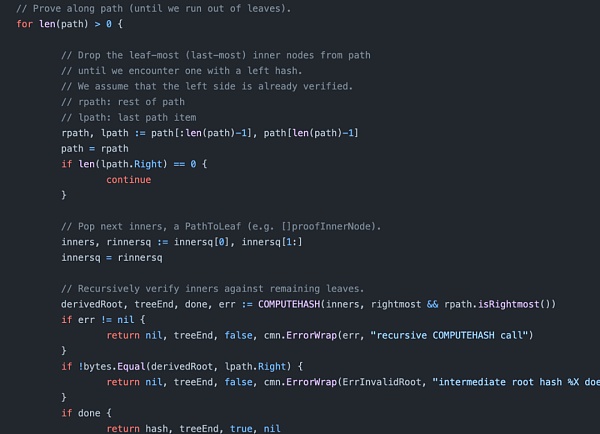
4. In the specific hash calculation of leafnode and innernode, we can see that when left is empty, the hash of leaf and right will be calculated, and when right is empty, the hash of leaf and left will be calculated. But when both left and right exist, right will be ignored, and the hash of leaf and left will be calculated, that is, roothash will not be affected by right.
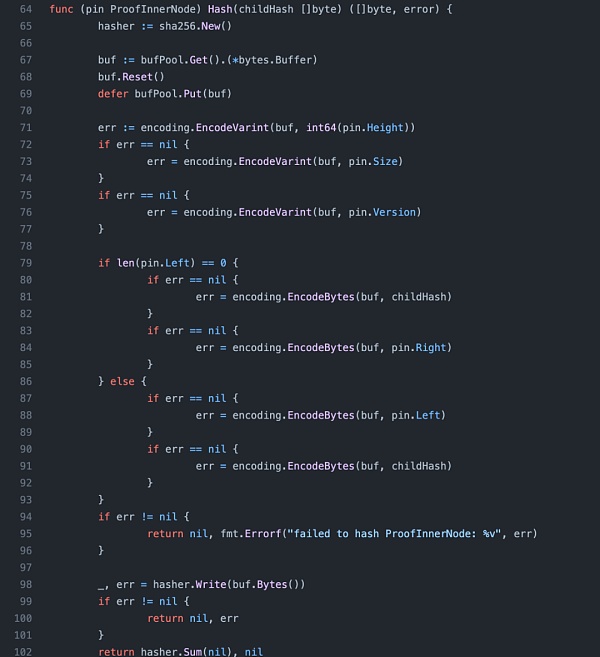
5. So we can know that in the path, when both left and right exist, right will be ignored, and the hash of leaf and left will be returned. In the recursive hash check, it will be checked whether this hash is consistent with the right of the last path node. This is where right is checked in the recursive check, but ignored in the roothash calculation. As a result, an attacker can add a hash of leaf and innernode to the path as the right of the last path node and add an empty innernode to ensure verifiability. This allows malicious data to be inserted to steal funds while keeping the roothash untouched.
MistTrack Analysis
According to the analysis of the SlowMist MistTrack anti-money laundering tracking system, the initial funds for this hack came from ChangeNOW.
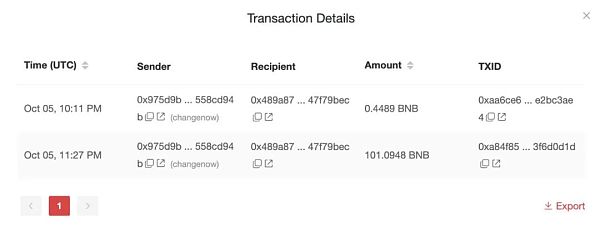
The hacker address of this attack has interacted with multiple DApps, including Multichain, Venus Protocol, Alpaca Finance, Stargate, Curve, Uniswap, Trader Joe, PancakeSwap, SushiSwap, etc. In addition, 4.8 million USDT transferred by hackers to Ethereum has been blacklisted by Tether, 1.7 million USDT on AVAX has been blacklisted, and 2 million USDT on Arbitrum has been blacklisted. Due to the timely suspension of the BNB Chain, the hacker’s over $410 million on BSC could no longer be transferred. On October 8, the hacker address transferred about 33,771 ETH to a new address starting with 0xFA0a3, or about $45 million.

SlowMist MistTrack will continuously monitor the movement of stolen funds.
Like what you're reading? Subscribe to our top stories.
We will continue to update Gambling Chain; if you have any questions or suggestions, please contact us!